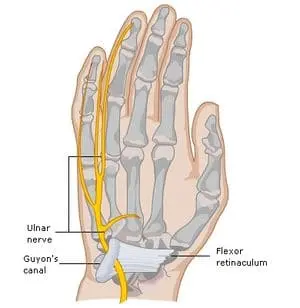
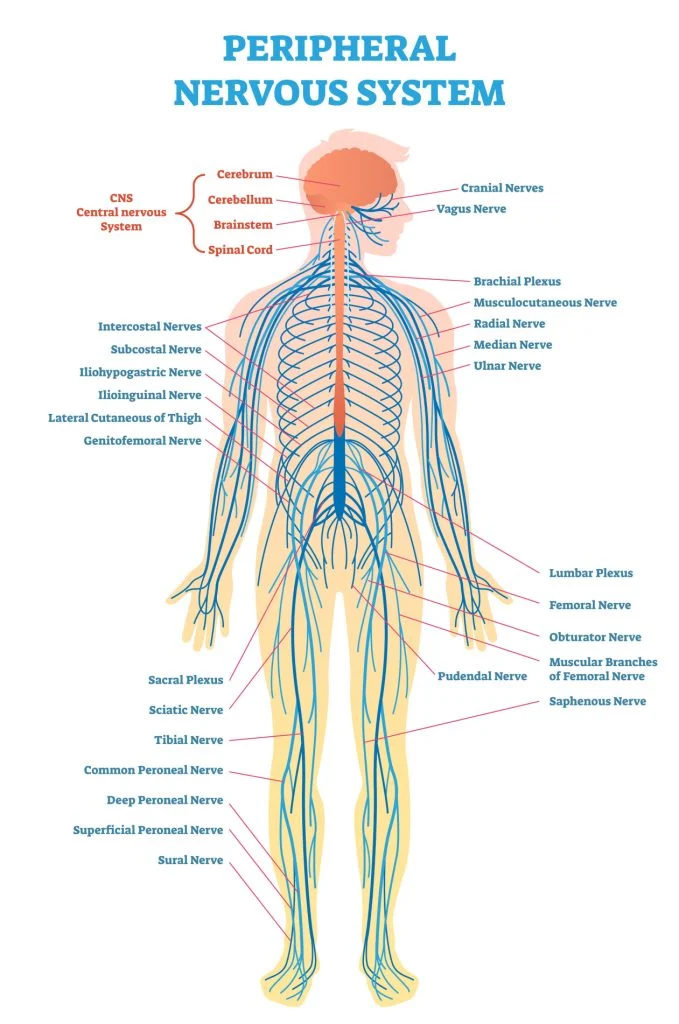
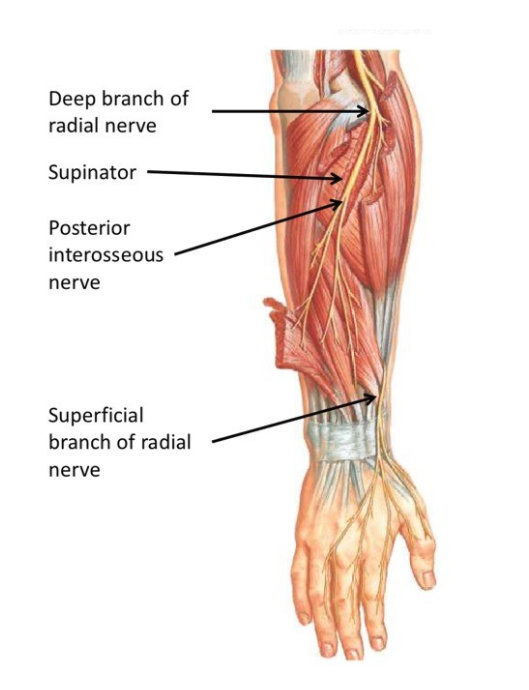
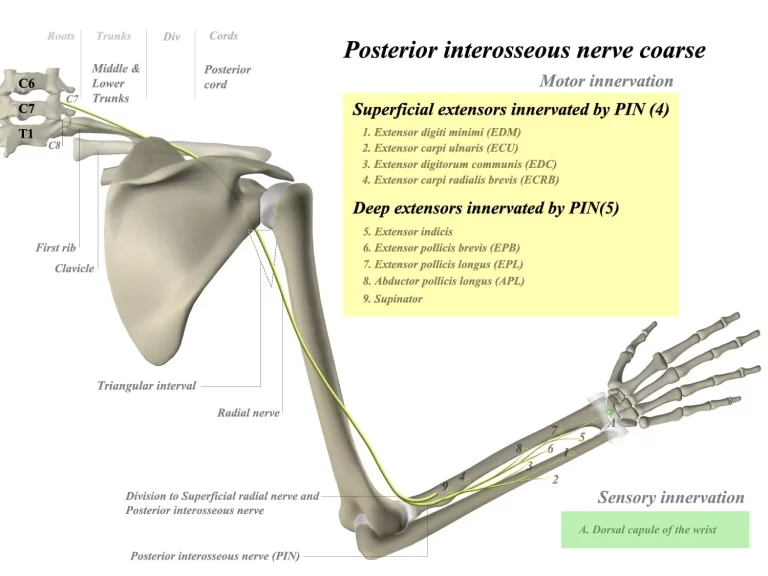
Guyon Canal
The Guyon Canal, also known as the ulnar canal or Canal of Guyon, is a narrow passageway located in the wrist, specifically at the ulnar side. Named after French surgeon Jean Casimir Félix Guyon, who extensively studied the anatomy of the hand, this canal serves as a conduit for the ulnar nerve and artery as…