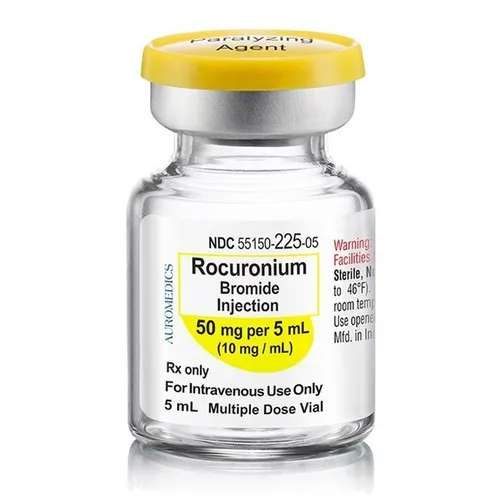
Rocuronium Bromide
Introduction
Rocuronium bromide is a medication belonging to the class of non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents. It is commonly used in anesthesia to induce muscle relaxation during surgical procedures or to facilitate endotracheal intubation.
Rocuronium bromide works by blocking the transmission of nerve impulses at the neuromuscular junction, leading to temporary paralysis of skeletal muscles. When administered intravenously, rocuronium bromide quickly takes effect, typically within one to two minutes, and its effects can last for approximately 30 to 60 minutes. The dosage and duration of action may vary depending on the patient’s age, weight, and overall health.
This medication is commonly used in operating rooms, intensive care units, and emergency settings where temporary muscle relaxation is required. It allows for easier insertion of a breathing tube into the patient’s trachea, ensuring adequate ventilation during anesthesia or critical care.
Generic Name – Rocuronium
Type – Small Molecule
Groups – Approved
Chemical Formula – C32H53N2O4
Synonyms
- Rocuronio
- Rocuronium
Associated Conditions
- Muscle fasciculation caused by succinylcholine
Associated Therapies
- Curarization therapy
- Neuromuscular blocking therapy
- Facilitation of small bowel intubation therapy
As with any medication, rocuronium bromide carries potential risks and side effects. These may include allergic reactions, changes in heart rate or blood pressure, and prolonged muscle weakness. It is important for healthcare professionals to carefully monitor patients receiving rocuronium bromide to ensure proper dosing and minimize the occurrence of adverse effects. Rocuronium bromide should only be administered by trained medical professionals in a controlled environment due to its potent muscle-relaxing properties. Dosage and administration should be individualized based on the patient’s specific needs and closely monitored throughout the procedure.
It is worth noting that this information is accurate as of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021. It is always essential to consult the latest medical guidelines, product information, and the advice of a qualified healthcare professional for specific and up-to-date information about rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
What is rocuronium bromide?
Rocuronium bromide is a medication that belongs to the class of non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents, also known as neuromuscular blockers or muscle relaxants. It is used to induce muscle relaxation during surgical procedures or to facilitate endotracheal intubation. Neuromuscular blocking agents like rocuronium bromide work by blocking the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting nerve impulses to the muscles. By interfering with the transmission of these signals at the neuromuscular junction, rocuronium bromide temporarily paralyzes the skeletal muscles.
The primary use of rocuronium bromide is in anesthesia. When administered intravenously, it quickly takes effect, typically within one to two minutes. The duration of action can vary, but it generally lasts for around 30 to 60 minutes. This allows for muscle relaxation and immobilization during surgical procedures, ensuring better surgical access and preventing involuntary muscle movements that could interfere with the surgery. Rocuronium bromide is also commonly used to facilitate endotracheal intubation, which involves inserting a breathing tube into the patient’s trachea. By inducing muscle relaxation, it helps to facilitate the placement of the tube, ensuring proper ventilation during anesthesia or in critical care settings.
It’s important to note that rocuronium bromide should only be administered by trained healthcare professionals in controlled medical settings. Dosage and administration should be individualized based on factors such as the patient’s age, weight, and overall health. Close monitoring is necessary to ensure appropriate dosing and minimize the risk of adverse effects. Like any medication, rocuronium bromide may have potential side effects and risks, including allergic reactions, changes in heart rate or blood pressure, and prolonged muscle weakness. These should be carefully monitored and managed by healthcare professionals.
As always, it’s crucial to consult the latest medical guidelines, product information, and the advice of a qualified healthcare professional for specific and up-to-date information about rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Who can take rocuronium bromide?
Rocuronium bromide is a prescription medication that should only be administered by trained healthcare professionals in controlled medical settings such as operating rooms, intensive care units, or emergency departments. It is not intended for self-administration or use by the general public.
Rocuronium bromide is typically used in the following situations:
- Anesthesia: It is commonly used during surgical procedures to induce muscle relaxation. By temporarily paralyzing the skeletal muscles, it facilitates surgery by providing optimal surgical access and preventing involuntary muscle movements that could interfere with the procedure.
- Endotracheal Intubation: Rocuronium bromide is often used to facilitate the insertion of a breathing tube into the patient’s trachea. This is important for ensuring proper ventilation during anesthesia or in critical care settings.
The use of rocuronium bromide may be contraindicated or require caution in certain individuals. The medication should be used with caution or avoided altogether in individuals who:
- Are known to be allergic or hypersensitive to rocuronium bromide or any other neuromuscular blocking agents.
- Have a known or suspected genetic condition called malignant hyperthermia, which can lead to a life-threatening reaction to certain medications used during anesthesia.
- Have certain medical conditions such as severe burns, skeletal muscle myopathies, or conditions affecting the neuromuscular junction.
Additionally, specific considerations may be necessary for special populations, such as pediatric or geriatric patients, as they may have unique dosage requirements or increased susceptibility to the effects of rocuronium bromide. The dosage and administration of rocuronium bromide should be individualized based on factors such as the patient’s age, weight, and overall health. Close monitoring of the patient’s response and adequate adjustments in dosage is necessary to ensure optimal muscle relaxation and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
It is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can assess an individual’s specific medical condition, take into account their medical history and other medications they may be taking, and determine the appropriateness of rocuronium bromide for their particular situation. Please note that the information provided here is not exhaustive, and it is crucial to consult the latest medical guidelines, product information, and the advice of a qualified healthcare professional for specific and up-to-date information about the use of rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Who cannot take rocuronium bromide?
Rocuronium bromide is a powerful medication that is not suitable for everyone. There are certain individuals and medical conditions in which the use of rocuronium bromide is contraindicated or requires extreme caution. It is important for healthcare professionals to carefully assess each patient’s medical history and overall health before administering this medication. Below are some situations in which rocuronium bromide should generally be avoided:
- Allergy or Hypersensitivity: Individuals who have a known allergy or hypersensitivity to rocuronium bromide or any other neuromuscular blocking agents should not receive this medication. Allergic reactions to rocuronium bromide can be severe and life-threatening.
