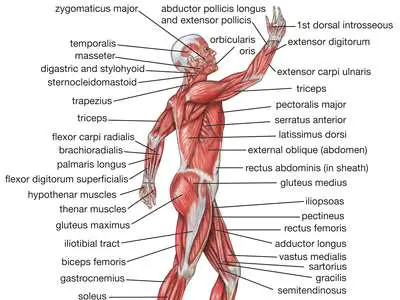
LIST OF BODY MUSCLES and THEIR FUNCTIONS
List of Body muscles are nearly 600 muscles. The three main types of muscles – skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Here we Update List of Skeletal Body Muscles.
LIST OF BODY MUSCLES IN HEAD AND NECK
| MUSCLES LIST | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Function / Action |
| occipitofrontalis | 2 occipital bellies and 2 frontal bellies | galea aponeurotia | facial nerve [CNVII] | raises the eyebrows |
| occipitalis | superior nuchal line of the occipital bone mastoid part of the temporal bone | galea aponeurotica | posterior auricular nerve (facial nerve [CNVII]) | moves the scalp back |
| frontalis | skin of the eyebrow and Glabella | galea aponeurotica | facial nerve [CNVII] | wrinkles eyebrow |
| Orbicularis oculi | Orbital part: frontal bone Palpebral part: medial palpebral ligament. Lacrimal part: Posterior crest of lacrimal bone | Orbital part: lateral palpebral raphe Palpebral part: lateral palpebral raphe Lacrimal part: Edges of eyelids | zygomatic branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | levator palpebrae superioris |
| Corrugator supercilii | Nasal part of frontal bone | Intermediate third of skin of eyebrow | Facial nerve [CNVII] | Moves skin of forehead medially and inferiorly (towards root of nose) |
| depressor supercilii | Nasal part of the frontal bone, medial rim of orbit | Medial third of skin of eyebrow | Facial nerve [CNVII] | Moves skin of eyebrows inferiorly |
Extraocular muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| levator palpebrae superioris | sphenoid bone | tarsal plate, upper eyelid | oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | retracts/elevates eyelid |
| superior tarsal | underside of levator palpebrae superioris | superior tarsal plate of the eyelid | sympathetic nervous system | raise the upper eyelid |
Rectus muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| superior | annulus of Zinn at the orbital apex | 7.5 mm superior to the corneal limbus | oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | elevates, adducts, and rotates medially the eye |
| inferior | 6.5 mm inferior to the corneal limbus | inferior branch of oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | depression and adduction | |
| medial | 5.5 mm medial to the corneal limbus | inferior division of the oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | adducts the eyeball | |
| lateral | 7 mm temporal to the corneal limbus | abducens nerve [CNVI] | abducts the eyeball |
Oblique muscles :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Superior | annulus of Zinn at the orbital apex, medial to optic canal | outer posterior quadrant of the eyeball | trochlear nerve [CNIV] | primary: intorsion. secondary:abduct (laterally rotate) and depress the eyeball |
| Inferior | orbital surface of the maxilla, lateral to the lacrimal groove | laterally onto the eyeball, deep to the lateral rectus, by a short flat tendon | oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | extorsion, elevation, abduction |
EAR :
Muscles of the inner ear :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| stapedius | neck of stapes | facial nerve [CNVII] | control the amplitude of sound waves to the inner ear | |
| tensor tympani | Eustachian tube | handle of the malleus | medial pterygoid nerve from mandibular nerve [CNV3] | tensing the tympanic membrane |
Nose :
NASALIS :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| transverse part (compressor naris) | Alveolar yoke of the canine tooth | lateral nasal cartilage | buccal branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | compression of nostrils |
| Alar part (dilator naris) | Alveolar yoke of lateral incisor tooth greater and lesser alar cartilages | skin near the margin of the nostril | buccal branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | dilation of nostrils |
Mouth :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| levator anguli oris | maxilla | modiolus of mouth | facial nerve [CNVII] | smile (elevates angle of mouth) |
| depressor anguli oris | tubercle of mandible | modiolus of mouth | mandibular branch of the facial nerve [CNVII] | depresses angle of mouth |
| levator labii superioris | Medial part of infra-orbital margin of maxilla | skin and muscle of the upper lip (labii superioris) | buccal branch of the facial nerce [CNVII] | Elevates the upper lip |
| depressor labii inferioris | oblique line of the mandible, between the symphysis and the mental foramen | integument of the lower lip, orbicularis oris fibers, its fellow of the opposite side | facial nerve [CNVII] | Depresses the lower lip |
| Mentalis | Alveolar yoke of the lower, lateral incisor tooth, found on the anterior mandible | skin of the chin | mandibular branch of the facial nerve [CNVII] | elevates and wrinkles skin of chin, protrudes lower lip |
| Buccinator | Alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible, pterygomandibular raphe | in the fibres of the orbicularis oris | buccal branch of the facial nerve [CNVII] | compress the cheeks against the teeth (blowing), mastication. |
| Orbicularis oris | maxilla and mandible | skin around the lips | puckers the lips | |
| Risorius | parotid fascia | modiolus of mouth | draw back angle of mouth |
Zygomatic muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Major | zygomatic bone in region of zygomaticomaxillary suture | modiolus of mouth | buccal branch of the facial nerve [CNVII] | draws the angle of the mouth upward and laterally |
| Minor | zygomatic bone in region of zygomaticomaxillary suture | skin of the upper lip | buccal branch of the facial nerve [CNVII] | elevates upper lip |
Mastication:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| masseter | anterior two-thirds of inferior margin of the zygomatic arch and maxilla | Angle of mandible, masseteric tuberosity | Masseteric nerve, from mandibular nerve [CNV3] | Elevation (as in closing of the mouth) and retraction of mandible |
