Talar tilt test of the Ankle
- This test is applied to the clinic the check the ligaments injury of the ankle joint.
- This test is applied by physiotherapists when the patient complains is ankle pain like severe pain.
- Sometimes part of this test is called to inversion stress test.
Purpose of the Talar tilt test
- This test is used To examine ankle joint injury, mostly the Calcaneofibular ligament & Anterior Talofibular ligament.
The technique of the performance of the Talar tilt test:
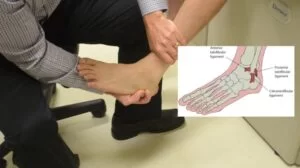
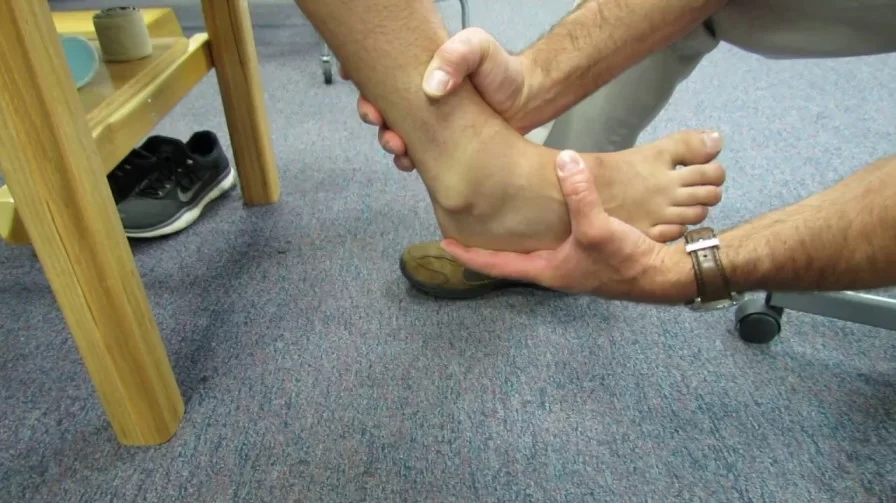
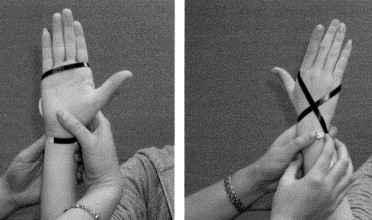
- The patient lies in the supine/side-lying position with the foot relaxed, it is starting position of the test.
- The patient’s gastrocnemius muscle may be relaxed by flexion of the knee.
- This test is to determine whether the calcaneofibular ligament is torn.
- The normal side is tested first for comparison.
- The foot is held in the anatomical 90′ position, which brings the calcaneofibular ligament perpendicular to the long axis of the talus.
- If the foot is plantar flexed, the anterior talofibular ligament is more likely to be tested like an inversion stress test.
- The talus is then tilted from side to side into inversion & eversion.
- Inversion tests the calcaneofibular ligament &, to some degree, the anterior talofibular ligament by increasing the stress on the ligament.
- Eversion stresses the deltoid ligament,primarily the tibionavicular,tibiocalcaneal ,& posterior tibiotalar ligaments.
- On a radiograph, the talar tilt may be measured by obtaining the angle between the distal aspect of the tibia & the proximal surface of the talus.
Evidence of the Talar tilt test:
- In a prospective study, this study was applied to 244 patients who have suffered from ankle lesions.
- Do the comparison between the anterior drawer sign & the talar tilt which is leading to the following conclusions:
- Ligament lesions of the ankle which are not identified by this talar tilt test are an examination by the test of the anterior drawer sign.
- So that The anterior drawer sign is not replaced with the talar tilt examination/vice versa.
- Two methods are with the comparison.
- This test is not possible to differentiate between the isolated lesion of the ankle of the ligament of the anterior talofibular & a combined lesion of the ankle of the anterior talofibular & the calcaneofibular ligaments.
- Radio graphic talar tilt reliability of this test
- Which is evaluated form using the MRI into 112 athletes who are suffering from injuries to the lateral ligaments of the ankle.
- 25 athletes who have suffered from the talar tilt of 15″ which is treated operatively.
- These intraoperative findings & the talar tilt test compared with the result of MRI imaging.
- These results are suggested that MRI is a reliable method for diagnosing injuries of the lateral ankle ligaments.
- This talar tilt test is not evaluated for the specific pathology of the lateral ankle ligaments, but this test was reliable which is in indicating the complete rupture of the double-ligament means calcaneofibular ligaments & anterior talofibular, when the talar tilt is 15″/more than on the unaffected side.
- Sensitivity of the Talar tilt test = 67
- Specificity of the Talar tilt test = 75,
- LR+ of the Talar tilt test = 2.7,
- LR- of the Talar tilt test = 0.44
FAQs
What does the Talar tilt test for?
A typical orthopedic test used to evaluate the lateral ankle ligaments following an inversion injury is the talar tilt test. It evaluates the ankle’s lateral ligaments in three different postures.
What is a positive talar tilt test ankle?
A positive talar tilt test in the ankle indicates that there is excessive or abnormal movement of the talus bone within the ankle joint, specifically in response to an inversion (tilting inward) force. This suggests instability in the lateral ligaments of the ankle, primarily the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) and the calcaneofibular ligament (CFL).
A positive talar tilt test can help confirm the diagnosis of an ankle sprain and guide appropriate treatment and rehabilitation strategies to promote healing and restore stability to the joint.
What is the normal range for talar tilt?
0° to 23°
According to published studies, the uninjured ankle’s normal ranges for the anterior drawer test and talar tilt test, respectively, are 3 to 10 mm and 0° to 23°, respectively. This leads to a variety of possible interpretations.
What ligament does the talar tilt test stress?
The talar tilt test can determine whether the calcaneofibular ligament has been injured, however there is no sensitive clinical diagnostic for the ligament. The ability to grade ligamentous injuries beyond the binary (damaged vs. uninjured) is unknown, and clinical examinations of the ligaments around the subtalar joint are not well understood.

![Oppenheim test purpose = this test is used to check the lesion of the upper motor neuron. technique = starting position of the patient for the test is the supine position. the examiner runs a fingernail along the crest of the patient's tibia. result = a negative Oppenheim test is indicated by no rection or no pain. a positive test is indicated by a positive Babinski sign [ positive pathological reflex ] & suggests an upper motor neuron lesion.](https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/filp-test.jpg)

One Comment