- Malignant Hyperthermia Susceptibility: Rocuronium bromide should be used with caution or avoided in individuals with a known or suspected susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition characterized by a severe reaction to certain medications used during anesthesia, including neuromuscular blocking agents like rocuronium bromide.
- Severe Burns: In patients with severe burns, the distribution of the medication may be altered, potentially leading to unpredictable effects. Caution should be exercised when administering rocuronium bromide to these patients.
- Skeletal Muscle Myopathies: Patients with certain skeletal muscle myopathies (muscle diseases) may be more sensitive to the effects of rocuronium bromide. In such cases, alternative muscle relaxants or anesthesia techniques may be considered.
- Conditions Affecting the Neuromuscular Junction: Certain medical conditions affecting the neuromuscular junction, where nerves meet muscles, can alter the response to rocuronium bromide. Caution is needed when using this medication in patients with such conditions.
- Preexisting Neuromuscular Disorders: Patients with preexisting neuromuscular disorders may have altered responses to rocuronium bromide. Special care and monitoring are required in these cases.
- Pediatric and Geriatric Patients: The use of rocuronium bromide in pediatric and geriatric populations requires careful consideration of dosage adjustments and monitoring, as these populations may have a unique sensitivity to the medication.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Rocuronium bromide should only be utilized during pregnancy if the potential benefits outweigh the risks. It may pass into breast milk, so its use should be carefully evaluated for breastfeeding mothers.
Healthcare professionals must review a patient’s medical history and perform a thorough physical examination before considering the use of rocuronium bromide. Proper monitoring and dose adjustments are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of the medication for each patient. As always, patients should communicate any existing medical conditions or allergies to their healthcare providers to avoid potential adverse reactions to medications like rocuronium bromide.
Classification of rocuronium bromide
Rocuronium bromide is classified as a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent. This classification refers to its mechanism of action and its effects on the neuromuscular junction. Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs) are medications that act on the neuromuscular junction, the site where nerve impulses from motor neurons transmit signals to the muscles. NMBAs can be categorized into two main classes: depolarizing and non-depolarizing agents.
- Depolarizing NMBAs: Depolarizing agents, such as succinylcholine, initially cause muscle depolarization, which leads to muscle contraction. However, they remain bound to the receptors for an extended period, preventing the muscles from repolarizing and leading to a prolonged state of muscle paralysis.
- Non-depolarizing NMBAs: Non-depolarizing agents, including rocuronium bromide, act by competitively blocking the binding of acetylcholine to the nicotinic receptors on the motor end-plate of the muscle fibers. By doing so, they prevent the transmission of nerve impulses, resulting in muscle relaxation and paralysis. Unlike depolarizing agents, non-depolarizing NMBAs do not cause initial muscle depolarization.
Rocuronium bromide specifically falls into the non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent category. It is widely used in anesthesia to provide muscle relaxation during surgical procedures or to facilitate endotracheal intubation. Its effects are reversible, and the duration of action is typically around 30 to 60 minutes, making it suitable for short to intermediate-duration procedures. The classification of rocuronium bromide as a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent helps differentiate it from other types of muscle relaxants and provides insight into its specific mechanism of action and clinical applications.
Mechanism of Action of rocuronium bromide
The mechanism of action of rocuronium bromide involves its competitive antagonism of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. Here is a detailed explanation of how rocuronium bromide works:
- Binding to Nicotinic Receptors: Rocuronium bromide binds to the nicotinic receptors located on the motor end-plate of the muscle fibers. These receptors are normally activated by acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that transmits nerve impulses from motor neurons to the muscles.
- Competitive Antagonism: By binding to the nicotinic receptors, rocuronium bromide competes with acetylcholine for the same receptor sites. It acts as a competitive antagonist, meaning it blocks the binding of acetylcholine to the receptors.
- Inhibition of Muscle Contraction: When rocuronium bromide occupies the nicotinic receptors, it prevents acetylcholine from binding and activating the receptors. As a result, the normal transmission of nerve impulses from the motor neurons to the muscles is inhibited.
- Muscle Relaxation: The inhibition of acetylcholine binding and nerve impulse transmission leads to muscle relaxation. Rocuronium bromide temporarily paralyzes the skeletal muscles, preventing them from contracting in response to nerve signals. This muscle relaxation is crucial during surgical procedures, as it facilitates better surgical access and prevents involuntary muscle movements that could interfere with the surgery.
It’s important to note that rocuronium bromide’s effects are reversible, and its duration of action can be influenced by factors such as dosage, patient characteristics, and the presence of other medications. After administration, the effects of rocuronium bromide gradually diminish as the medication is metabolized and eliminated from the body. The reversal of muscle relaxation can be achieved by administering medications called acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, which increase the levels of acetylcholine and help restore muscle function.
Overall, rocuronium bromide’s mechanism of action as a competitive antagonist of acetylcholine at the nicotinic receptors results in temporary muscle relaxation and paralysis, making it a valuable tool in anesthesia and critical care settings.
Pharmacodynamics of rocuronium bromide
The pharmacodynamics of rocuronium bromide describes the drug’s effects on the body and how it interacts with receptors and tissues. Here are the key pharmacodynamic properties of rocuronium bromide:
- Neuromuscular Blocking Activity: Rocuronium bromide is a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent. It competitively binds to the nicotinic receptors at the motor end-plate of skeletal muscles, blocking the action of acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting nerve impulses. This inhibition of acetylcholine binding leads to muscle relaxation and paralysis.
- Onset and Duration of Action: Rocuronium bromide has a rapid onset of action, typically taking effect within one to two minutes after intravenous administration. The duration of action is dose-dependent, lasting approximately 30 to 60 minutes. These characteristics make rocuronium bromide suitable for short to intermediate-duration procedures.
- Dose-Dependent Effect: The effects of rocuronium bromide are dose-dependent, meaning that higher doses result in more profound muscle relaxation and paralysis. The dosage and administration of rocuronium bromide are tailored to the specific patient and procedure, taking into account factors such as age, weight, and clinical requirements.
- Reversibility: The effects of rocuronium bromide are reversible, which is an advantage in clinical practice. After administration, the drug is gradually metabolized and eliminated from the body, leading to the return of muscle function. Reversal agents, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., neostigmine), can be used to accelerate the recovery of neuromuscular function if necessary.
- Individual Variability: The pharmacodynamic response to rocuronium bromide can vary among individuals. Factors such as age, gender, weight, and certain medical conditions may influence the sensitivity to the drug’s effects. Additionally, interactions with other medications, especially those affecting neuromuscular function, can alter the response to rocuronium bromide.
