A Bone-Related Special Test of Ankle Joint
- These all tests are applied in the clinic to check bone-related problems in the ankle joint.
- These orthopedic or clinical tests are applied by to therapist or doctor when the patient is complaining about ankle pain.
Name of the bone-related special test of ankle joint
- Functional hallux limitus test
- Hoffa’s test
- Homan sign
- Morton’s test
- Swings test
- Test for peroneal tendon dislocation
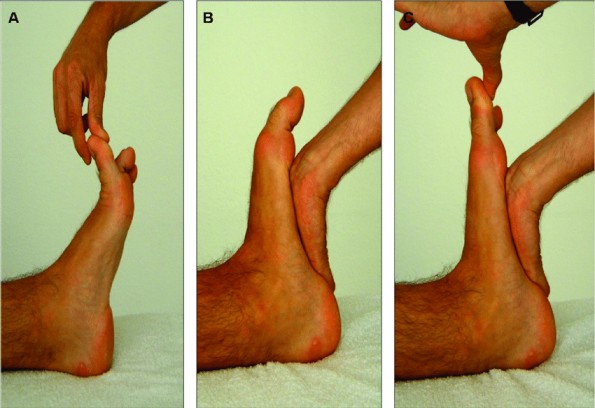
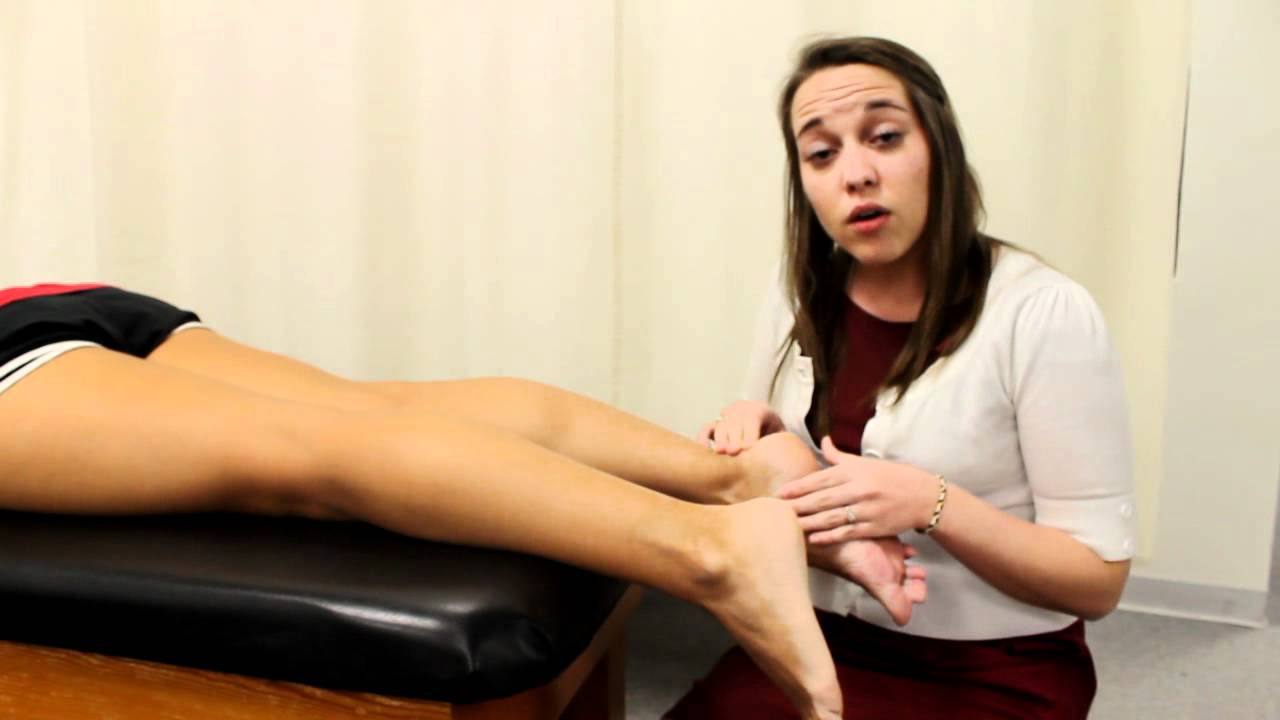
Functional hallux limitus test
- Purpose = This test is used to check the joint function of the midtarsal joint.
- Technique = The patient lies supine with the leg supported on the bed.
- The examiner uses one hand to keep the subtalar joint in neutral while using the same hand to keep the first metatarsal in dorsiflexion.
- The examiner do dorsiflexes the proximal phalanx of the hallux by the help of other hand.
- Result = If the first metatarsal plantar flexes when the toe is dorsiflexed, the test is considered positive for abnormal mid-tarsal joint function leading to abnormal midtarsal joint pronation during late midstance.
Hoffa’s test

- Purpose = This test is used to check the fracture of the calcaneal.
- Technique = The patient lies prone with the feet extended over the edge of the examining table.
- The examiner palpates the Achilles tendon while the patient plantar flexes & dorsiflexes the foot.
- Result = If one Achilles tendon [ the injured one ] feels less taut than the other one, the test is considered positive for a calcaneal fracture.
- positive dorsiflexion on the affected side is also greater.
Homan sign:
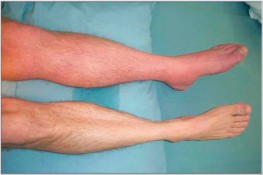
- Purpose = This test is used to check the deep vein thrombophlebitis.
- Technique = The patient is in the supine position for the test.
- Examiner do The patient’s foot dorsiflexed passively with the knee of patient is extended.
- Result = pain in the calf indicates a positive Homans sign for deep vein thrombophlebitis.
- When the presence of tenderness is also elicited on palpations of the calf muscle.
- In addition to these findings, the examiner may find pallor & swellings in the leg & a loss of the dorsalis pedis pulse.
Morton’s test
- Purpose = This test is used to check the stress fracture or neuroma of the ankle.
- Technique = The patient lies supine.
- The examiner grasps the foot around the metatarsal heads together.
- Result = If the patient feels the pain, it indicates a positive sign for stress fracture or neuroma.
Swings test
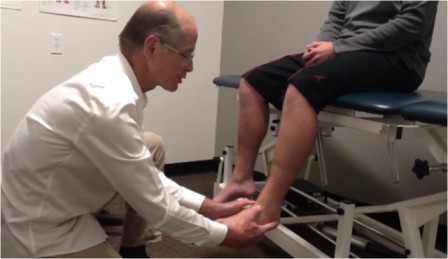
- Purpose = This test is used to check the posterior tibiofibular subluxation.
- Technique = The patient sits with feet dangling over the edge of the examining table.
- The examiner places their hands around the dorsum of the foot for using the fingers over to keep the feet parallel on to the floor.
- With the thumbs, the examiner then passively plantar flexes & dorsiflexes the foot & compares the quality & degree of movement between feet, especially into dorsiflexion.
- Result = Resistance to normal dorsiflexion in the injured ankle indicates a positive test for posterior tibiofibular subluxations.
Test for peroneal tendon dislocation
- Purpose = This test is used to check the tendon subluxes form behind the lateral malleolus.
- Technique = The patient is placed prone on the examining table with the knee flexed to 90′.
- The posterolateral region of the ankle joint is inspected for swelling.
- The patient is then asked to actively dorsiflexes & plantarflex the ankle along with eversion against the examiner’s resistance.
- Result = If the tendon subluxes from behind the lateral malleolus, the test is positive.