| Temporalis | Temporal lines on the parietal bone of the skull | coronoid process of the mandible | mandibular nerve [CNV3] | elevation and retraction of mandible |
Pterygoid muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Lateral | greater wing of sphenoid and lateral pterygoid process | condyloid process of mandible | external pterygoid nerve from the mandibular nerve [CNV3] | depresses mandible |
| Medial | deep head: medial side of lateral pterygoid plate behind the upper teeth superficial head: pyramidal process of palatine bone and maxillary tuberosity | medial angle of the mandible | medial pterygoid nerve from the mandibular nerve [CNV3] | elevates mandible, closes jaw, helps lateral pterygoid muscle in moving the jaw from side to side |
Tongue
Extrinsic muscle
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Genioglossus | Superior part of mental spine of mandible (symphysis menti) | Dorsum of tongue and body of hyoid | hypoglossal nerve | Complex – Inferior fibers protrude the tongue, middle fibers depress the tongue, and its superior fibers draw the tip back and down |
| Hyoglossus | hyoid | side of the tongue | hypoglossal nerve | depresses tongue |
| Chondroglossus | lesser cornu and body of the hyoid bone | intrinsic muscular fibers of the tongue | hypoglossal nerve | depresses tongue (some consider this muscle to be part of hyoglossus) |
| Styloglossus | Styloid process of temporal bone | tongue | Hypoglossal nerve | elevates and retracts tongue |
| Palatoglossus | palatine aponeurosis | tongue | vagus nerve and cranial accessory nerve | raising the back part of the tongue |
Intrinsic muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Superior longitudinal | Close to the epiglottis, from the median fibrous septum | edges of the tongue | hypoglossal nerve | shortens, turns tip upward, turns lateral margins upward |
| Transversus | Median fibrous septum | sides of the tongue | hypoglossal nerve | narrows and not elongated |
| Inferior longitudinal | Root of the tongue | apex of the tongue | Hypoglossal nerve | shortens, retracts, pulls tip downward |
| verticalis muscle | Dorsum of tongue | inferior surface borders of tongue | hypoglossal nerve | flattens |
Soft palate:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| musculus uvulae | hard palate | Moves and changes shape of the uvula | ||
| Palatoglossus | palatine aponeurosis | tongue | vagus nerve and cranial accessory nerve | Aids in respiration by raising the back part of the tongue |
| Palatopharyngeus | palatine aponeurosis and hard palate | upper border of thyroid cartilage (blends with constrictor fibers) | vagus nerve and cranial accessory nerve | Aids in respiration by pulling the pharynx and larynx |
Pharynx :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Stylopharyngeus | temporal styloid process | thyroid cartilage (pharynx) | glossopharyngeal nerve | elevate the larynx, elevate the pharynx, swallowing |
| salpingopharyngeus | Cartilage of the Eustachian tube | posterior fasciculus of the pharyngopalatinus muscle | vagus nerve and cranial accessory nerve | raise the nasopharynx |
Pharyngeal muscles :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Inferior | cricoid and thyroid cartilage | pharyngeal raphe | external laryngeal branch of the vagus | Swallowing |
| Middle | hyoid bone | pharyngeal raphe | vagus nerve | Swallowing |
| Superior | medial pterygoid plate, pterygomandibular raphé, alveolar process | pharyngeal raphe, pharyngeal tubercle | vagus nerve | Swallowing |
Larynx:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| cricothyroid | anterior and lateral cricoid cartilage | inferior cornu and lamina of the thyroid cartilage | external laryngeal branch of the vagus | tension and elongation of the vocal folds (has minor adductory effect) |
| Arytenoid | arytenoid cartilage on one side | arytenoid cartilage on the opposite side | recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus | approximate the arytenoid cartilages (close rima glottidis) |
| thyroarytenoid | inner surface of the thyroid cartilage (anterior aspect) | anterior surface of arytenoid cartilage | recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus | thickens the vocal folds and decreases length; also helps to adduct the vocal folds during speech |
Cricoarytenoid muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Posterior | posterior part of the cricoid | muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage | recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus | abducts and laterally rotates the cartilage, pulling the vocal ligaments away from the midline and forward and so opening the rima glottidis |
| Lateral | lateral part of the arch of the cricoid | muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage | recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus | adduct and medially rotate the cartilage, pulling the vocal ligaments towards the midline and backwards and so closing off the rima glottidis |
List of Body Muscles in Neck:
Clavicular muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Platysma | base of mandible | inferior clavicle and fascia of chest | cervical branch of the facial nerve [CNVII] | Tenses the skin of the neck |
| Sternocleidomastoid : | Sternal head : manubrium sterni Clavicular head : medial portion of the clavicle | mastoid process of the temporal bone, superior nuchal line | motor : accessory nerve sensory : cervical plexus | Acting alone, tilts head to its own side and rotates it so the face is turned towards the opposite side. Acting together, flexes the neck, raises the sternum and assists in forced inspiration. |
Suprahyoid muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Digastric | Anterior belly: digastric fossa (mandible) Posterior belly: mastoid process of temporal bone | Intermediate tendon (lesser horn of hyoid bone) | Anterior belly : mandibular nerve [CNV3] via the mylohyoid nerve Posterior belly : facial nerve [CNVII] | Opens the jaw when the masseter and the temporalis are relaxed. |
