Special test for the neurological dysfunction of the elbow joint:
- These tests are applied to the clinic to check the neurological dysfunction of the elbow joint
- These clinical or neurological tests are applied by the physiotherapist [ examiner ] when the patient is complaining about the tingling or paresthesia of the forearm and hand.
- These tests are applied in the examination part of the assessment of the elbow joint.
Name of the special tests for the neurological dysfunction of the elbow joint:
- Elbow flexion test
- MacKinnon’s scratch collapse test
- Pinch grip test
- Test for pronator teres syndrome
- Tinel sign [ at the elbow joint ]
- Wartenberg sign
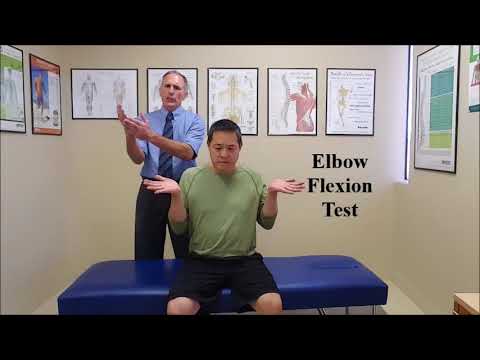
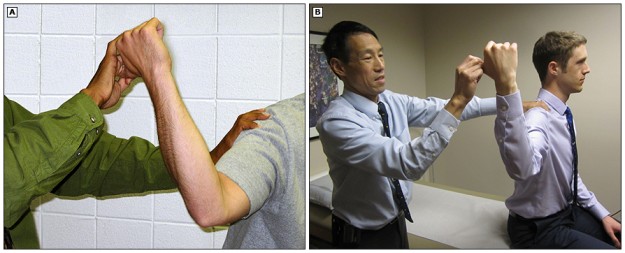
Elbow flexion test :
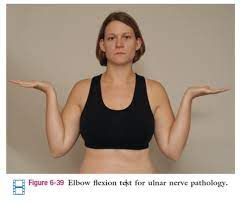
- Purpose = This elbow flexion test is used to determine cubital tunnel syndrome.
- This elbow flexion test is also used to check the problem in the ulnar nerve distribution.
- Technique = The patient position for the test is sitting or supine position.
- The patient is asked to fully flex the elbow with the extension of the wrist & shoulder girdle abduction [ 90′] & depression.
- Then the examiner instructs the patient to hold this position for 3 to 5 minutes.
- Ochi, et al. modified the test to include medial rotation means internal rotation of the shoulder in this test.
- This test is called the shoulder internal [ medial ] rotation elbow flexion test.
- Result = Patients feel that symptoms should develop in less than 5 seconds.
- Tingling & paresthesia in the ulnar nerve distribution of the forearm & hand indicates a positive test.
- The modification test helps to determine whether a cubital tunnel syndrome is present.
- The test may be modified by the examiner applying direct pressure over the ulnar nerve with the index & middle finger between the posteromedial olecranon & the medial epicondyle.
- This modification test is called the elbow flexion compression test or cubital tunnel compression test.
![shoulder internal [ medial ] rotation elbow flexion test.](https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/SOULDER-MEDIAL-ROTATION-ELBOW-FLEXION-TEST.jpg)

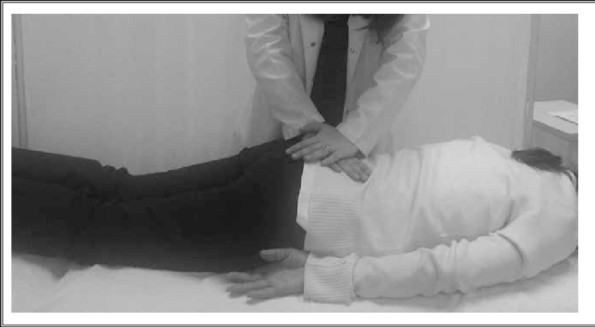
MacKinnon’s scratch collapse test:
- Purpose = This MacKinnon’s scratch collapse test is used to check the scratches along the course of the ulnar nerve.
