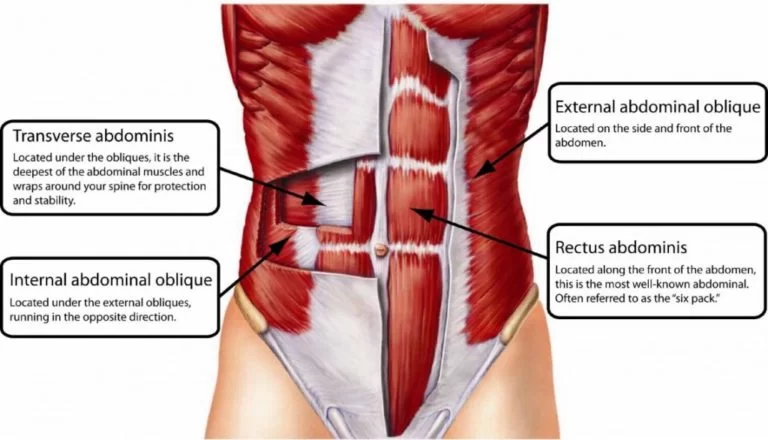
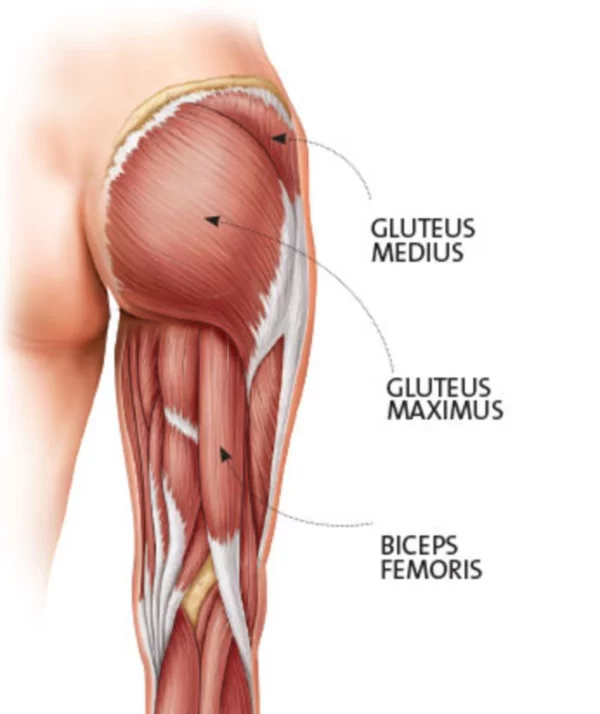
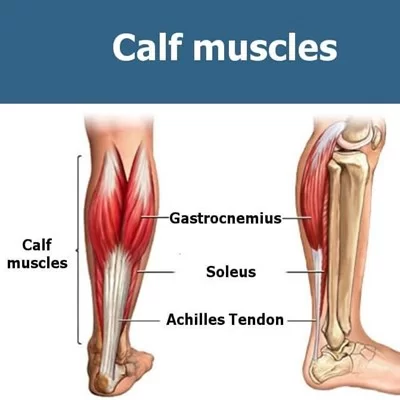
Paraspinal Muscle – Anatomy and Exercise
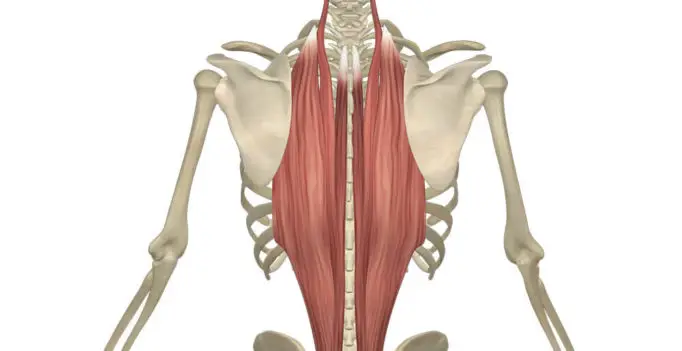
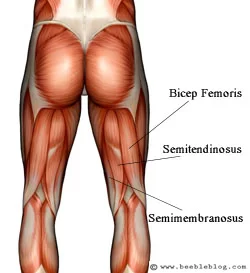
Anatomy: The paraspinal muscles, sometimes called the erector spinae, are three muscle groups that support your back. The paraspinal muscles are located on the left and right sides of your spine and are made up of three groups. These include: a) Iliocostalis b) Longissimus c) Spinalis A) ILIOCOSTALIS MUSCLE: The iliocostalis muscle is the most…