- Hemodynamic Effects: Rocuronium bromide has minimal direct effects on the cardiovascular system. However, at higher doses, it may cause transient changes in blood pressure and heart rate due to the associated muscle relaxation. These effects are generally well-tolerated in healthy individuals, but caution should be exercised in patients with preexisting cardiovascular conditions.
It is important to note that the pharmacodynamics of rocuronium bromide should be carefully considered and monitored by trained healthcare professionals to ensure adequate muscle relaxation, minimize the risk of complications, and maintain patient safety during anesthesia or critical care procedures. Please remember that this information is based on my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, and it’s always essential to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the guidance of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on rocuronium bromide.
Metabolism of rocuronium bromide drug
Rocuronium bromide undergoes hepatic metabolism in the body. The main metabolic pathway involves the enzymatic hydrolysis of the ester linkage in the molecule. Here are the key points regarding the metabolism of rocuronium bromide:
- Ester Hydrolysis: The primary metabolic pathway of rocuronium bromide involves the hydrolysis of the ester bond by nonspecific plasma esterases. This process converts rocuronium bromide into 17-desacetyl-rocuronium, which is an inactive metabolite.
- Inactive Metabolite: 17-desacetyl-rocuronium, the major metabolite formed by ester hydrolysis, is pharmacologically inactive and does not possess neuromuscular blocking properties.
- Elimination: After metabolism, both rocuronium bromide and its metabolite, 17-desacetyl-rocuronium, are excreted primarily through the biliary system into the feces. Renal excretion plays a minor role in the elimination of the drug.
- Elimination Half-Life: The elimination half-life of rocuronium bromide is approximately 60 to 75 minutes in healthy individuals with normal hepatic function. The half-life may also be prolonged in patients with inadequate liver function.
- Factors Affecting Metabolism: The metabolism of rocuronium bromide can be influenced by various factors. For instance, liver disease or impaired hepatic function may slow down the metabolism and clearance of the drug, potentially prolonging its effects. Additionally, drug interactions with other medications that affect hepatic enzymes (such as cytochrome P450 enzymes) can impact the metabolism of rocuronium bromide.
It’s worth noting that the metabolites of rocuronium bromide, including 17-desacetyl-rocuronium, are not considered to have significant pharmacological activity or contribute to the neuromuscular blocking effects of the drug. As always, it’s important to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the advice of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on the metabolism of rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Absorption of rocuronium bromide drug
Rocuronium bromide is administered intravenously and is not intended for oral use. As a result, absorption is not a relevant pharmacokinetic parameter for this drug. Upon intravenous administration, rocuronium bromide is rapidly distributed throughout the body. The drug enters the bloodstream directly, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract and absorption processes that are typical for orally administered medications. Intravenous administration allows for immediate and predictable onset of action.
Therefore, while other pharmacokinetic parameters such as distribution, metabolism, and elimination are important for understanding the overall disposition of rocuronium bromide, absorption does not apply to this drug due to its route of administration.
The volume of distribution of rocuronium bromide drug
The volume of distribution (Vd) of a drug is a pharmacokinetic parameter that provides an estimation of the extent of distribution of a drug throughout the body. The Vd indicates how extensively a drug is distributed into tissues compared to the plasma concentration. For rocuronium bromide, the volume of distribution is approximately 0.3 to 0.4 L/kg in healthy adult individuals. This value suggests that rocuronium bromide is primarily distributed within the extracellular fluid compartment of the body.
It’s important to note that the volume of distribution can vary depending on factors such as age, weight, and specific patient characteristics. Additionally, certain conditions, such as liver or renal impairment, may impact the volume of distribution of rocuronium bromide. The relatively high volume of distribution of rocuronium bromide indicates that it has a substantial distribution beyond the bloodstream and can reach peripheral tissues. This extensive distribution contributes to the drug’s onset and duration of action, as well as its clearance from the body.
As always, it’s important to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the advice of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on the volume of distribution of rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Protein binding of rocuronium bromide drug
Rocuronium bromide exhibits minimal protein binding in the bloodstream. Approximately 30% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins, primarily albumin. This relatively low protein binding indicates that a significant portion of rocuronium bromide remains in its unbound form and is freely available for distribution and action. The limited protein binding of rocuronium bromide contributes to its rapid onset of action and predictable pharmacokinetics. Unbound drug molecules are responsible for exerting the neuromuscular blocking effects at the neuromuscular junction.
It’s worth noting that the lack of extensive protein binding also reduces the potential for drug interactions through displacement from protein binding sites. However, interactions at other sites, such as metabolism or renal elimination, may still occur with certain medications. As with any pharmacokinetic parameter, it’s essential to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the advice of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on the protein binding of rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Route of elimination of rocuronium bromide drug
Rocuronium bromide is primarily eliminated from the body through hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion. The drug is not significantly eliminated by the kidneys (renal excretion), as it is mainly metabolized in the liver and then excreted into the bile. The primary route of elimination of rocuronium bromide involves enzymatic hydrolysis of the ester linkage in the molecule. This metabolic process converts rocuronium bromide into an inactive metabolite called 17-desacetyl-rocuronium.
After metabolism, both rocuronium bromide and its metabolite are excreted in the bile and eventually eliminated from the body through feces. Only a small fraction of the drug and its metabolite is eliminated through the urine. Due to its predominantly hepatic elimination, patients with liver impairment may experience alterations in the pharmacokinetics of rocuronium bromide, potentially leading to prolonged effects of the drug. In such cases, careful monitoring and dose adjustments may be necessary to ensure patient safety.
As with any medication, it’s essential to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the advice of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on the elimination of rocuronium bromide or any other drug.
The half-life of rocuronium bromide drug
The elimination half-life of rocuronium bromide, a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, is influenced by several factors, including patient characteristics and liver function. The average elimination half-life of rocuronium bromide in healthy individuals with normal hepatic function is approximately 60 to 75 minutes. It’s important to note that the half-life of rocuronium bromide can vary depending on various factors such as age, weight, underlying health conditions, and the presence of liver disease. Impaired liver function can prolong the elimination half-life of the drug, leading to a longer duration of action and potential accumulation in the body.
It’s worth mentioning that the duration of neuromuscular blockade following a single administration of rocuronium bromide is influenced by both the elimination half-life and the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug. Reversal agents, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, can be administered to accelerate the recovery of neuromuscular function following the use of rocuronium bromide.
As always, it’s essential to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the advice of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on the half-life of rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Clearance of rocuronium bromide drug
The clearance of rocuronium bromide refers to the rate at which the drug is eliminated from the body, typically measured as the volume of plasma cleared of the drug per unit of time (e.g., milliliters per minute or liters per hour). Rocuronium bromide clearance is primarily influenced by hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion. The average total body clearance of rocuronium bromide in healthy individuals with normal liver function is approximately 3.0 to 5.5 mL/kg/min. This clearance value indicates the efficiency at which the drug is metabolized and eliminated from the body.