- Technique = Patient position for the test is standing position.
- The patient stands with the elbow flexed to 90 ‘ & by the side.
- The patient is asked to laterally rotate means external rotate& abduct the forearm against resistance & then relaxes.
- The examiner then scratches along the course of the ulnar nerve at the elbow joint & then asks the patient to repeat the movement against resistance.
- Result = If the patient cannot momentarily laterally rotate against the examiner, it is considered a positive test.
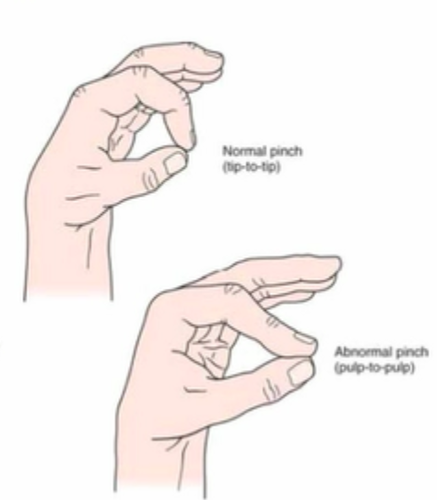
Pinch grip test :
- Purpose = This pinch grip test is used to check the entrapment of the anterior interosseous nerve.
- Technique = The patient is asked to pinch the tips of the index finger & thumb together.
- Normally, there should be a tip-to-tip pinch.
- Result = if the patient is unable to pinch tip-to-tip & instead has an abnormal pulp – to pulp pinch of the index finger & thumb, this is a positive sign for pathology to the anterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the median nerve.
- This finding may indicate an entrapment of the anterior interosseous nerve which it passes between the two heads of the pronator teres muscle.
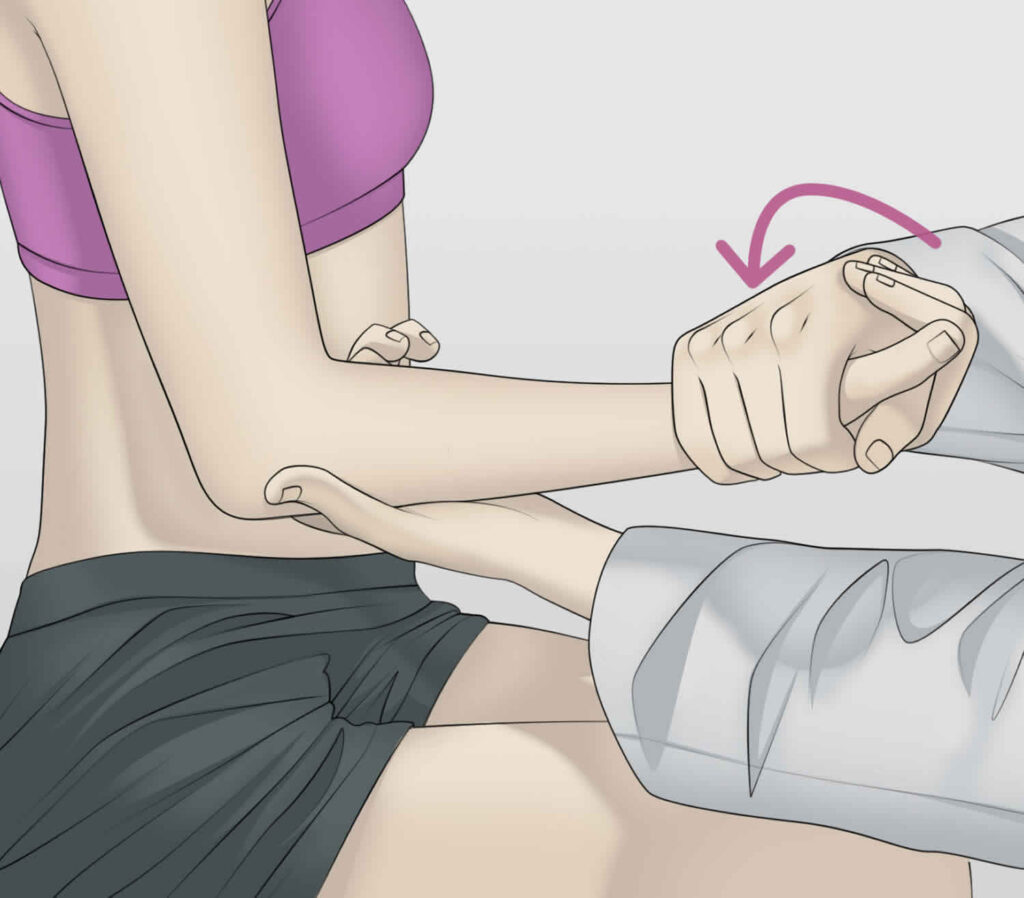
Test for pronator teres syndrome:
- Purpose = This test for pronator teres syndrome is used to check the median nerve distribution in the forearm.
