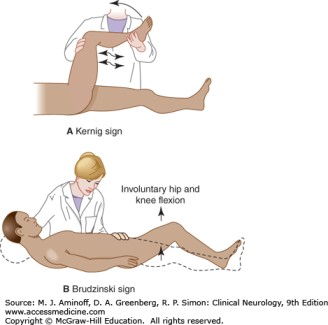
Brudzinski – Kernig test :
- Brudzinski – Kernig test is one of the physically demonstrable tests which is become for symptoms of meningitis.
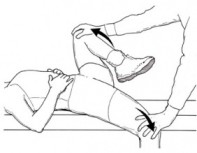
- This clinical test is applied by the therapist when the patient is doing complaints about Severe neck stiffness with the patient’s hips & knees are in the flex position when the neck is in the flex position.
Purpose of the Brudzinski – Kernig test:
- This Brudzinski – Kernig test is used for the diagnosis of meningitis.
- This test is also used to check meningeal irritation.
What is techinque of performance of the Brudzinski – Kernig test?
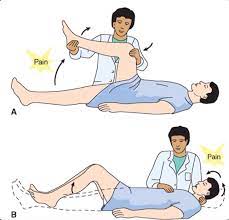
- The patient position for the test is supine with the patient’s hands are cupped behind the patient’s head.
- After that instruct the patient for flex the head onto the chest.
- The patient raise the extended leg actively by flexing the hip until pain is felt.
- The patient then flexes the knee,& if the pain disappears,it is considered a positive test.
- The mechanics of the Brudzinski – Kernig test are similar to those of the straight leg raising test expect that the patient performs the movement actively.
- Pain is a positive sign & may indicate meningeal irritation,nerve root involvement,or dural irritation.
- Brudzinski originally described the neck flexion aspect of the test,& Kernig described the hip flexion component.
- The two parts of the test means Brudzinski + Kernig part are done individually,in which case both test are described as the test of the original author.
Evidence of the Brudzinski – Kernig test :
- The study of the Brudzinski – Kernig test
- This study used 297 adults who are suspected of meningitis to determine the diagnostic accuracy of the Brudzinski – Kernig test & Nuchal rigidity for meningitis.
- This study shows the diagnostic value:
- Sensitivity of the Brudzinski – Kernig test = 5%
- Specificity of the Brudzinski – Kernig test = 95%
- Positive predictive value of the Brudzinski – Kernig test = 27%
- Negative predictive value of the Brudzinski – Kernig test = 72%
- Results of the study show that the diagnostic accuracy of this test is poor for the patients with moderate & severe meningeal inflammation & the patients with the microbiological evidence of infection of the CSF.
- Patients who have suffered from severe meningitis based on the laboratory evidence both this test as the low diagnostic value.
- Another study of the Brudzinski – Kernig test suggests:
- Sensitivity of the Brudzinski – Kernig test = low
- Specificity of the Brudzinski – Kernig test = high for diagnosing meningitis.
- Low sensitivity of this test is suggested when both tests are absent it is not concluded so that there is no evidence are present of meningitis.
- The high specificity of this test is suggested when both tests are present there is too high a likelihood for meningitis.
- In the clinical examination time, both the Kerning’s and Brudzinski’s tests are frequently performed with each other.