It’s important to note that clearance may vary based on factors such as age, weight, underlying health conditions, and liver function. Impaired liver function can decrease the clearance of rocuronium bromide, leading to a prolonged duration of action and potential accumulation in the body. The clearance of rocuronium bromide also affects dosing and titration during anesthesia or critical care procedures. Healthcare professionals carefully consider factors such as patient characteristics, co-administered medications, and desired depth of neuromuscular blockade to determine appropriate dosage regimens.
As always, it’s essential to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the advice of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on the clearance of rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Pathways of rocuronium bromide drug
The pathways of rocuronium bromide refer to the various processes involved in the metabolism and elimination of the drug from the body. Here are the key pathways of rocuronium bromide:
- Hepatic Metabolism: Rocuronium bromide undergoes hepatic metabolism, primarily through ester hydrolysis. This process involves the enzymatic cleavage of the ester bond in the molecule, resulting in the formation of an inactive metabolite called 17-desacetyl-rocuronium. This metabolic pathway is mediated by nonspecific plasma esterases.
- Biliary Excretion: After undergoing metabolism, both rocuronium bromide and its inactive metabolite, 17-desacetyl-rocuronium, are excreted primarily through the bile. The drug and its metabolite are transported via the hepatobiliary route into the intestines, ultimately being eliminated from the body through feces.
- Limited Renal Excretion: Rocuronium bromide has minimal renal excretion, with only a small fraction of the drug and its metabolite being eliminated via urine. Renal excretion plays a minor role in the overall elimination of rocuronium bromide from the body.
It’s important to note that the pathways of rocuronium bromide are primarily related to its metabolism and excretion. The drug is not subject to significant reabsorption or enterohepatic circulation. Individual factors such as liver function, age, and the presence of liver disease can affect the metabolism and elimination of rocuronium bromide. Impaired liver function, for example, may prolong the elimination half-life and lead to a more extended duration of action.
It’s always crucial to consult the latest medical literature, product information, and the advice of healthcare professionals for specific and up-to-date information on the pathways of rocuronium bromide or any other medication.
Toxicity of rocuronium bromide drug
Rocuronium bromide is generally considered a safe and effective medication when administered by trained healthcare professionals in appropriate clinical settings. However, like any medication, it can have potential side effects and adverse reactions, especially if not used correctly or in certain patient populations. Here are the key points regarding the toxicity of rocuronium bromide:
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic or hypersensitive to rocuronium bromide, leading to allergic reactions. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin rashes and itching to severe anaphylactic reactions, which are potentially life-threatening. Healthcare professionals should be vigilant for signs of an allergic reaction and be prepared to manage it appropriately.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Rocuronium bromide can cause transient changes in blood pressure and heart rate, especially at higher doses. While these effects are generally well-tolerated in healthy individuals, caution should be exercised in patients with preexisting cardiovascular conditions.
- Prolonged Muscle Weakness: In some cases, the duration of action of rocuronium bromide may be longer than expected, especially in patients with impaired liver function. Prolonged muscle weakness can lead to respiratory complications and require supportive measures or the use of reversal agents to accelerate neuromuscular recovery.
- Malignant Hyperthermia Susceptibility: Individuals with a known or suspected susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia, a rare but potentially life-threatening condition triggered by certain medications used during anesthesia, may be at increased risk of adverse reactions to rocuronium bromide.
- Metabolic Acidosis: In rare cases, the administration of rocuronium bromide has been associated with the development of metabolic acidosis, particularly in patients with underlying health conditions.
- Drug Interactions: Rocuronium bromide can interact with other medications, especially those affecting neuromuscular function or hepatic metabolism. Drug interactions may alter the response to rocuronium bromide and lead to unexpected side effects.
It’s crucial for healthcare professionals to carefully assess patients’ medical history, allergies, and current medications before administering rocuronium bromide. Proper dosing, monitoring, and preparation to manage potential adverse reactions are essential to ensure patient safety. In the event of an adverse reaction or toxicity, healthcare professionals should be ready to provide appropriate supportive care and consider the use of reversal agents, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, to reverse the neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium bromide.
As always, patients should communicate any preexisting medical conditions, allergies, or concerns to their healthcare providers to minimize the risk of adverse reactions to medications like rocuronium bromide.
What is the function of the rocuronium bromide drug?
The primary function of rocuronium bromide is to induce muscle relaxation during surgical procedures or to facilitate endotracheal intubation. As a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, rocuronium bromide acts at the neuromuscular junction to temporarily paralyze skeletal muscles.
Here are the details of its functions:
- Muscle Relaxation: Rocuronium bromide is administered intravenously to induce muscle relaxation during surgical procedures. By blocking the transmission of nerve impulses at the neuromuscular junction, it prevents muscle contractions and enables optimal surgical conditions. Muscle relaxation is particularly important for surgeries that require precise access, such as abdominal surgeries or orthopedic procedures.
- Endotracheal Intubation: Rocuronium bromide is commonly used to facilitate endotracheal intubation, which involves inserting a breathing tube into the patient’s trachea. Muscle relaxation is essential during intubation as it allows for easier insertion of the tube and reduces the risk of complications. Intubation is often required during general anesthesia or in critical care settings to ensure proper ventilation.
- Controlled Ventilation: In certain medical situations, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or severe asthma exacerbation, patients may require controlled ventilation using a mechanical ventilator. Rocuronium bromide can be administered to induce muscle relaxation and facilitate effective mechanical ventilation in these cases.
- Prevention of Involuntary Muscle Movements: During surgery, involuntary muscle movements can occur due to inadequate anesthesia or nerve stimulation. These movements can interfere with the surgical procedure. Rocuronium bromide is used to prevent such movements by temporarily paralyzing the muscles.
It’s important to note that the use of rocuronium bromide requires careful titration and monitoring by trained healthcare professionals. The dosage and administration of rocuronium bromide should be individualized based on factors such as the patient’s age, weight, and overall health. The primary function of rocuronium bromide is to provide muscle relaxation, allowing for successful surgical procedures, smooth endotracheal intubation, and controlled ventilation in appropriate clinical settings.
How long should I use an over-the-counter rocuronium bromide drug?
It seems to be a misunderstanding. Rocuronium bromide is not available over-the-counter (OTC). It is a potent prescription medication used in medical settings, particularly during anesthesia and surgical procedures. Rocuronium bromide should only be administered by trained healthcare professionals in controlled environments such as operating rooms, intensive care units, or emergency departments. It is not intended for self-administration or use without proper medical supervision.