- Technique = The patient position for the test is sitting position.
- The patient sits with the elbow flexed up to 90′.
- Then the examiner [ therapist ] strongly resists pronation as the elbow is extended.
- Result = tingling/paresthesia in the median nerve distribution in the forearm & hand indicates a positive test.
Tinel sign [ at the elbow joint ]:
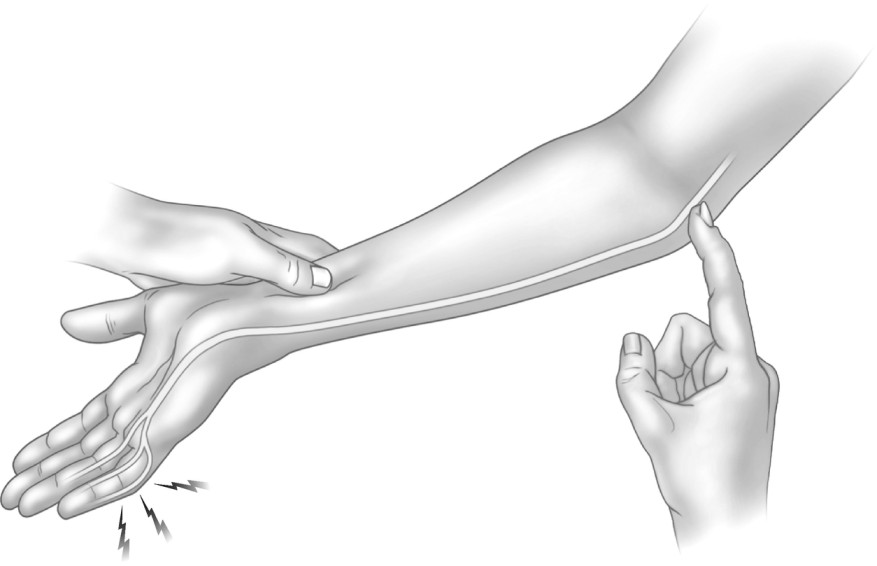
- Purpose = This tinel sign [ at the elbow joint ] is used to check the point of regeneration of the sensory fibres of a nerve.
- Technique = the patient position for the test is sitting position.
- The area of the ulnar nerve in the groove [ between the olecranon process & medial epicondyle ] is tapped.
- Result = a positive sign in indicated by a tingling sensation in the ulnar distribution of the forearm & hand distal to the point of compression of the nerve.
- The test indicates the point at which the patient feels the abnormal sensation represents the limit of nerve regeneration.
Wartenberg sign :
- Purpose = this Wartenberg sign is used to check the ulnar neuropathy.
- Technique = the patient position for the test is sitting position.
- The patient sits with his or her hands resting on the table.
- The examiner [ therapist ] passively spreads the finger apart.
- Then instruct the patient for doing to bring them together again.
- Result = inability to squeeze the little finger to the remainder of the hand indicates a positive test for ulnar neuropathy.