Distal Muscular Dystrophy
What is a Distal Muscular Dystrophy?
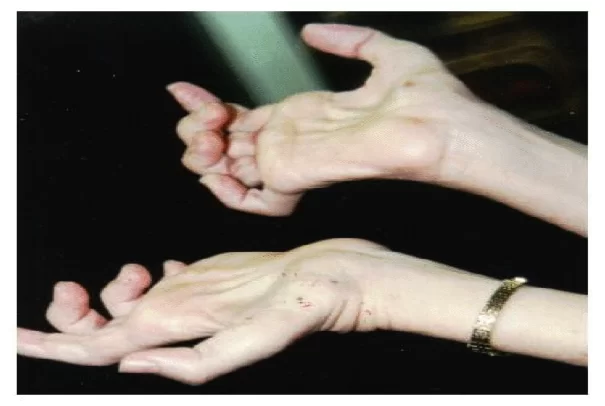
• Distal muscular dystrophy (or distal myopathy) is a group of disorders characterized by onset in the hands or feet. Age of onset 40-60 years.
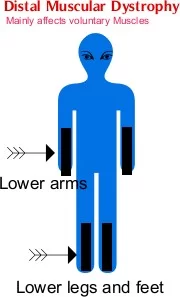
• Distal muscular dystrophy is a type of muscular dystrophy that affects the muscles of the extremities, the hands, feet, lower arms, or lower legs.
Causes of Distal Muscular Dystrophy
• The cause of this dystrophy is very hard to determine because it can be a mutation in any of at least eight genes and not all are known yet. These mutations can be inherited from one parent, autosomal dominant, or from both parents, autosomal recessive. Along with being able to inherit the mutated gene, distal muscular dystrophy has slow progress therefore the patient may not know that they have it until they are in their late 40’s or 50’s. There are eight known types of distal muscular dystrophy.
Types of Distal Muscular Dystrophy
• There are eight known types of distal muscular dystrophy. They are
• Welander’s distal myopathy,
• Finnish (tibial) distal myopathy,
• Miyoshi distal myopathy,
• Nonaka distal myopathy,
• Gowers–Laing distal myopathy,
• hereditary inclusion-body myositis type 1,
• distal myopathy with vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness,
• ZASP-related myopathy.
All of these affect different regions of the extremities and can show up as early as 5 years of age to as late as 50 years old.
Diagnosis
• Usually, the origin of the weakness can be pinpointed by a physical exam. Occasionally, special tests called nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) are done.
In these tests, electricity and very fine pins are used to stimulate and assess the muscles or nerves individually to see where the problem lies. Electromyography is uncomfortable but not usually very painful.
• Early in the diagnostic process doctors often order a special blood test called a CK level. CK stands for creatine kinase, an enzyme that leaks out of damaged muscle.
When elevated CK levels are found in a blood sample, it usually means the muscle is being destroyed by some abnormal process, such as muscular dystrophy or inflammation. Therefore, a high CK level often suggests that the muscles themselves are the likely cause of the weakness, but it doesn’t tell exactly what the muscle disorder might be.
To determine which disorder is causing CK elevation, a doctor may order a muscle biopsy, the surgical removal of a small sample of muscle from the patient.
• By examining this sample, doctors can tell a great deal about what’s actually happening inside the muscles. Modern techniques can use biopsy to distinguish muscular dystrophies from infections, inflammatory disorders, and other problems.
Treatment of Distal Muscular Dystrophy
• There’s no cure for any form of muscular dystrophy. But treatment can help prevent or reduce problems in the joints and spine to allow people with muscular dystrophy to remain mobile as long as possible. Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, and surgical and other procedures.
PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT:-
• Calf and hamstring stretching and threatening
• Crawling
• Low dog crawling
• Arm support


This disease will be cure in future?