Vertebral Artery Test = VAT:
- The vertebral artery test = VAT is used in physiotherapy to test the vertebral artery blood flow to the brain, then searching for the symptoms of the vertebral artery insufficiency & disease.
- This Vertebral Artery Test = VAT test manoeuvre causes a reduction of the lumen at the 3 divisions of the vertebral artery, resulting in the decreased blood flow of the intracranial VA = Vertebral Artery of the contra lateral side.
- Causes of the test ischemia due to the blood loss in the pons & the medulla oblongata of the brain.
- This Vertebral Artery Test = VAT results in dysarthria, dizziness, paresis or paralysis of patients with Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency (VBI), syncope, nausea, dysphagia & disturbances of the hearing/vision,
What is the Purpose of the Vertebral Artery Test = VAT?
- The vertebral artery test = VAT is used to check the vertebral artery blood flow & search for the symptoms of the insufficiency of vertebral artery = VA.
- Reduction of the blood flow results in the transient ischemic attack = TIA & a critical sign of the impending stroke.
- This test is could mean that if the disease is not quickly diagnosed so the risk of missing the opportunity to prevent permanent disability/even death.
- If the cervical spine is placed into the compromising position so that risk of causing is permanent disability /even death.
- According to Johnston et al
- The 90-day risk of stroke which is applied after a transient ischemic attack = TIA is estimated to be approximately 10%.
- 50% of these strokes are occurring within the first two days after a TIA = transient ischemic attack.
- So, it is important to send a person with a positive test score to the hospital, where they are examined further for tests. TIA = transient ischemic attack is often misdiagnosed to peripheral neuropathy, migraine, seizure/anxiety.
How do you perform the Vertebral Artery Test = VAT?
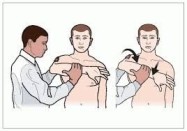
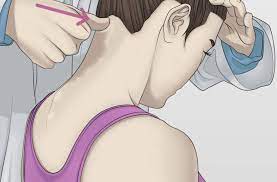
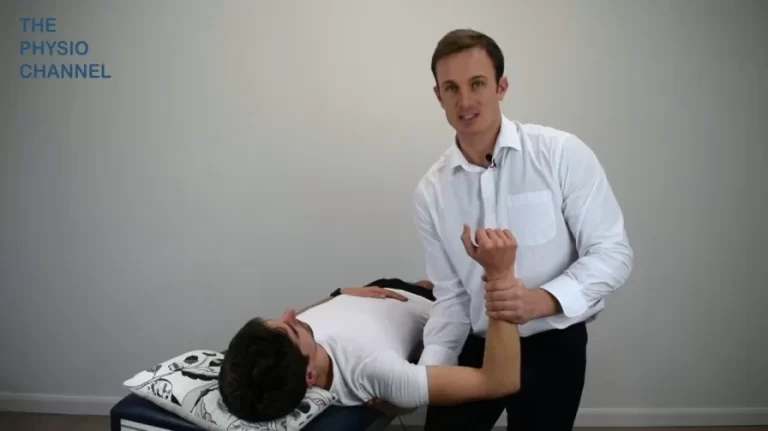
- With the patient supine, the examiner [ therapist ] passively takes the patient’s head & neck into extension movement & side flexion.
- After this movement is achieved, the examiner [ therapist ] rotates the patient’s neck to the same side & holds it for approximately 30 seconds.
What is the result of the Vertebral Artery Test = VAT?
- A positive test provokes referring symptoms if the opposite artery is affected.
- This test must be done with care.
- If dizziness or nystagmus occurs, it is an indication that the vertebral arteries are being compressed.
- The Dekleyan – Nieuwenhuyse test performed a similar function but involves extension & rotation instead of extension & side flexion.
- Both tests may also be used to assess nerve root compression in the lower cervical spine.
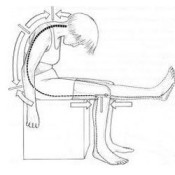
- To test the upper cervical spine, the examiner [ therapist ] pokes the patient’s chin & flows with extension, side flexion & rotation.
What is Modification of the Vertebral Artery Test = VAT?
- The therapist is Rotate to the head opposite to the tested side to maximally & holds the position for 10 seconds.
- The Return to neutral for 10 seconds.
- Then Extend to the head for 10 seconds
- After that Return to neutral for 10 seconds
- Then the therapist is Extends & rotate the head against the opposite tested side maximally for the 10 seconds.
- Positive symptoms of the Vertebral Artery Test include The 5 D means = drop attacks, dysarthria, dizziness, dysphagia, diplopia, sensory changes, nystagmus & nausea/vomiting.
- Below of an alternate vertebral artery test, which is used in certain settings.
- For example, in the assessment for the individual with the suspected BPPV.
What is Evidence of the Vertebral Artery Test = VAT?
- This test is commonly used over the past 30 years.
- This reduction of the lumen is reported by many authors, but it is a lot of these studies for not sufficient enough because of the lack of good samples of healthy people & VBI patients over the wide range of age.
- A study on the vertebral artery testing & differential diagnosis in dizzy patients which is also concluded that VAT = Vertebral Artery Test is not to be consistently validated as to clinical test for VBI.
- There are also a lot of inconsistencies in today’s literature on the vertebral artery.
- r
- Review of all the Mitchell et al which is found that from the 20 studies is reviewed for four studies measured in the blood flow for the transverse part of the VA vertebral artery in the first division with the 11 in the second division, none – 0 in the third division & 5 in the fourth division.
- In the 7 of the 20 studies, which is not found any loss of the blood flow in the VAI Vertebral Artery.
- Because of that inconsistency in the literature, it will be falsely positive or negative blood flow results in the cervical spine rotation.
- So that, the controversial findings in this today’s literature is not be used to guide evidence & based practice except to support the need for educated caution & authority in the pre-treatment screening & also the treatment of the patients.
- Côté et al
- Which is says that the positive predictive value of this test means the proportion of subjects with a positive test who are correctly diagnosed with the 0%.
- The negative predictive value of this test which is ranged from 63%-97%.
- The test is found not valid enough to detect a reduction in blood flow in the VA = Vertebral Artery.
- So that, the value of this test is questionable.