| Stylohyoid | Styloid process (temporal) | greater cornu of hyoid bone | facial nerve [CNVII] | Elevate the hyoid during swallowing |
| Mylohyoid | Mylohyoid line (mandible) | Median raphe | mylohyoid nerve, from inferior alveolar branch of mandibular nerve [V3] | Raises oral cavity floor, elevates hyoid, depresses mandible |
| Geniohyoid | Symphysis menti | Anterior surface of body of hyoid bone | C1 via hypoglossal nerve | Elevates the hyoid and the tongue upward during deglutition |
Infrahyoid muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Sternohyoid | manubrium of sternum | hyoid bone | Ansa cervicalis | depress hyoid bone |
| Sternothyroid | manubrium | thyroid cartilage | Ansa cervicalis | Depresses larynx, may slightly depress hyoid bone. |
| Thyrohyoid | thyroid cartilage | hyoid bone | C1 | depress hyoid bone |
| Omohyoid | Upper border of the scapula | Hyoid bone | Ansa cervicalis | Depresses the larynx and hyoid bone. Carries hyoid bone backward and to the side |
Neck
Anterior muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Longus colli | Transverse processes of C-3 – C-6 | Anterior arch of atlas | C2, C3, C4, C5, C6 | Flexes the neck and head |
| Longus capitis | Anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae | basilar part of the occipital bone | C1, C2, C3/C4 | flexion of neck at atlanto-occipital joint |
| Rectus capitis anterior | atlas | occipital bone | C1 | flexion of neck at atlanto-occipital joint |
| Rectus capitis lateralis | Upper surface of the transverse process of the atlas | Under surface of the jugular process of the occipital bone | C1 | Sidebend at atlanto-occipital joint |
Lateral muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Scalene muscles | Cervical vertebrae | first and second ribs | cervical nerves (C3, C4, C5, C6, C7) | elevation of ribs I&II |
| Anterior | C3-C6 | first rib | ventral ramus of C5, C6 | When the neck is fixed, elevates the first rib to aid in breathing or when the rib is fixed, bends the neck forward and sideways and rotates it to the opposite side |
| Medius | C2-C6 | first rib | ventral rami of the third to eighth cervical spinal nerves | Elevate 1st rib, rotate the neck to the opposite side |
| posterior | transverse processes of C4 – C6 | 2nd rib | ascending cervical artery, superficial cervical artery C6, C7, C8 | Elevate 2nd rib, tilt the neck to the same side |
| Levator scapulae | Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 – C4 | Superior part of medial border of scapula | cervical nerve (C3, C4) and dorsal scapular nerve (C5) | Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula |
| Rectus capitis lateralis | upper surface of the transverse process of the atlas (C1) | under surface of the jugular process of the occipital bone | C1 | |
| Obliquus capitis superior | lateral mass of atlas | lateral half of the inferior nuchal line | suboccipital nerve | |
| Obliquus capitis inferior | spinous process of the axis | lateral mass of atlas | suboccipital nerve |
Posterior muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Rectus capitis posterior minor | The tubercle on the posterior arch of the atlas (C1) | the medial part of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone and the surface between it and the foramen magnum | a branch of the dorsal primary division of the suboccipital nerve | extends the head at the neck, but is now considered to be more of a sensory organ than a muscle |
| Rectus capitis posterior major | Spinous process of the axis (C2) | inferior nucheal line of the occipital bone | Dorsal ramus of C1 (suboccipital nerve) | |
| Semispinalis capitis | Articular processes of C4-C6; transverse processes of C7 and T1-T7 | occipital bone between the superior and inferior nuchal lines | greater occipital nerve | Extension of the head |
| Longissimus capitis | Articular processes of C4-C7; transverse processes of T1-T5 | posterior margin of the mastoid process | posterior branch of spinal nerve | Laterally: Flex the head and neck to the same side Bilaterally: Extend the vertebral column. |
| Splenius capitis | Ligamentum nuchae,spinous processes of C7-T6 | Mastoid process | C3, C4 | Extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head |
| Obliquus capitis superior | Lateral mass of atlas | lateral half of the inferior nuchal line | suboccipital nerve | |
| Obliquus capitis inferior | spinous process of the axis | lateral mass of atlas | suboccipital nerve |
Torso
Back muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Erector spinae | on the spines of the last four thoracic vertebrae | both the spines of the most cranial thoracic vertebrae and the cervical vertebrae | posterior branch of spinal nerve | extends the vertebral column |
| Longissimus | transverse process | transverse process | posterior branch of spinal nerve | |
| Spinalis | spinous process | spinous process | ||
| Latissimus dorsi | spinous processes of thoracic T6-T12, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and inferior 3 or 4 ribs | floor of intertubercular groove of the humerus | thoracodorsal nerve | pulls the forelimb dorsally and caudally deltoid, trapezius |
| Transversospinales | transverse process | spinous process | posterior branches | |
| Semispinalis thoracis (dorsi) | transverse processes of the sixth to the tenth thoracic vertebrae | spinous processes of the upper four thoracic and lower two cervical vertebrae | ||
| Semispinalis cervicis (colli) | transverse processes of the upper five or six thoracic vertebrae | cervical spinous processes, from the axis to the fifth | ||
| Semispinalis capitis (complexus) | Transversal process of lower cervical and higher thoracal columna | area between superior and inferior nuchal line | greater occipital nerve | Extends the head |
| Multifidus | sacrum, erector spinae aponeurosis, PSIS, and iliac crest | spinous process | posterior branch of spinal nerve | Stabilizes vertebrae in local movements of vertebral column |
