Paxino’s test of the shoulder :
- This test is applied by to therapist or doctor to check the pain of the shoulder.
- It is the development of an acromioclavicular joint instability [ ACH ] scoring system to determine disability associated with injury to the acromioclavicular joint.
- This clinical test is applied in the clinic in examine part of the assessment.
- This test is applied with the other special test of the shoulder.
Purpose of Paxino’s test :
- This test is used to detect the presence of acromioclavicular joint pain.
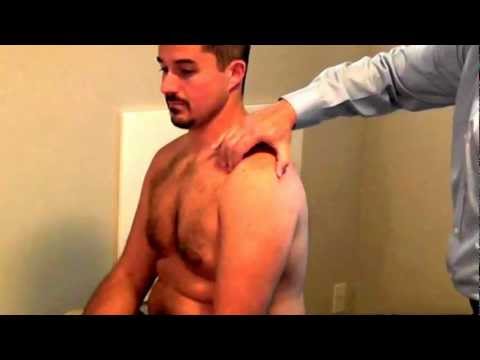
The technique of performance of Paxino’s test :
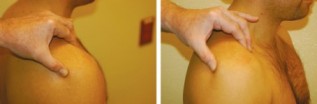
- The starting position for the test is the sitting position & the arm is relaxed at the side.
- The examiner stands beside the test arm & places one hand over the shoulder so that the thumb is placed under the posterolateral aspect of the acromion & the index & long fingers of the same[ the fingers of the opposite hand is also instead of over to middle part of the clavicle on the same side.
- Examiner is then applies to pressure to the acromion with the thumb anterosuperiorly while applying an inferior directed applied to counter force with to the clavicle of the fingers.
Result of Paxino’s test :
- The test is considered positive if the pain in the area of the acromioclavicular joint is increased.
Evidence of Paxino’s test:
- Sensitivity of Paxino’s test (%) = 79
- Specificity of Paxino’s test (%)= 50
- Positive Predictive Value of Paxino’s test (%) = 61
- Negative Predictive Value of Paxino’s test (%) = 70
- Positive Likelihood Ratio of Paxino’s test = 1.58
- Negative Likelihood Ratio of Paxino’s test = 0.42
Crossover test :-
- this test is also known as the acromioclavicular crossover/horizontal adduction test.
- The patient stands & reaches the hand across to the opposite shoulder.
- This test is also perform also passively.
- With the patient in a sitting position, the examiner passively forward flexes the arm to 90′ & then horizontal adducts the arm as far as possible.
- This test is positive when the patient feels localized pain over the acromioclavicular joint.
- A localized pain in the sternoclavicular joint is at fault.