If you have any concerns or questions about medication use, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can provide appropriate guidance based on your specific medical condition and needs. They can advise you on the appropriate medications, including any over-the-counter options that may be suitable for your situation. It’s always important to seek personalized medical advice from a healthcare professional regarding specific medications and their appropriate use.
How long does the rocuronium bromide drug take to work?
Rocuronium bromide, when administered intravenously, has a rapid onset of action. The time it takes for the drug to take effect depends on various factors, including the dose administered, patient characteristics, and the rate of administration. Here are the details regarding the onset of action of rocuronium bromide:
- Rapid Onset: Rocuronium bromide typically begins to take effect within one to two minutes after intravenous administration. This rapid onset allows for quick muscle relaxation, making it suitable for procedures requiring a prompt onset of action.
- Dose-Dependent Effect: The onset of action of rocuronium bromide is influenced by the dose administered. Higher doses generally result in a more rapid onset of muscle relaxation.
- Individual Variability: The onset of action can vary among individuals due to factors such as age, weight, and overall health. Certain patient characteristics, such as liver or kidney dysfunction, can affect the pharmacokinetics and onset of action of rocuronium bromide.
It’s important to note that while the onset of action of rocuronium bromide is relatively rapid, the full extent of muscle relaxation may take slightly longer to achieve. Healthcare professionals closely monitor the patient’s reaction to the medication and modify the dose as necessary to achieve the expected level of muscle relaxation. It’s crucial to follow the guidance and administration protocols provided by healthcare professionals when using rocuronium bromide. They will determine the appropriate dose, rate of administration, and monitoring required for each specific patient and procedure.
Please remember that the information provided here is based on general knowledge and specific dosing and administration details should be discussed with a qualified healthcare professional who can consider individual factors and provide personalized guidance.
Why this rocuronium bromide drug is prescribed?
Rocuronium bromide is primarily prescribed and used in medical settings, such as operating rooms, intensive care units, and emergency departments. It is a prescription medication with specific indications and is administered by trained healthcare professionals for the following purposes:
- Muscle Relaxation during Surgical Procedures: One of the main uses of rocuronium bromide is to induce muscle relaxation during surgical procedures. By temporarily paralyzing the skeletal muscles, rocuronium bromide helps facilitate surgery by providing better surgical access and preventing involuntary muscle movements that could interfere with the procedure. It is commonly used in a wide range of surgical specialties, including general surgery, orthopedics, cardiovascular surgery, and more.
- Facilitation of Endotracheal Intubation: Rocuronium bromide is often used to facilitate endotracheal intubation, which involves the insertion of a breathing tube into the patient’s trachea. Muscle relaxation is necessary for successful and smooth intubation, as it allows for easier insertion of the tube and reduces the risk of complications. Endotracheal intubation is commonly performed during general anesthesia or in critical care settings to ensure adequate ventilation.
It’s important to note that rocuronium bromide is administered intravenously and is not intended for self-administration or use without proper medical supervision. The dosage and administration of rocuronium bromide should be determined by healthcare professionals based on factors such as the patient’s age, weight, overall health, and specific surgical or intubation requirements. As always, it’s essential to consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized medical advice regarding the appropriate use of rocuronium bromide or any other medication. They can provide specific guidance based on an individual’s medical condition, needs, and the latest medical guidelines.
How does my doctor choose a rocuronium bromide drug that’s good for me?
The selection of rocuronium bromide or any medication is typically based on several factors that your doctor will consider to determine what is best for you. Here are a few of the key considerations:
- Medical Condition: Your doctor will evaluate your specific medical condition and the purpose for which rocuronium bromide is being prescribed. They will assess factors such as the type of surgery or procedure you are undergoing, the need for muscle relaxation, and the desired level of paralysis.
- Individual Characteristics: Your doctor will take into account various individual factors, including your age, weight, overall health, and any preexisting medical conditions. These factors can influence the appropriate dosage, rate of administration, and monitoring required to ensure safe and effective use of rocuronium bromide.
- Medical History and Allergies: Your doctor will review your medical history, including any previous experiences with anesthesia or neuromuscular blocking agents. They will also consider any known allergies or sensitivities you may have to medications, including rocuronium bromide or other similar drugs.
- Contraindications and Precautions: Your doctor will carefully assess any contraindications or precautions associated with the use of rocuronium bromide. This includes considering conditions such as malignant hyperthermia susceptibility, severe burns, skeletal muscle myopathies, or conditions affecting the neuromuscular junction.
- Interactions and Medication Profile: Your doctor will review your current medication profile to check for potential interactions between rocuronium bromide and any other medications you are taking. They will ensure that there are no medications that could adversely affect the safety or efficacy of rocuronium bromide or vice versa.
- Anesthesia Plan: If rocuronium bromide is being used as part of an anesthesia plan, your doctor will consider the overall anesthesia plan and work in collaboration with the anesthesiologist to determine the appropriate use of rocuronium bromide within that plan.
- Professional Guidelines: Your doctor will adhere to professional guidelines and best practices established by medical associations and organizations. These guidelines provide recommendations for the appropriate use of rocuronium bromide and help ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes.
Your doctor will utilize their clinical expertise and consider all these factors to make an informed decision about the suitability and dosing of rocuronium bromide specifically tailored to your needs. It’s important to communicate openly with your doctor, provide accurate information about your medical history, allergies, and medications, and ask any questions or express any concerns you may have. This will enable your doctor to make the best decisions regarding your treatment and ensure your well-being throughout the process.
What are the side effects of the rocuronium bromide drug?
Rocuronium bromide, like any medication, can have side effects. While not everyone participates in these side effects, it is important to be conscious of potential adverse reactions. Here are some of the common side effects associated with rocuronium bromide:
- Respiratory Effects: Rocuronium bromide can affect the respiratory system, potentially causing respiratory depression or difficulty breathing. This is more likely to occur at higher doses or in individuals with respiratory conditions. Adequate ventilation and monitoring are essential during the administration of rocuronium bromide.
- Hypotension and Bradycardia: Rocuronium bromide can cause transient changes in blood pressure and heart rate, leading to low blood pressure (hypotension) and a slower heart rate (bradycardia). These effects are usually mild and well-tolerated in healthy individuals, but caution should be exercised in patients with cardiovascular conditions.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, allergic reactions to rocuronium bromide can occur. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include skin rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, or anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction. Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience signs of an allergic reaction.
- Prolonged Muscle Weakness: In some cases, the duration of action of rocuronium bromide may be longer than anticipated, resulting in prolonged muscle weakness or paralysis. This can delay the recovery of neuromuscular function and require supportive measures or the administration of reversal agents.
- Metabolic Acidosis: Rarely, the use of rocuronium bromide has been associated with the development of metabolic acidosis, a condition characterized by an imbalance in the body’s acid-base status. This can occur particularly in patients with certain underlying health conditions.
