Special test for the ligamentous instability in the ankle:
- These tests are applied to the clinic the check the ligamentous instability in the ankle.
- These tests are clinical diagnostic test which is applied in the clinic.
- These tests are applied by physiotherapists or doctors when the patients complain about ankle pain.
Name of the special test of ligamentous instability in the ankle:
- Dorsiflexion compression test
- Dorsiflexion maneuver
- Fibular translation test
Purpose of the Special test for the ligamentous instability in the ankle:
- These tests are used to check the ligamentous instability in the ankle.
- It is also used to check the problems in syndesmosis.
- It is applied with the check of the ROM of the ankle.
Dorsiflexion compression test :-
The technique of dorsiflexion compression test :
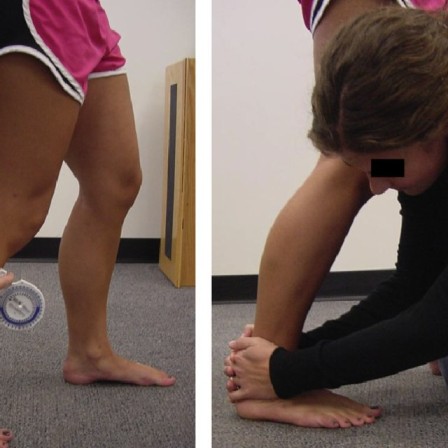
- The starting position of the test is standing.
- While in bilateral weight-bearing, the patient is asked to move their ankle into extreme dorsiflexion.
- The patient has noted whether this maneuver is painful while the examiner notes the end ROM.
- After that, the patient is returned to a normal standing position again.
- Then the examiner applies a force of compression with the help of two hands surrounding the malleoli of the affected leg.
- While this compression is maintained, the patient is asked to move into dorsiflexion again.
- Result = a decrease in pain on dorsiflexion or an increase in dorsiflexion range indicates a positive test.
Dorsiflexion maneuver :-
The technique of dorsiflexion maneuver :
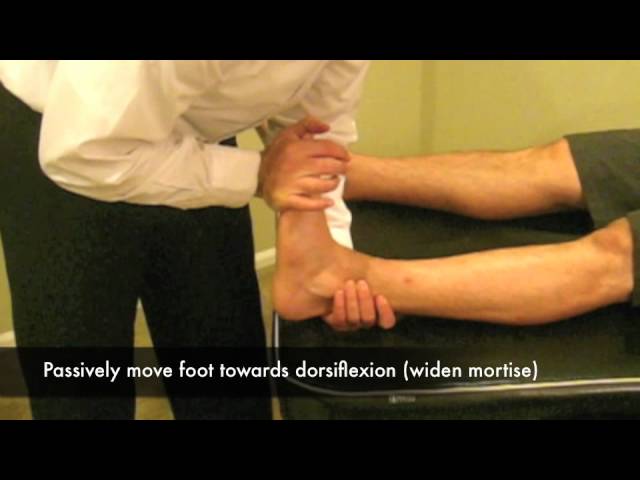
- The starting position of the test is sitting.
- The patient sits on the edge of the examiner table.
- The examiner stabilizes the patient’s leg with the help of one hand & with the help of the other hand passively & forcefully dorsiflexes the foot by holding onto the heel & using the forearm to dorsiflex the foot.
- Result = pain on forced dorsiflexion indicates a positive test for a syndesmosis problem.
Fibular translation test :-
The technique of dorsiflexion maneuver :
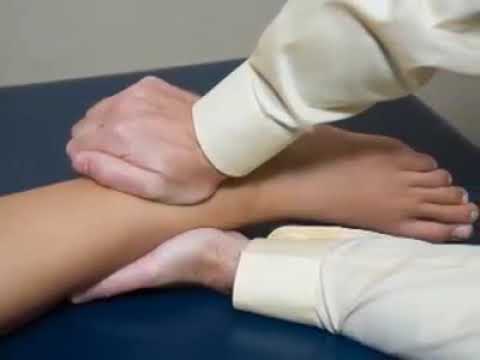
- The starting position of the test is side – lying.
- The examiner faces the foot to be examined from the front & stabilizes the tibia with the help of one hand & translates the fibular malleolus anteriorly & posteriorly with the help of the other hand.
Result = if pain occurs during the translation/if the movement is greater on the affected side, the test is considered positive for a
syndesmosis injury.