PLEURAL EFFUSION
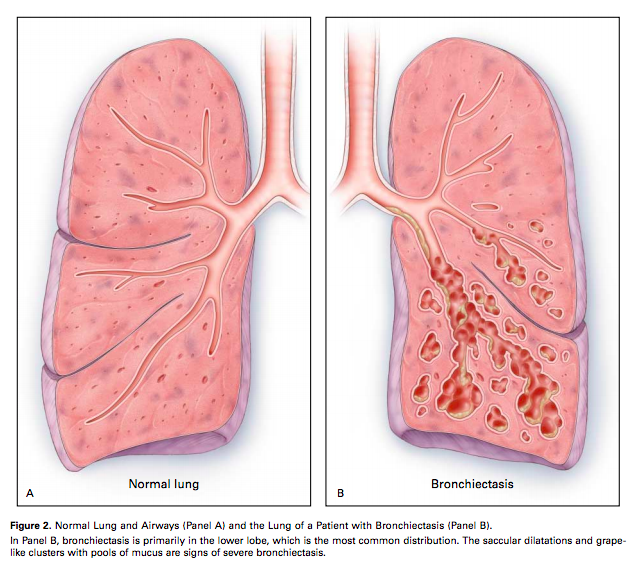
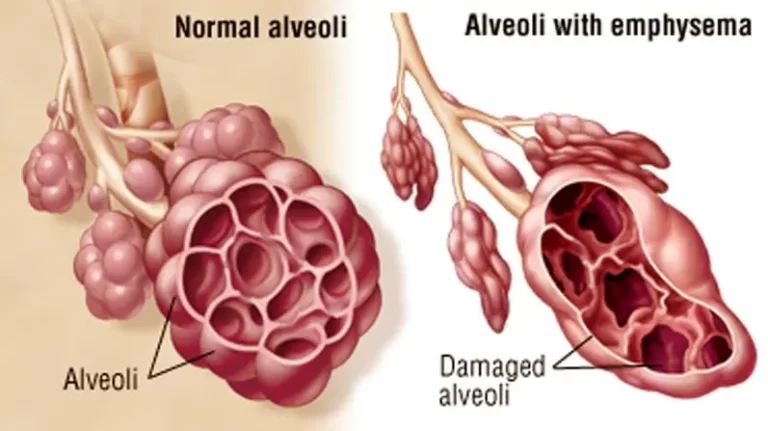
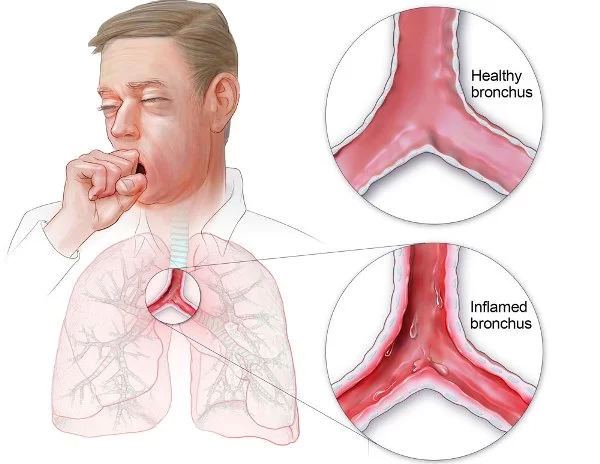
DEFINATION- ”A pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates in the pleural cavity, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs. This excess fluid can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs”. Various kinds of pleural effusion, depending on the nature of the fluid and what caused its entry into the pleural space, are…