Dellon’s moving two-point discrimination test
- This test is described as to Dellon in 1978.
- This test is similar to Weber’s two-point discrimination test except that the two points are moved during the test.
- This test was applied to the clinic to check the functional recovery of the patient.
- This clinical test is applied by to therapist when the patient complains of no sensation in the hand.
- This Dellon moving two-point discrimination test is best for hand sensation related to activity & movement.
What is the purpose of this Dellon’s moving two-point discrimination test?
- This Dellon moving two-point discrimination test is used to predict functional recovery.
- This test measures the quickly adapting mechanoreceptor system.
- This test is mostly used for heck the anterior digital pulp.
What is the technique of performance of this Dellon’s moving two-point discrimination test?
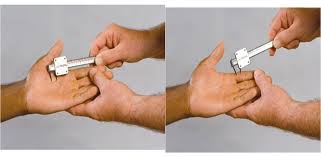
- The patient is in a sitting position for the test & hand is resting on the examining table.
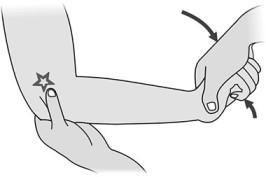
- Then the examiner [ therapist ] moves two blunt points from proximal to distal along the long axis of the limb or digit, starting with a distance of 8 mm between the points.
- The distance between the points is increased /decreased depending on the response of the patient until the two points can no longer be distinguished.
- During the test, the patient’s eyes are closed & the hand is cradled in the examiner’s hand means the therapist’s hand.
- The two smooth/calipers are gently placed longitudinally.
- There should be no blanching of the skin indicating too much pressure when the points are applied.
- If the patient is feeling whether one or two points are felt.
- If the patient is hesitant to respond or becomes inaccurate, the patient is required to respond accurately 7 or 8 of 10 times before the distance is narrowed & the test is repeated.
- Normal discrimination distance recognition is 2 to 5 mm.
- The values obtained for this test are slightly lower than those obtained for Weber’s static two-point discrimination test.
- Although the entire hand may be tested, it is more common to test only the anterior digital pulp.