| Rotatores | transverse process | spinous process | posterior branch | |
| Interspinales | spinous process | spinous process | posterior rami of spinal nerves | Extension, flexion and rotation of vertebral column. |
| Intertransversarii | transverse process | transverse process above | anterior rami of spinal nerves | Lateral flexion of trunk |
Splenius muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Capitis | ligamentum nuchae, spinous process of C7-T6 | Mastoid process of temporal and occipital bone | C3, C4 | Extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head |
| Cervicis | spinous processes of T3-T6 | transverse processes of C1, C2, C3 | C5, C6 |
Chest muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Intercostals | Ribs 1–11 | Ribs 2–12 | intercostal nerves | |
| External | intercostal nerves | Inhalation | ||
| Internal | Rib – inferior border | rib – superior border | intercostal nerves | hold ribs steady |
| Innermost | intercostal nerves | Elevate ribs | ||
| Subcostales | Inner surface of one rib | inner surface of the second or third rib above, near its angle | intercostal nerves | intercostal nerves |
| Transversus thoracis | Costal cartilages of last 3–4 ribs, body of sternum, xiphoid process | ribs/costal cartilages 2–6 | intercostal nerves | depresses ribs |
| Levatores costarum | Transverse processes of C7 to T12 vertebrae | superior surfaces of the ribs immediately inferior to the preceding vertebrae | dorsal rami – C8, T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11 | Assists in elevation of the thoracic rib cage |
Serratus posterior muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Inferior | vertebrae T11 – L3 | the inferior borders of the 9th through 12th ribs | intercostal nerves | depress the lower ribs, aiding in expiration |
| Superior | nuchal ligament (or ligamentum nuchae) and the spinous processes of the vertebrae C7 through T3 | the upper borders of the 2nd through 5th ribs | 2nd through 5th intercostal nerves | elevate the ribs which aids in inspiration |
| Diaphragm | phrenic and lower intercostal nerves | respiration |
Abdomen muscle:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Transversus abdominis | Ribs and the iliac crest | inserts into the pubic tubercle via the conjoint tendon, also known as the falx inguinalis | intercostal nerves T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, subcostal nerve (T12), iliohypogastric nerve, ilioinguinal nerve, genitofemoral nerve | compress the ribs and viscera, providing thoracic and pelvic stability |
| Rectus abdominis | pubis | costal cartilages of ribs 5–7, xiphoid process of sternum | segmentally by thoraco-abdominal nerves (T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12) | flexion of trunk/lumbar vertebrae |
| Pyramidalis | pubic symphysis and pubic crest | linea alba | subcostal nerve (T12) | tensing the linea alba |
| Cremaster | inguinal ligament | genital branch of genitofemoral nerve | raise and lower the scrotum | |
| Quadratus lumborum | iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament | last rib and transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae | anterior branches of T12, L1, L2, L3, L4 | Alone, lateral flexion of vertebral column; Together, depression of thoracic rib cage |
Oblique muscles:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| External | Lower 8 costae | Crista iliaca, ligamentum inguinale | intercostal nerves T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, subcostal nerve (T12) | Rotates torso |
| Internal | inguinal ligament, iliac crest and the lumbodorsal fascia | linea alba, xiphoid process and the inferior ribs | intercostal nerves T8, T9, T10, T11, subcostal nerve (T12), iliohypogastric nerve, ilioinguinal nerve | Compresses abdomen and rotates vertebral column |
Pelvis:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Coccygeus | sacrospinous ligament | sacral nerves: S4, S5 or S3-S4 | closing in the back part of the outlet of the pelvis | |
| Levator ani : | ||||
| Iliococcygeus | ischial spine and from the posterior part of the tendinous arch of the pelvic fascia | coccyx and anococcygeal raphe | levator ani nerve (S4) inferior rectal nerve from pudendal nerve (S3, S4) coccygeal plexus | Supports the viscera in pelvic cavity |
| Pubococcygeus | back of the pubis and from the anterior part of the obturator fascia | coccyx and sacrum | levator ani nerve (S4) inferior rectal nerve from pudendal nerve (S3, S4) coccygeal plexus | controls urine flow and contracts during orgasm |
| Puborectalis | lower part of the pubic symphysis | S3, S4. levator ani nerve | inhibit defecation |
Perineum :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Sphincter ani: | ||||
| Externus | S4 and twigs from inferior anal nerves of pudendal nerve | keep the anal canal and anus closed, aids in the expulsion of the feces | ||
| Internus | pudendal nerve | keep the anal canal and anus closed, aids in the expulsion of the feces | ||
| Superficial perineal pouch : | ||||
| Transversus perinei superficialis | anterior part of ischial tuberosity | central point of perineum | pudendal nerve | |
| Bulbospongiosus | median raphé | pudendal nerve | in males, empties the urethra; in females, clenches the vagina | |
| Ischiocavernosus | pudendal nerve | assists the bulbospongiosus muscle | ||
| Deep perineal pouch : | ||||
| Transversus perinei profundus | inferior rami of the ischium | its fellow of the opposite side | pudendal nerve | |
| Sphincter urethrae membranaceae | junction of the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium to the extent of 1.25–2 cm., and from the neighboring fasciae | its fellow of the opposite side | perineal branch of the pudendal nerve (S2, S3, S4) | Constricts urethra, maintain urinary continence |
List of Body Muscles of Upper limbs
Vertebral column:
