Understanding Chest Pain While Deep Breathing
Chest Pain while Breathing Deeply
Chest Pain while Breathing Deeply
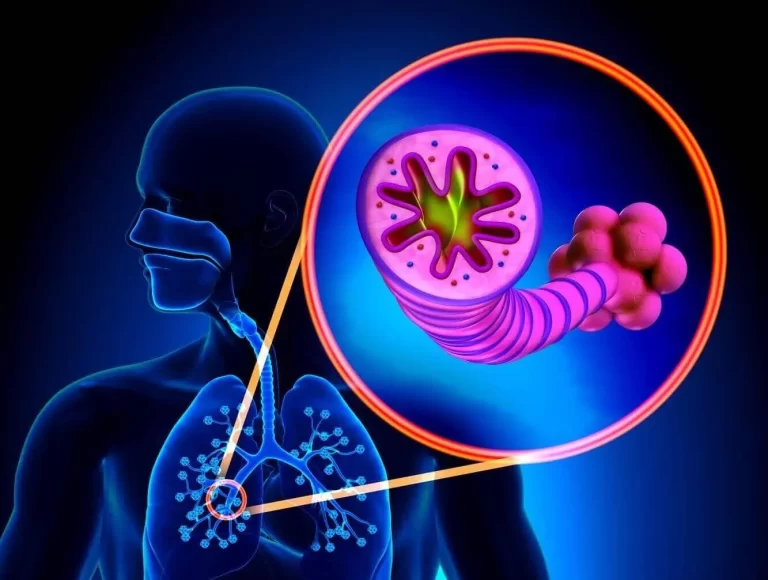
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, is a disorder that makes breathing difficult by blocking airflow and damaging the lung’s other tissues. Two primary conditions are referred to by the term COPD. 1 When there is damage to the walls separating several air sacs in the lungs, emphysema…
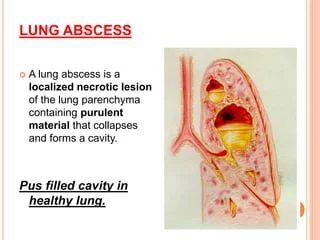
What is a Lung Abscess? A microbial lung infection that causes the pulmonary parenchyma to necrotize is called a lung abscess. It can be categorized as acute (less than four weeks) or chronic (greater than four weeks) based on how long it lasts. They can be categorized as primary if they arise without underlying pulmonary…
What is Respiratory Depression? Respiratory depression is a medical condition characterized by the reduced rate and depth of breathing, leading to inadequate oxygen exchange in the lungs. It occurs when the respiratory system fails to function properly, resulting in decreased levels of oxygen in the bloodstream and an increased concentration of carbon dioxide. Respiratory distress,…
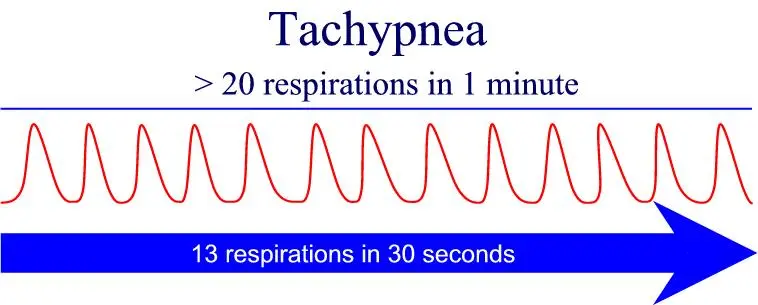
What is Tachypnea? Tachypnea or tachypneic breathing is fast and shallow breathing. If your breath speed gets quick but then returns to normal speed it is understood as transient tachypnea. Various medical diseases induce tachypnea. Tachypnea can impact newborns and adults. It is considered ordinary among newborns who were born prematurely (preterm) and among adults…
What is Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome? Acute respiratory distress syndrome occurs when fluid builds up in the tiny, alveoli in your lungs. The fluid keeps your lungs from filling with little air, which means less oxygen reaches your bloodstream. ARDS is a type of respiratory failure caused by the rapid onset of the spread of…
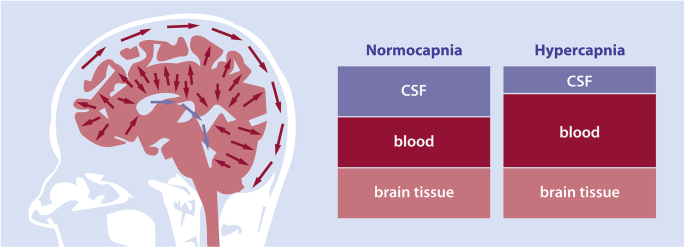
What is Hypercapnea? Hypercapnia (from the Greek word hyper means too much and kapos means smoke), also called hypercarbia (CO2 retention) is a disease of abnormally increased levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood. Carbon dioxide is a gaseous outcome of the body’s metabolism and is generally expelled via the lungs. Carbon dioxide may…

What is Hypoxia? Hypoxia is when the tissues of your body don’t have adequate oxygen. When you breathe, you carry oxygen into your lungs, where it crosses via your airways out into small sacks known as alveoli. From there, it brings picked up by your blood in tiny vessels that cross close to the alveoli…
Introduction Exercise-induced asthma is a condition in which the airways of the lungs are narrowed and triggered by strenuous activities. It causes breathlessness, wheezing, coughing, and other symptoms during or after exercise. The preferable diagnosis for this condition is exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Its name suggests that asthma is triggered by vigorous or prolonged exercise or physical…
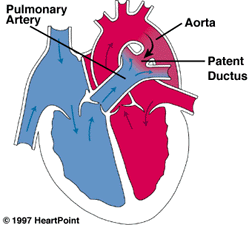
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS PDA is a heart problem that is frequently noted in the first few weeks or months after birth. It is characterized by the persistence of a normal fetal connection between the aorta and the pulmonary artery which allows oxygen-rich (red) blood that should go to the body to recirculate through the lungs….