Prone segmental instability test:
- This prone segmental instability test is applied in the clinic to check the lumbar instability in the patient.
- This clinical test is applied by the therapist when the patient is doing complaints about the low back pain with the leg pain.
- This test is applied in the examination part of the assessment of the back pain.
What is the Purpose of the prone segmental instability test?
- This prone segmental instability test is used to check the lumbar instability in the patient when the patient is complaining about the low back pain.
How do you perform the prone segmental instability test?
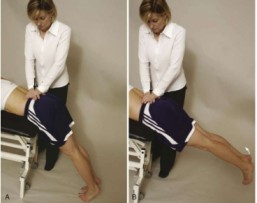
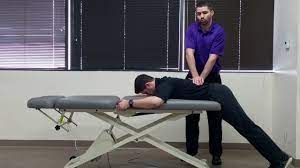
- The patient lies prone with the body on the examining table & the legs over the edge resting on the floor.
- Then the examiner [ therapist ] applies pressure to the posterior aspect of the lumbar spine while the patient rests in this position.
- The patient then lifts the legs off the floor, & the examiner again applies posterior compression to the lumbar spine.
What is the result of the prone segmental instability test?
- If the pain is elicited in the resting position only, the test is positive, because the action masks the instability.
What is Evidence of the prone segmental instability test?
- Sensitivity of the prone segmental instability test = 72
- Specificity of the prone segmental instability test = 58
- LR [ negative likehood ratio ] of the prone segmental instability test = 48
- LR [ positive likehood ratio ] of the prone segmental instability test = 1.7
- This prone segmental instability test is used in conjunction with the other tests to confirm the signs & symptoms of lumbar spine instability.
- This prone segmental instability test is also included in the clinical prediction rule which is developed by the Hicks for the patients with favorable responses to spinal stabilization exercise.
- Therefore, positive test results of prone segmental instability test correlated with the patient’s favorable responses & negative test results prone segmental instability test were correlated with the patients without favorable responses to the spinal stabilization exercise programs.