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Trapezius | down the midline, from the external occipital protuberance, the nuchal ligament, the medial part of the superior nuchal line, and the spinous processes of the vertebrae C7-T12 | at the shoulders, into the lateral third of the clavicle, the acromion process and into the spine of the scapula | major nerve supply is the cranial nerve XI. cervical nerves C3 and C4 receive information about pain in this muscle | Retraction and elevation of scapula. |
| latissimus dorsi | spinous processes of thoracic T6-T12, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and inferior 3 or 4 ribs | floor of intertubercular groove of the humerus | thoracodorsal nerve | pulls the forelimb dorsally and caudally |
| Rhomboids | nuchal ligaments, spinous processes of C7-T5 vertebrae | medial border of the scapula | dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5) | Retracts the scapula and rotates it to depress the glenoid cavity. fixes the scapula to the thoracic wall. |
| Rhomboid major | spinous processes of the T2 to T5 vertebrae | medial border of the scapula, inferior to the insertion of rhomboid minor muscle | dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5) | Retracts the scapula and rotates it to depress the glenoid cavity. It also fixes the scapula to the thoracic wall. |
| Rhomboid minor | nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7- to T1 vertebrae | medial border of the scapula, superior to the insertion of rhomboid major muscle | dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5) | Retracts the scapula and rotates it to depress the glenoid cavity. It also fixes the scapula to the thoracic wall. |
| levator scapulae | posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 – C4 vertebrae | superior part of medial border of scapula | cervical nerve (C3, C4) and dorsal scapular nerve (C5) | Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula |
Thoracic walls :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Pectoralis major | anterior surface of the medial half of the clavicle. Sternocostal head: anterior surface of the sternum, the superior six costal cartilages | intertubercular groove of the humerus | lateral pectoral nerve and medial pectoral nerve Clavicular head: C5 and C6 Sternocostal head: C7, C8 and T1 | Clavicular head: flexes the humerus Sternocostal head: extends the humerus As a whole, adducts and medially rotates the humerus. It also draws the scapula anteriorly and inferiorly. |
| Pectoralis minor | 3rd to 5th ribs, near their costal cartilages | medial border and superior surface of the coracoid process of the scapul | Medial pectoral nerves (C8, T1) | stabilizes the scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against the thoracic wall |
| Subclavius | first rib | subclavian groove of clavicle | nerve to subclavius | Depresses the clavicle |
| Serratus anterior | fleshy slips from the outer surface of upper 8 or 9 ribs | costal aspect of medial margin of the scapula | long thoracic nerve (from roots of brachial plexus C5, C6, C7) | protract and stabilize scapula, assists in upward rotation |
Shoulder Muscle :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Deltoid | clavicle, acromion, spine of the scapula | deltoid tuberosity of humerus | Axillary nerve | shoulder abduction, flexion, and extension |
| Teres major | posterior aspect of the inferior angle of the scapula | medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus | Lower subscapular nerve (segmental levels C5 and C6) | Internal rotation of the humerus |
| Rotator cuff : | ||||
| Supraspinatus | supraspinous fossa of scapula | superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus | suprascapular nerve | abduction of arm and stabilizes humerus |
| Infraspinatus | infraspinous fossa of the scapula | middle facet of greater tubercle of the humerus | suprascapular nerve | Lateral rotation of arm & Adduction of arm and stabilizes humerus |
| Teres minor | lateral border of the scapula | inferior facet of greater tubercle of the humerus | axillary nerve | laterally rotates and adducts the arm |
| Subscapularis | subscapular fossa | lesser tubercle of humerus | upper subscapular nerve, lower subscapular nerve (C5, C6) | rotates medially humerus stabilizes shoulder |
Arm :
Anterior compartment :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Coracobrachialis | coracoid process of scapula | medial humerus | musculocutaneous nerve | flexes and adducts at shoulder joint |
| Biceps brachii | short head: coracoid process of the scapula. long head: supraglenoid tubercle | radial tuberosity | Musculocutaneous nerve (Lateral cord: C5, C6, C7) | flexes elbow and supinates forearm |
| Brachialis | anterior surface of the humerus, particularly the distal half of this bone | coronoid process and the tuberosity of the ulna | musculocutaneous nerve | flexion at elbow joint |
Posterior compartment :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Triceps brachii | long head:Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula lateral head: posterior humerus – above radial grove medial head: posterior humerus-under radial groove | olecranon process of ulna | radial nerve | extends forearm, caput longum adducts shoulder, medial head does not function at shoulder |
| Anconeus | Lateral epicondyle of the humerus | lateral surface of the olecranon process and the superior part of the posterior ulna | radial nerve (C7, C8, and T1) | partly blended in with the triceps, which it assists in extension of the forearm. Stabilises the elbow and abducts the ulna during pronation. |
Forearm :
Anterior compartment :
Superficial :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| pronator teres | humeral head: medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon) ulnar head: coronoid process of the ulna | radius pronator tuberosity | median nerve | pronation of forearm, flexes elbow |
| Flexor carpi radialis | medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon) | Bases of second and third metacarpal bones | median nerve | Flexion and abduction at wrist |
