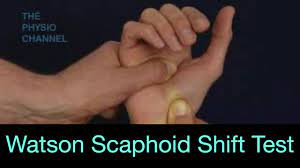
Scaphoid shift test:
- This test is also known as the Watson test.
- This test is described to Watson in the American Research in General Orthopedics in march 1978 in New Orleans
- This test is a provocative manoeuvre type test, which is used to examine the dynamic stability of the scaphoid bone &
- Reproduce the patient’s symptoms.
- Besides the stability, the examiner is also able to reflect on the quality of the adjoining articular surfaces.
Purpose of the Scaphoid shift test:
- This test is used to check the dynamic stability of the scaphoid bone.
- This test is also used to diagnose the scapholunate interosseous ligament instability = SLIL.
- This test is also helpful during the examination of the wrist joint & more specifically of the scaphoid bone.
The technique of the performance of the Scaphoid shift test:
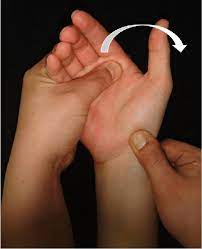
- The patient sits with the elbow resting on the table & forearm pronated.
- The examiner faces the patient.
- With the help of one hand, the examiner takes the patient’s wrist joint into full ulnar deviation & slight extension while holding the metacarpals.
- The examiner presses the thumb with the help of the other hand against the distal pole of the scaphoid on the palmar side
- To prevent it from moving towards the palm while the fingers provide counter pressure on the dorsum of the forearm.
- With the first hand, the examiner radially deviates & slightly flexes the patient’s hand while maintaining pressure on the scaphoid.
- This creates subluxation stress if the scaphoids are unstable.
- If the scaphoid is unstable, the dorsal pole of the scaphoids sublexes / shifts over the dorsal rim of the radius bone & the patient complains of pain, indicating a positive test.
- If the scaphoid sublaxes with the thumb pressure when the thumb is removed, the scaphoid commonly returns to its normal position with a thunk.
- If the ligaments tissue is intact, the scaphoid normally moves forward, pushing the thumb forward with it.
- The test may also be used if a scaphoid fracture is suspected.
- In this case, the pain occurs without the thunk.
Interpretation of the Scaphoid shift test:
- A positive test of Scaphoid shift test: A palpable & audible reduction of the subluxated scaphoid bone & elicitation of the symptomatic pain, usually on to the dorsal side.
- Negative test of Scaphoid shift test: Scaphoid bone moves normally, pushing the back on the examiner’s thumb with the ulnar deviation of the wrist joint, & there is no symptomatic of the pain.
- The examiner must be able to conclude a variety of the findings from this test so that the mobility itself is not directly be considered pathological because it is caused by hyper mobility syndrome.
- Though to unilateral hypermobility is rather than suspicious.
- Pain is similar to the patient’s symptoms during the dorsal shift indicates symptomatic subluxation of the scaphoid bone, pain which is less localised combined with the normal/limited movement point in the direction of periscaphoid arthritis / scaphoid-Iunate which is advanced the collapse pattern.
- A gritty, clicking / smooth sensation gives an idea about the state of the articular cartilage & bony form of the joint.
- When there are doubts and to have clear results about the actual shift, a radioscopy & mostly the fluoroscopic are used to get the clear images & information about the scaphoid shift test.