Special tests for Vertigo & Dizziness
Vertigo and dizziness can be caused by a variety of factors, and specialized tests are required to diagnose the underlying cause. Some of the commonly used tests include the Dizziness test, Dix-Hallpike maneuver, caloric testing, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine which tests are most appropriate for an individual case.
- These tests are applied to the clinic to check vertigo & dizziness in the patient.
- These clinical tests are applied by a therapist or doctor when the patient is complaining about the symptoms of vertigo & dizziness.
- These tests are applied to examine part of the assessment.
Name of special test for Vertigo and dizziness:
- Dizziness test
- Hall pike – Dix test
- Temperature [ caloric ] test
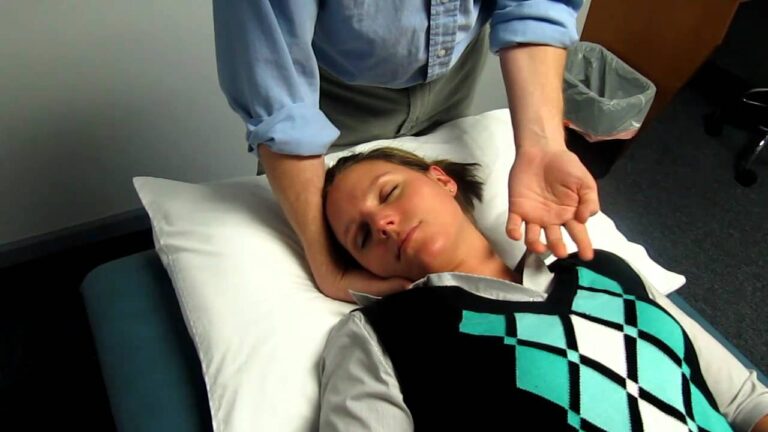
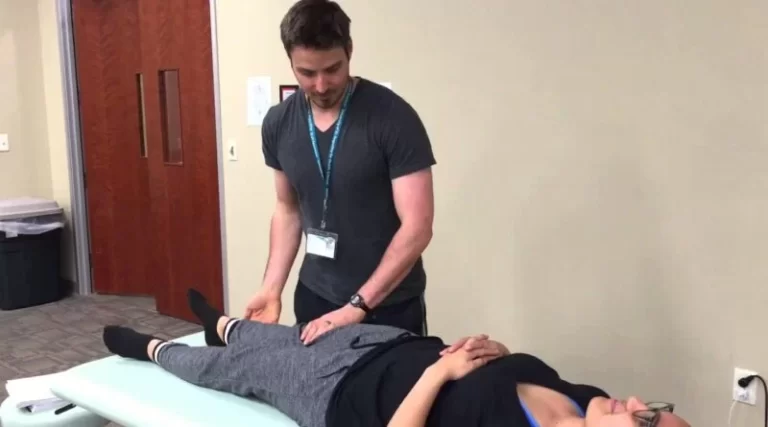
Dizziness test:

- Purpose = This dizziness test is used to check the dizziness in the patient.
- Technique = The patient sits & the examiner grasps the patient’s head.
- The examiner [ therapist ] head as far as possible to the right & then to the left, holding the head at the extreme of motion for a short time while the shoulders remain stationary.
- The patient’s head is then returned to neutral.
- Next, the patient’s shoulders are actively rotated as far as possible, holding for 10 to 30 seconds while keeping the head facing straight ahead.
- Result = If the patient experiences dizziness in both cases, the problem lies in the vertebral arteries, because in both cases the vertebral arteries, because in both cases the vertebral artery may be kinked, decreasing the blood flow.
- If the patient is experiencing dizziness only when the head is rotated the problem lies within the semicircular canals of the inner ear.
- Fitz-Ritson advocates a modification of this test.
- for the first part of the test, he advocates that the examiner [ therapist ] holds the shoulders still while the patient rapidly rotates the head left & right with eyes closed.
- If vertigo results, the problem is in the vestibular nuclei or muscles & joints of the cervical spine.
- In addition, patients may lose their balance, veer to one side, or possibly vomit.
- The second stage is the same as previously mentioned, except that the eye is closed.
- If vertigo is experienced this time, Fitz-Ritson believes that the problem is in the cervical spine because the vestibular apparatus is not being moved.
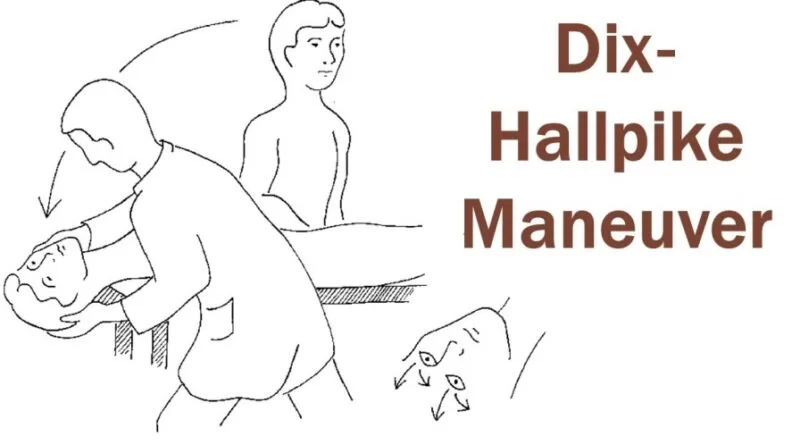
Hall Pike-Dix test:
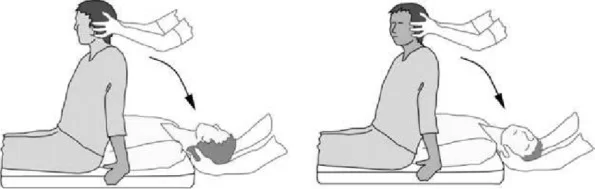
- Purpose = This hall pike – Dix test is used to check the identify benign paroxysmal positional vertigo = BPPV, a condition in which patients experience episodes of dizziness or vertigo, mostly if the head & neck are moved to different positions.
- Technique = The test is performed by having the patient long-sit on a plinth with the head rotated approximately 30 ‘ to 45’.
- The examiner [ therapist ] stands behind the patient with one hand supporting the head/neck & the other hand supporting the trunk.
- The patient is then assisted into a supine position with the patient’s head slightly below the horizontal plane,& the position is maintained for 30 to 60 seconds.
- The test is performed with the head rotated to both sides starting with the unaffected sign.
- Result = Signs of dizziness & nystagmus [ involuntary eye movement ] is considered a positive test.
Temperature test:
- This test is also known as the caloric test.
- Purpose = This test is also known as the caloric test.
- Technique = The examiner alternately applies hot & cold test tubes several times just behind the patient’s ears on the side of the head each side is done in turn.
- Result = A positive test is associated with the inducement of vertigo, which indicates inner ear problems.