| Palmaris longus | medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon) | palmar aponeurosis | median nerve | wrist flexor |
| Flexor carpi ulnaris | medial epicondyle of the humerus (common flexor tendon) | pisiform | muscular branches of ulnar nerve | flexion and adduction of wrist |
| Flexor digitorum superficialis | medial epicondyle of the humerus (common flexor tendon), as well as parts of the radius and ulna | phalanges II-V | median nerve | flexor of fingers (primarily at proximal interphalangeal joints) |
Deep :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| pronator quadratus | medial, anterior surface of the ulna | lateral, anterior surface of the radius | median nerve (anterior interosseous nerve) | weakly pronates the forearm |
| flexor digitorum profundus | ulna | distal phalanges | lateral belly by median (anterior interosseous), medial belly by muscular branches of ulnar | flex hand, interphalangeal joints |
| flexor pollicis longus | The middle 2/4 of the Volar surface of the radius and the adjacent interosseus membrane. (Also occasionally a small origin slightly on the medial epicondyle of the ulna.) | The base of the distal phalanx of the thumb | Anterior interosseous nerve (branch of median nerve) (C8, T1) | Flexion of the thumb |
Posterior compartment :
Superficial :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Extensor digitorum | lateral epicondyle (common extensor tendon) | 2nd–5th phalange | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | extension of hand and fingers |
| Extensor digiti minimi | the anterior portion of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus (common extensor tendon) | extensor expansion, located at the base of the proximal phalanx of the finger on the dorsal side | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | extends the little finger at all joints |
| Extensor carpi ulnaris | Common extensor tendon (lateral epicondyle), ulna | 5th metacarpal | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | extends and adducts the wrist |
| Brachioradialis | Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus | Distal radius (Radial styloid process) | radial nerve | Flexion of forearm |
| Extensor carpi radialis longus | lateral supracondylar ridge | 2nd metacarpal | radial nerve | extensor at the wrist joint, abducts the hand at the wrist |
| Extensor carpi radialis brevis | humerus at the anterior of lateral epicondyle (common extensor tendon) | base of the 3rd metacarpal | posterior interosseus nerve | extensor and abductor of the hand at the wrist joint |
Deep :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| supinator | Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, supinator crest of ulna, radial collateral ligament, annular ligament | Lateral proximal radial shaft | posterior interosseus nerve (C7, C8) | supinates forearm |
| Extensor indicis | ulna | index finger (extensor hood) | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | extends index finger, wrist |
Anatomical snuff box :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Abductor pollicis longus | ulna, radial styloid process | first metacarpal | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | abduction, extension of thumb |
| Extensor pollicis brevis | radius | thumb, proximal phalanx | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | extension of thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint |
Hand :
Lateral volar:
Thenar :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| opponens pollicis | trapezium and transverse carpal ligament | metacarpal bone of the thumb on its radial side | median nerve | Opposition of the thumb |
| Flexor pollicis brevis | trapezoid, flexor retinaculum | thumb, proximal phalanx | median nerve, deep branch of ulnar nerve (medial head) | Flexes the thumb |
| Abductor pollicis brevis | Transverse carpal ligament, the scaphoid and trapezium | Radial base of proximal phalanx of thumb and the thumb extensors | Median nerve | Abducts the thumb |
| Adductor pollicis | Transverse head: anterior body of the third metacarpal Oblique head: bases of the second and the third metacarpals and the adjacent trapezoid and capitate bones | medial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb and the ulnar sesamoid | deep branch of ulnar nerve (T1) | adducts the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint |
Medial volar :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Palmaris brevis | flexor retinaculum (medial), palmar aponeurosis | palm | superficial branch of ulnar nerve | wrinkle skin of palm |
| Hypothenar | ||||
| Abductor digiti minimi | pisiform | base of the proximal phalanx of the 5th digit on the ulnar or medial side | deep branch of ulnar nerve | Abduction of little finger |
| Flexor digiti minimi brevis | hamate bone | little finger | deep branch of ulnar nerve | flexes little finger extensor digiti minimi muscle |
| Opponens digiti minimi | Hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum | Medial border of 5th metacarpal | deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) | Draws 5th metacarpal anteriorly and rotates it, bringing little finger (5th digit) into opposition with thumb |
Intermediate :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| lumbrical | flexor digitorum profundus | extensor expansion | deep branch of ulnar nerve, median nerve | flex metacarpophalangeal joints, extend interphalangeal joints |
| dorsal interossei | metacarpals | proximal phalanges | deep branch of ulnar nerve | abduct finger |
| palmar interossei | metacarpals | proximal phalange | deep branch of ulnar nerve | adduction |
Lower limb :
Iliac region :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Iliopsoas | iliac fossa (iliacus), sacrum (iliacus), spine (T12, L1, lumbar vertebra, Psoas major, psoas minor) | femur—lesser trochanter (psoas major/minor), shaft below lesser trochanter (iliacus), tendon of psoas major & femur (iliacus) | femoral nerve, Lumbar nerves L1, L2 | flexion of hip (psoas major/minor, iliacus), spine rotation (psoas major/minor) |