- Other Side Effects: Additional potential side effects of rocuronium bromide may include nausea, vomiting, flushing, itching, and muscle pain. Typically, these side effects are mild and brief.
It is important to note that the occurrence and severity of side effects can vary among individuals, and not everyone will experience them. Healthcare professionals closely monitor patients during the administration of rocuronium bromide and take appropriate measures to address any adverse reactions that may arise. If you experience any concerning side effects or have any questions or concerns about rocuronium bromide, it’s crucial to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can provide further information, guidance, and appropriate management strategies based on your specific situation.
What should I know regarding the storage and disposal of this rocuronium bromide?
Storage and disposal guidelines for rocuronium bromide, or any medication, are important for ensuring medication effectiveness, maintaining safety, and protecting the environment. The following are a couples of central issues to remember:
Storage:
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Always refer to the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer or pharmacist regarding the storage of rocuronium bromide. These instructions may include temperature requirements and storage conditions.
- Protect from Light and Moisture: Medications, including rocuronium bromide, should be stored in a dry place away from direct light. Exposure to light and moisture can degrade the medication and affect its potency.
- Keep Out of Reach of Children and Pets: Store rocuronium bromide in a secure location that is out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or misuse.
- Temperature Considerations: Check the storage temperature requirements for rocuronium bromide. It is typically stored at a controlled room temperature, but specific instructions may vary. Avoid exposing the medication to extreme temperatures, such as excessive heat or cold, unless otherwise directed.
- Proper Packaging: Ensure that rocuronium bromide is stored in its original packaging or in a tightly sealed container to maintain its integrity and prevent contamination.
Disposal:
- Check Local Regulations: Follow the local regulations and guidelines for the disposal of medications, as they may vary depending on your location. These regulations are in place to protect the environment and prevent the misuse or accidental ingestion of medications.
- Do Not Flush: Do not flush rocuronium bromide down the toilet or pour it down the drain unless instructed to do so by specific disposal instructions or local regulations. Flushing medications can contaminate water sources and harm the environment.
- Medication Take-Back Programs: Check to see if there are any nearby medication take-back events or programs. Unwanted or expired medications can be disposed of in a secure and environmentally friendly manner through these programs.
- Safe Packaging: If there are no specific disposal instructions or take-back programs available, you can mix rocuronium bromide with an undesirable substance, such as cat litter or coffee grounds, and seal it in a secure container before disposing of it in the household trash. This helps prevent accidental ingestion.
- Remove Personal Information: Before discarding the medication packaging, ensure that any personal or sensitive information is removed or made unreadable to protect your privacy.
Always consult your local regulations and guidelines or contact your pharmacist or healthcare provider for specific instructions on the storage and disposal of rocuronium bromide. They can provide you with the most up-to-date and relevant information based on your location and circumstances.
In what circumstances should I check with my doctor before taking this rocuronium bromide drug?
It is important to consult with your doctor before taking rocuronium bromide or any medication to ensure it is appropriate and safe for you. Here are some specific circumstances in which it is crucial to check with your doctor:
Medical History: Inform your medic about your entire medical history, including any past or current medical needs. Certain conditions may require extra caution or monitoring when using rocuronium bromide. Examples include:
- Liver or Kidney Disease: Impaired liver or kidney function can affect the metabolism and elimination of rocuronium bromide, potentially prolonging its effects.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Patients with heart conditions or a history of cardiovascular disease may require careful monitoring as rocuronium bromide can cause changes in blood pressure and heart rate.
- Respiratory Conditions: Individuals with respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), may require extra caution during the administration of rocuronium bromide due to its potential respiratory effects.
- Allergies: Inform your doctor of any known allergies or sensitivities to medications, especially any previous reactions to neuromuscular blocking agents or similar medications.
Medications and Supplements: Discuss all medications, including prescription, over-the-counter medications, and supplements, that you are currently taking with your doctor. Certain medications can interact with rocuronium bromide, potentially affecting its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. It is essential to inform your doctor about all medications to ensure safe co-administration.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: If you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding, it is important to discuss the use of rocuronium bromide with your doctor. They can assess the potential risks and benefits and determine the appropriateness of the medication during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Previous Anesthesia or Surgical Experiences: Inform your doctor of any previous experiences with anesthesia, surgery, or the use of neuromuscular blocking agents. This information can help your doctor assess your response and tailor the treatment plan accordingly.
Other Considerations: If you have any concerns or questions about rocuronium bromide or its administration, it is important to discuss them with your doctor. They can provide detailed information, address your concerns, and provide guidance specific to your situation.
By discussing these factors with your doctor, they can evaluate the potential risks and benefits of rocuronium bromide and make an informed decision about its use in your particular case. Open communication and sharing accurate information with your healthcare provider are essential for safe and effective treatment.
Can rocuronium bromide drugs cause allergic reactions?
Yes, allergic reactions to rocuronium bromide are possible, although they are relatively rare. Allergic reactions occur when the body’s immune system reacts abnormally to a substance, perceiving it as a threat. Here are some details regarding allergic reactions to rocuronium bromide:
Symptoms: Allergic reactions to rocuronium bromide can manifest in various ways. Common symptoms may include:
- Skin reactions: Itching, hives (urticaria), redness, or rash on the skin.
- Respiratory symptoms: Difficulty breathing, wheezing, shortness of breath, or tightness in the chest.
- Swelling: Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, or other body parts (angioedema).
- Anaphylaxis: In severe cases, anaphylaxis can occur, which is a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. Anaphylaxis involves a rapid and systemic immune response and may include symptoms such as difficulty breathing, a drop in blood pressure, rapid heart rate, dizziness, and loss of consciousness.
Risk Factors: Certain individuals may be at a higher risk of experiencing an allergic reaction to rocuronium bromide. These may include individuals with a history of allergic reactions to other neuromuscular blocking agents or individuals with a known hypersensitivity to specific ingredients within the medication.
Cross-Reactivity: Cross-reactivity refers to the potential for an allergic reaction to occur when exposed to a structurally similar medication. While cross-reactivity between rocuronium bromide and other neuromuscular blocking agents is possible, it does not necessarily mean that an individual who is allergic to one specific agent will have an allergic reaction to all agents in the same class. Each case is unique, and individual testing and evaluation may be required.
Immediate Medical Attention: If you experience any signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction after receiving rocuronium bromide, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Allergic reactions can rapidly escalate and may require prompt treatment to ensure the best possible outcome.
It’s important to communicate any known allergies or hypersensitivities to medications, including neuromuscular blocking agents, with your healthcare provider. They can assess your risk and take necessary precautions to minimize the potential for an allergic reaction. If an allergy to rocuronium bromide is confirmed, alternative medications or strategies can be considered for muscle relaxation during procedures. This information is not exhaustive, and individual responses to medications can vary. If you have concerns or questions about allergic reactions to rocuronium bromide or any other medication, it’s crucial to discuss them with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.
