Special test for the Lumbar Instability
- Lumbar instability implies that during movement, the patient loses the ability to control the movement for a brief time..or it may mean the segment is structurally unstable.
- The brief loss of control often results in a painful catch, apprehension, or an instability jog [ sudden shift of movement in part of ROM].
- Pope called this instability loss of control in the neutral spine.
- It commonly occurs with spondylosis owing to degeneration of the disc.
- These all tests are applied to the clinic to check the lumbar instability of the patient by the therapist [ examiner ].
Purpose of the all special test for the lumbar instability:
- These all tests are used to check the lumbar instability of the patient when the patient is complaining is about lower back pain.
Name of the special test of the lumbar instability:
- Farfan torsion test
- Lateral lumbar spine stability test
- Passive lumbar extension test
- Pheasant test
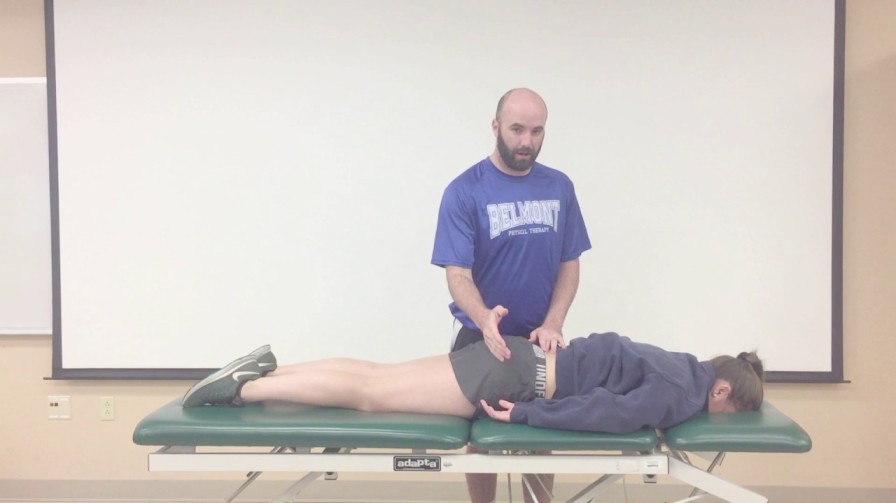
Farfan torsion test:
- This nonspecific test stresses the facet joint, joint capsule, supraspinous & infraspinous ligaments, neural arch, longitudinal ligaments,& the disc.
How do you perform the Farfan torsion test?
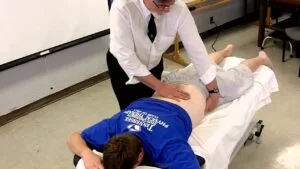
- The patient is in the prone position.
- The examiner stabilizes the ribs & spine [ at about T12 ] with the help of one hand & places the other hand of the examiner under the anterior aspect of the ilium.
- The examiner then pulls the ilium backward causing the spine to be rotated on the opposite side producing a torque on the opposite side.
What is the result of the Farfan torsion test?
- The test is said to be positive if it reproduces all or some of the patient’s symptoms.
- The other side is testes for compression.
Lateral lumbar spine stability test:-
How do you perform the lateral lumbar spine stability test?
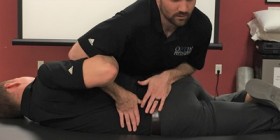
- The patient is placed in the side-lying position with the lumbar spine in neutral.
- The examiner places the forearm over the side of the thorax at about the L3 level as an example.
- The examiner then applies downward pressure to the transverse process of L3, which produces a shear to the side on which the patient is lying for vertebra below L3 & a relative lateral shear in the opposite direction to the segments above L3.
What is the result of the lateral lumbar spine stability test?
- The production of the patient’s symptoms indicates a positive test.
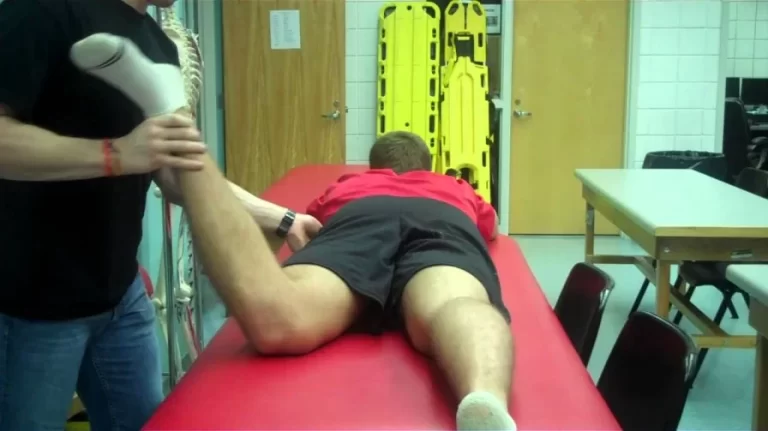
Passive lumbar extension test:-
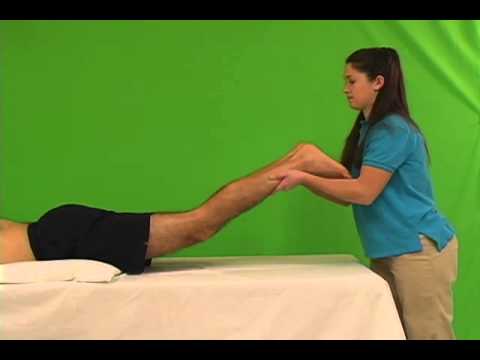
How do you perform the passive lumbar extension test?
- The patient lies prone & relaxed.
- The examiner passively lifts & extends both extremities at the same time to about 1 foot [ 30 cm ] from the bed.
- While maintaining the extension, the examiner gently pulls the legs.
What is the result of the passive lumbar extension test?
- The test is considered positive if, in the extended position, the patient complains of strong pain in the lumbar region, very heavy feeling in the low back, or it feels like the low back is coming off & the pain disappears when the legs are lowered to the start position.
- Numbness or prickling sensation are not positive signs.
Pheasant test:
How do you perform the pheasant test?
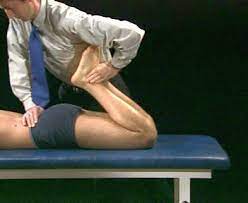
- The patient is in the prone position.
- With the help of one hand, the examiner gently applies pressure to the posterior aspect of the lumbar spine.
- With the help of the other hand, the examiner [ therapist] passively flexes the patient’s knee until the heels touch the buttocks.
What is the result of the pheasant test?
- If the hyper extension of the spine causes the patient to feel pain in the leg, the test is considered positive & indicates an unstable spine segment.