| Psoas major | transverse processes, bodies and discs of T12-L5 | in the lesser trochanter of the femur | Lumbar plexus via anterior branches of L1, L2, L3 | flexes and rotates laterally thigh |
| Psoas minor | Side of T11+L1 and IV Disc between | Pectineal line and iliopectineal eminence | L1 | Weak trunk flexor |
| Iliacus | iliac fossa | lesser trochanter of femur | femoral nerve (L2, L3) | flexes hip |
Gluteal :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Tensor fasciae latae | Iliac crest | iliotibial tract | Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5) | Thigh – flexion, medial rotation trunk stabilization. |
| Gluteus maximus muscle | Gluteal surface of ilium, lumbar fascia, sacrum, sacrotuberous ligament | Gluteal tuberosity of the femur, iliotibial tract | inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2 nerve roots) | external rotation and extension of the hip joint, supports the extended knee through the iliotibial tract, chief antigravity muscle in sitting |
| Gluteus medius muscle | Gluteal surface of ilium, under gluteus maximus | Greater trochanter of the femur | superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1 nerve roots) | abduction of the hip preventing adduction of the hip. Medial rotation of thigh. |
| Gluteus minimus muscle | Gluteal surface of ilium, under gluteus medius | Greater trochanter of the femur | superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1 nerve roots) | Works in concert with gluteus medius: abduction of the hip preventing adduction of the hip. Medial rotation of thigh. |
| Lateral rotator group | at or below the acetabulum of the ilium | on or near the greater trochanter of the femur | Obturator nerve, nerve to the Piriformis, nerve to quadratus femoris | lateral rotation of hip |
| Piriformis | Sacrum | greater trochanter | nerve to the Piriformis (S1 and S2 nerve roots) | laterally rotate (outward) the thigh |
| Obturator externus | obturator foramen and obturatory membrane | medial aspect of greater trochanter of femur | posterior branch of obturator nerve (L3, L4) | adduct thigh, rotate laterally thigh |
| Obturator internus | Ischiopubic ramus & obturator membrane | medial aspect of the Greater trochanter | Nerve to obturator internus (L5, S1, S2) | Abducts & rotates laterally thigh, and stabiliser of the hip during walking |
| Inferior gemellus | Ischial tuberosity | Obturator internus tendon | Nerve to Quadratus femoris (L4, L5, S1) | Rotates laterally thigh |
| Superior gemellus | spine of the ischium | Obturator internus tendon | Nerve to obturator internus (L5, S1, S2) | Rotates laterally thigh |
| Quadratus femoris | ischial tuberosity | intertrochanteric crest | nerve to quadratus femoris (L4, L5, -S1) | lateral rotation of thigh |
Thigh :
Anterior compartment :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Articularis genus | femur | suprapatellar bursa | femoral nerve | Pulling the suprapatellar bursa during extension of the knee. |
| Sartorius | superior to the anterior superior iliac spine | medial side of the upper tibia in the pes anserinus | femoral nerve | flexion, lateral rotation and abduction of thigh; flexion and medial rotation of leg |
| Quadriceps femoris | combined rectus femoris and vastus muscles | Patella and Tibial tuberosity via the Patellar ligament | Femoral nerve | Knee extension; Hip flexion (rectus femoris only) |
| Rectus femoris | anterior inferior iliac spine and the exterior surface of the bony ridge which forms the iliac portion of the acetabulum | Patella and Tibial tuberosity via the Patellar ligament | femoral nerve | knee extension,hip flexion |
| Vastus lateralis | Greater trochanter, Intertrochanteric line, and Linea aspera of the femur | patella and tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament | femoral nerve | Extends and stabilizes knee |
| Vastus intermedius | antero/ lateral femur | patella and tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament | femoral nerve | extends knee |
| Vastus medialis | femur | patella and tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament | femoral nerve | extends knee |
Posterior compartment/ Hamstring Muscles :
Hamstring muscles are located at the back of the thigh.
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Biceps femoris | long head: tuberosity of the ischium, short head: linea aspera, femur | the head of the fibula which articulates with the back of the lateral tibial condyle | long head: medial (tibial) part of sciatic nerve, short head: lateral (common fibular) part of sciatic nerve | flexes knee joint, laterally rotates leg at knee (when knee is flexed), extends hip joint (long head only) |
| Semitendinosus | tuberosity of the ischium | pes anserinus | sciatic (tibial, L5, S1, S2) | flexes knee, extends hip joint, medially rotates leg at knee |
| Semimembranosus | tuberosity of the ischium | Medial surface of tibi | sciatic nerve | flexes knee, extends hip joint, medially rotates leg at knee |
Medial compartment :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| adductor muscles of the hip | pubis | femur, tibia | obturator nerve | adduction of hip |
| Gracilis | inferior pubic ramus | tibia (pes anserinus) | anterior branch of obturator nerve | adduction of hip, flexion of hip, medial rotation of knee |
| Pectineus | superior pubic ramus | lesser trochanter, linea aspera | femoral nerve and obturator nerve (medial compartment) | flexion & adduction of hip |
| Adductor brevis | anterior surface of the inferior pubic ramus | the lesser trochanter and linea aspera of the femur | anterior branch of obturator nerve | adduction of hip |
| Adductor longus | pubic body just below the pubic crest | middle third of linea aspera | anterior branch of obturator nerve | adduction & medial rotation of hip |