What should I do if I forget a dose of the rocuronium bromide drug?
As rocuronium bromide is a medication administered by healthcare professionals in medical settings, it is unlikely that you would be responsible for remembering or administering a dose yourself. The administration of rocuronium bromide is typically managed by trained healthcare providers who follow specific protocols and guidelines. However, if you have any concerns or questions about a missed dose or the administration of rocuronium bromide, it is important to reach out to your healthcare provider or the healthcare team responsible for your care. They can also provide you with specific recommendations based on your circumstances.
It’s important to note that the administration of rocuronium bromide is carefully monitored and adjusted by healthcare professionals to ensure optimal muscle relaxation and patient safety. If a dose is missed, healthcare providers will assess the situation, potentially adjust the dosing regimen, or take appropriate actions to ensure continued effectiveness.
Remember, this information is provided for general knowledge, and it is essential to consult your healthcare provider or the healthcare team responsible for your care for personalized advice regarding rocuronium bromide or any medication. They have access to your specific medical information and can provide you with the most appropriate guidance based on your individual needs.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes rocuronium bromide drug
The use of rocuronium bromide, like any medication, involves an interprofessional healthcare team working together to ensure optimal outcomes and patient safety. Collaboration and effective communication among healthcare professionals is essential. Here’s how the healthcare team can enhance outcomes related to the use of rocuronium bromide:
- Anesthesiologist: Anesthesiologists play a crucial role in the administration and monitoring of rocuronium bromide during anesthesia. They determine the appropriate dosage, assess the patient’s response, and manage any potential complications. Anesthesiologists closely monitor the patient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, to ensure patient safety.
- Surgeon: Surgeons work closely with the anesthesiologist to determine the timing and dosage of rocuronium bromide administration during surgical procedures. They communicate their needs and preferences to ensure optimal muscle relaxation for a successful surgery.
- Nurses: Nurses are responsible for administering rocuronium bromide under the supervision of the healthcare team. They follow specific protocols for preparation, administration, and monitoring. Nurses also provide continuous patient care, monitor vital signs, and assist with any potential side effects or complications that may arise.
- Pharmacists: Pharmacists play a crucial role in medication management, including rocuronium bromide. They ensure accurate medication dosing, check for potential interactions with other medications, provide guidance on storage and handling, and assist in the prevention and management of medication errors.
- Respiratory Therapists: Respiratory therapists are involved in the management of the patient’s airway and ventilation. They collaborate with the anesthesiologist to ensure proper respiratory function before, during, and after the administration of rocuronium bromide. They may also assist with intubation, mechanical ventilation, and monitoring respiratory status during procedures.
- Laboratory Technicians: Laboratory technicians may be involved in monitoring certain laboratory values, such as electrolyte levels, that can impact the response to rocuronium bromide. They assist in ensuring that the patient’s biochemical parameters are within acceptable ranges for safe administration.
- Allergy Specialists: Allergy specialists may be consulted if there is a suspected or confirmed allergy to rocuronium bromide or other neuromuscular blocking agents. They can provide expertise in assessing the allergy, conducting appropriate testing, and recommending alternative medications or strategies for muscle relaxation.
Effective communication, collaboration, and a shared understanding of the patient’s needs are crucial among the healthcare team to optimize outcomes when using rocuronium bromide. Each team member contributes their expertise and ensures patient safety throughout the process. It’s important for patients to actively participate in their care, provide accurate information about their medical history and allergies, and ask questions to understand the medication’s purpose, potential side effects, and the role of each healthcare team member in their treatment journey.
What is the dosage of the rocuronium bromide drug?
The dosage of rocuronium bromide can vary depending on various factors, including the patient’s age, weight, medical condition, the desired level of muscle relaxation, and the specific procedure being performed. The dosage is determined by trained healthcare professionals, typically anesthesiologists or other healthcare providers administering the medication in medical settings. Here are some general considerations regarding the dosage of rocuronium bromide:
- Individualized Dosage: The dosage of rocuronium bromide is individualized for each patient based on their specific needs. It is tailored to achieve the desired level of muscle relaxation while minimizing the risk of side effects.
- Weight-Based Dosage: The weight of the patient is an important consideration in determining the dosage. In general, rocuronium bromide is administered at a dose of approximately 0.6 to 1.2 mg/kg of body weight.
- Titration and Monitoring: The administration of rocuronium bromide is titrated based on the patient’s response, to achieve the appropriate level of muscle relaxation for the duration required during the procedure. Healthcare professionals closely monitor the patient’s response, adjusting the dosage as necessary to maintain the desired level of muscle relaxation.
- Reversal Agents: In some cases, reversal agents, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., neostigmine), may be administered to reverse the effects of rocuronium bromide once the procedure is completed. The dosage and administration of reversal agents are determined separately based on the specific patient’s needs.
It’s important to note that the dosage of rocuronium bromide should only be determined and administered by trained healthcare professionals who have the necessary knowledge and expertise. They consider various factors, including the patient’s medical history, overall health, and specific surgical or procedural requirements, to determine the appropriate dosage for each case. It is always recommended to follow the guidance and instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding the dosage and administration of rocuronium bromide or any other medication. They have access to your specific medical information and can make the best decisions based on your individual needs.
What other drugs interact with the rocuronium bromide drug?
Rocuronium bromide can interact with several other medications, and it’s important to be aware of these potential interactions. Informing your healthcare provider about all the medications, including prescription, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements you are taking, is crucial to minimize the risk of interactions. Here are some examples of medications that may interact with rocuronium bromide:
- Anesthetics: Other anesthetic agents, such as volatile inhalation anesthetics (e.g., isoflurane, sevoflurane) or intravenous anesthetics (e.g., propofol), can potentiate the effects of rocuronium bromide, leading to increased muscle relaxation and prolonged duration of action.
- Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, including neostigmine and pyridostigmine, are used as reversal agents to counteract the effects of rocuronium bromide. When administered together, these medications can work in opposition to each other, with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors reversing the muscle relaxation induced by rocuronium bromide.
- Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, such as aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin, tobramycin) and tetracyclines, can enhance the neuromuscular blockade produced by rocuronium bromide. These antibiotics may potentiate the effects of rocuronium bromide, resulting in increased muscle relaxation.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Magnesium sulfate, commonly used for various medical conditions, can potentiate the effects of rocuronium bromide, leading to a prolonged duration of action.
- Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers, medications used to treat conditions like hypertension and heart disease, may interact with rocuronium bromide and enhance the muscle-relaxing effects of the drug. This interaction can potentially result in prolonged neuromuscular blockade.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil and diltiazem, have been reported to enhance the neuromuscular blocking effects of rocuronium bromide. Co-administration of these medications can increase the depth and duration of muscle relaxation.
