Emery–Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD)
What is an Emery–Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD)?
• Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy is a condition that mainly affects muscles used for movement, such as skeletal muscles, and also affects the cardiac muscle.
• It is named after Alan Emery and Fritz Dreifuss, physicians who first described the disorder among a Virginia family in the 1960s.
Symptoms of Emery–Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD)
Symptoms of EDMD begin in the teenage years with toe-walking, a rigid spine, face weakness, hand weakness, and calf hypertrophy. Among other signs/symptoms of Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy are
• Muscle weakness EDMD can affect the shoulders and lower legs
• Cardiac involvement can affect an individual’s heart rate (bradycardia, palpitations)
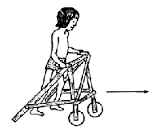
• Contractures of the muscles occurs slowly, eventually leading to the need for orthopedics (walker, cane)
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy can be established via single-gene testing or genomic testing, and clinically diagnosed via the following exams/methods
• CAT scan
• Serum CK analysis
• EKG
• Echocardiogram
• Electromyogram
• Immunodetection
In order to differentiate EDMD from a neurological problem, a neurological screening can be performed.
Upper Motor Neuron Clinical Signs:
• Weakness or paralysis
• Spasticity
• Increased tendon reflexes
• Babinski sign
• Loss of superficial abdominal reflexes
• Little, if any, muscle atrophy
Lower Motor Neuron Clinical Signs:
• Weakness or paralysis
• Wasting and fasciculations of involved muscles
• Hypotonia or flaccidity
• Loss of tendon reflexes
• Normal abdominal reflexes and negative Babinski sign
TREATMENT:-
The treatment (management) of Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy can be done via several methods, however, secondary complications should be considered in terms of the progression of EDMD, therefore cardiac defibrillators may be needed at some point by the affected individual. Other possible forms of management and treatment are the following
• ACE inhibitor
• Orthopaedics
• Surgery
• Monitor/treat any cardiac issues
• Medication (beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors)
• Respiratory aid
• Physical therapy
→ Passive and active stretching to increase flexibility and prevent contractures
→ Strength exercises in order to maintain and improve muscle strength
→ Encouragement of activity: Assistive devices such as canes, braces, and wheelchairs may be needed to maintain mobility


2 Comments