| Adductor magnus | tuberosity of the ischium | femur and adductor tubercle of femur | posterior branch of obturator nerve (adductor) and tibial part of sciatic nerve (vertical head) | adduction of hip |
Leg :
Anterior compartment :
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve | Action |
| Tibialis anterior | body of tibia | medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot | Deep Fibular (peroneal) nerve | dorsiflex and invert the foot |
| Extensor hallucis longus | middle portion of the fibula on the anterior surface and the interosseous membrane | dorsal side of the base of the distal phalanx of the Hallux | Deep Fibular (peroneal) nerve | Extends the big toe and assists in dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle. Also is a weak invertor |
| Extensor digitorum longus | Lateral Condyle of tibia and superior ¾ of interosseous membrane | Middle and Distal phalanges of lateral four digits | Deep Fibular (peroneal) nerve | extension of toes and ankle |
| Fibularis tertius | distal anterior surface of the fibula | dorsal surface of metatarsal 5 | Deep Fibular (peroneal) nerve | dorsi flexes and everts foot |
Posterior compartment :
Superficial muscles List :
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| Triceps surae | achilles tendon, calcaneus | posterior tibial artery | tibial nerve | plantarflexes ankle joint | |
| gastrocnemius | medial condyle and lateral condyle of femur | calcaneus | sural arteries | tibial nerve | plantarflexes ankle joint |
| soleus fibula | medial border of tibia (soleal line) | tendo calcaneus | sural arteries | tibial nerve | plantarflexes ankle joint |
| plantaris | lateral supracondylar ridge of femur above lateral head of gastrocnemius | Calcaneal tendon (medial side, deep to gastrocnemius tendon) | sural arteries | tibial nerve | plantarflexes ankle joint |
DEEP
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| popliteus | middle facet of lateral surface of lateral femoral condyle | posterior tibia under tibial condyles | popliteal artery | tibial nerve | medially rotates and flexes knee |
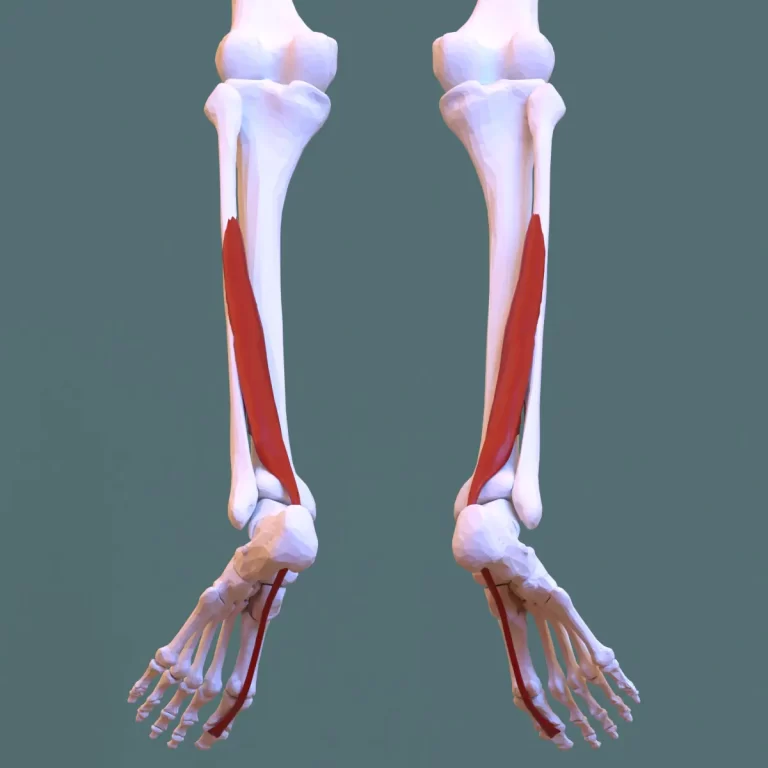
| flexor hallucis longus | posterior surface of upper 1/3 of fibula | base of distal phalanx of hallux | fibular artery (peroneal branch of posterior tibial artery | Tibial nerve, S1, S2 nerve roots | flexes all joints of big toe, plantarflexes ankle |
| flexor digitorum longus | medial tibia | distal phalanges of lateral four digits | posterior tibial artery | tibial nerve | flexes toes |
Lateral compartment
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| fibularis muscles | fibula | first metatarsal, medial cuneiform | fibular artery | superficial fibular nerve | plantarflexes ankle, everts ankle |
| fibularis longus | fibula | first metatarsal, medial cuneiform | fibular artery | superficial fibular nerve | plantarflexes ankle, everts ankle |
| fibularis brevis | fibula | fifth metatarsal | fibular artery | superficial fibular nerve | plantarflexes ankle, everts ankle |
Foot
Dorsal
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| extensor digitorum brevis | calcaneus | toes | deep fibular nerve | extends digits 2, 3, and 4 | |
| extensor hallucis brevis | calcaneus deep | base of proximal phalanx of big toe | deep fibular nerve | extends big toe | |
| dorsal interossei of foot | metatarsals | proximal phalanges | lateral plantar nerve(fourth interosseous space: superficial branch others: deep branch), first and second interossei: lateral branch of deep fibular nerve | abducts toes |
Plantar
First layer
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| abductor hallucis | medial process of calcaneus, flexor retinaculum, plantar aponeurosis | medial side of base of proximal phalanx of first digit | medial plantar nerve | abducts hallux | |
| flexor digitorum brevis | medial process of calcaneus, plantar aponeurosis, intermuscular septa | middle phalanges of digits 2–5 | medial plantar nerve | flexes lateral four toes | |
| abductor digiti minimi | plantar aponeurosis | phalanges of fifth toe | lateral plantar artery | lateral plantar nerve (S1, S2) | flexes and abducts fifth toe |
Second layer
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| quadratus plantae | calcaneus | tendons of flexor digitorum longus | lateral plantar nerve (S1, S2) | flexes distal interphalangeal joints (assists flexor digitorum longus) | |
| lumbricals | tendons of flexor digitorum longus | medial surface of extensor expansion of proximal phalanges of lateral four toes | lateral plantar artery, plantar arch, four plantar metatarsal arteries | lateral plantar nerve (lateral three lumbricals) and medial plantar nerve (first lumbrical) | maintain extension of digits at interphalangeal joints |
Third layer
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| flexor hallucis brevis | plantar surface of cuneiforms, plantar calcaneocuboid ligament, long plantar liga | medial head: medial sesamoid bone of metatarsophalangeal joint, proximal phalanx of great toe lateral head: lateral sesamoid bone of metatarsophalangeal joint, proximal phalanx of great toe | medial plantar nerve | flexes big toe | |
| adductor hallucis | oblique head: proximal ends of middle 3 metatarsals | lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of big toe, sesamoid | lateral plantar nerve | adducts big toe | |
| flexor digiti minimi brevis | fifth metatarsal bone | phalanx of fifth toe | lateral plantar nerve (superficial branch) | extends and adducts fifth toe |
Fourth layer
| Muscle Name | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action |
| plantar interossei | tendons of plantar Interossei | proximal phalanges III-V – muscles cross the metatarsophalangeal joint of toes III-V so the insertions correspond with the origin and there is no crossing between toes | plantar arch, dorsal metatarsal artery | lateral plantar nerve | adducts toes 3 – 5, strengthens transverse arch |
| dorsal interossei | metatarsals | proximal phalanges | lateral plantar nerve | abducts toes |

One Comment