These are just a few examples of medications that can interact with rocuronium bromide. However, there may be other medications, including herbal supplements and over-the-counter drugs, that can also interact with rocuronium bromide. Always inform your healthcare provider about all the medications and supplements you are taking to ensure the safe and effective use of rocuronium bromide. Your healthcare provider will assess the potential interactions and determine the best course of action to minimize any risks. They may adjust the dosage or timing of administration or consider alternative medications if necessary.
It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance and ask any specific questions regarding potential interactions with rocuronium bromide or any other medication you are prescribed.
Precautions to take when using this rocuronium bromide drug
When using rocuronium bromide, it is important to take certain precautions to ensure safe and effective administration. Here are a few key points for precautions to remember:
- Administration by Trained Healthcare Professionals: Rocuronium bromide should only be administered by trained healthcare professionals who are experienced in its use. They have the necessary knowledge and expertise to determine the appropriate dosage, monitor the patient’s response, and manage any potential complications.
- Patient Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the patient is essential during the administration of rocuronium bromide. This includes monitoring vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and respiratory function. Close monitoring allows for the early detection of any adverse reactions or complications.
- Individualized Dosing: The dosage of rocuronium bromide should be individualized based on factors such as the patient’s age, weight, overall health, and the specific procedure being performed. The dosage should be tailored to achieve the desired level of muscle relaxation while minimizing the risk of side effects.
- Allergy and Hypersensitivity: Inform your healthcare provider of any known allergies or hypersensitivity reactions to medications, especially neuromuscular blocking agents. This information is crucial in assessing the risk of potential allergic reactions to rocuronium bromide and determining the appropriate course of action.
- Resuscitation Equipment: Adequate resuscitation equipment, including airway management devices, should be readily available during the administration of rocuronium bromide. This allows for prompt intervention in case of respiratory distress or other emergencies.
- Special Patient Populations: Extra caution should be exercised when using rocuronium bromide in certain patient populations, such as elderly patients, patients with underlying cardiovascular or respiratory conditions, or patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Close monitoring and potential dose adjustments may be necessary in these cases.
- Proper Storage and Handling: Ensure proper storage and handling of rocuronium bromide according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This includes protecting it from light, moisture, and extreme temperatures. Follow the recommended storage guidelines to maintain the medication’s integrity and effectiveness.
- Drug Interactions: Inform your healthcare provider about all the medications, including prescription, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements you are taking. Certain medications can interact with rocuronium bromide, potentially affecting its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Your healthcare provider can assess these interactions and make necessary adjustments or recommendations.
It is crucial to follow the guidance and instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding the precautions associated with rocuronium bromide. This ensures that the medication is used safely and effectively, minimizing potential risks and optimizing patient outcomes. Always communicate openly with your healthcare provider, provide accurate information about your medical history, allergies, and medications, and ask any questions or express any concerns you may have. This promotes a collaborative approach to your care and enhances patient safety.
Conclusion
Rocuronium bromide is a medication used to induce muscle relaxation during surgical procedures or facilitate endotracheal intubation. It works by blocking the transmission of nerve impulses at the neuromuscular junction, temporarily paralyzing skeletal muscles. Rocuronium bromide is administered intravenously by trained healthcare professionals in controlled medical settings. It has a rapid onset of action, individualized dosing, and requires careful monitoring. While generally well-tolerated, rocuronium bromide can have potential side effects such as respiratory effects, hypotension, allergic reactions, and prolonged muscle weakness. Precautions should be taken, including proper patient monitoring, allergy assessment, and considerations for special patient populations. It is important to follow healthcare provider instructions and communicate openly for the safe and effective use of rocuronium bromide.
Disclaimer: The following article is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. The information contained in this article is based on the author’s understanding and interpretation of the subject at the time of writing. The content of this article should not be considered exhaustive, and additional research or consultation with experts may be necessary. The reader is encouraged to independently verify the accuracy, currency, and relevance of the information provided.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any organization, company, or individual. Any reference or mention of specific products, services, or organizations does not imply endorsement or recommendation by the author or the publisher. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented, the author and the publisher assume no responsibility for any errors, omissions, or damages arising from the use of the information provided in this article.
FAQs
What class of medication is rocuronium bromide?
Neuromuscular specialists are named depolarizing or nondepolarizing. Rocuronium is a nondepolarizing neuromuscular obstructing specialist with a quick to middle beginning relying upon portion and moderate length.
What is the contrast between succinylcholine and rocuronium bromide?
Succinylcholine has been customarily utilized as a first-line incapacitated because of its fast beginning of activity and short half-life. Succinylcholine’s length of activity is 10 — 15 minutes, while the half-existence of rocuronium is somewhere in the range of 30 — an hour and a half, contingent upon the portion.
What is the cure for rocuronium?
Sugammadex is a specific relaxant restricting specialist demonstrated for the inversion of moderate to profound NMB,3 with a high partiality for rocuronium. Sugammadex inactivates neuromuscular blocking agents like rocuronium by encapsulating them, causing the NMB to reverse.
What are the contraindications of rocuronium?
Patients who are known to be hypersensitive to rocuronium bromide or other neuromuscular blocking agents (such as anaphylaxis) should not take rocuronium bromide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. You might be able to look through our database of Scientific Response Documents if you provide additional keywords.
Might neostigmine at any point turn around rocuronium?
Neostigmine is ineffectual at such profound degrees of neuromuscular block. Hypothetically, if quick inversion of rocuronium is expected after its organization, as in an inability to intubate circumstance, then, at that point, sugammadex 16 mg kg−1 is encouraged.
Is bradycardia possible with rocuronium?
Significant bradycardias (pulse < 30 beats. min-1) occurred in 5% of vecuronium-treated patients, but none of the patients in the rocuronium study group experienced it.
Does rocuronium influence the heart?
Results. When compared to the control group, pancuronium caused a dose-dependent increase in heart rate (P 0.027). Vecuronium, rocuronium, and mivacurium likewise expanded pulse in a portion subordinate way, yet the progressions were not genuinely huge.
What are the upsides of rocuronium?
Its fundamental benefit over other such specialists is its fast beginning of the activity, which might prompt its utilization as the relaxant of decision when quick intubation is required. That’s what an extra benefit is, dissimilar to other amino-steroidal NDNMBAs, rocuronium doesn’t deliver dynamic metabolites.
Is rocuronium eliminated by dialysis?
Conclusions: Haemodialysis utilizing a high-transition dialysis technique is compelling in eliminating sugammadex and the sugammadex-rocuronium complex in patients with extreme renal debilitation.