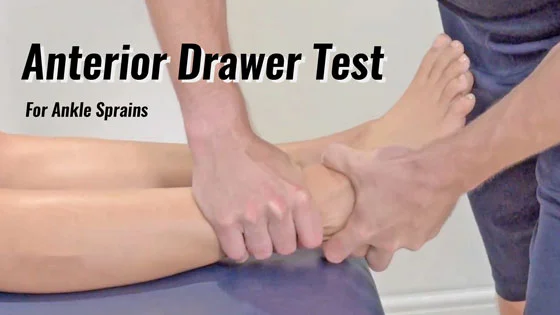
Anterior Drawer of the Ankle:
- This test is used in the clinic to check the ligament instability in the ankle.
- This test is applied by to therapist or doctor in the clinic.
- This test is determined to ankle mechanical hyper mobility /instability in the sagittal plane of the joint of talocrural joint/upper ankle joint is present.
Purpose of the Anterior Drawer of the Ankle :
- This test is designed primarily to test for injuries to the anterior talofibular ligament in the ankle.
How to perform the Anterior Drawer of the Ankle ?
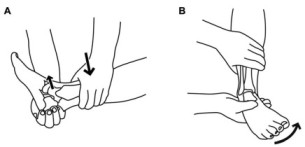
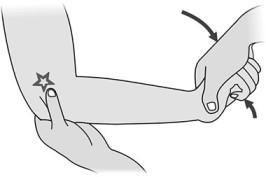
- The starting position of the patient for the test is supine.
- In the supine position with the foot relaxed.
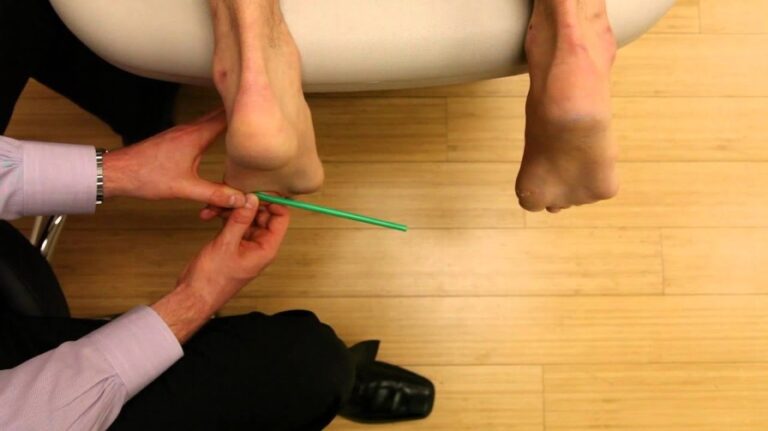
- The examiner stabilizes the tibia & fibula, holds the patient’s foot in 20′ of plantar flexion,& draws the talus forward in the ankle mortise.
- sometimes, a dimple appears over the area of the anterior talofibular ligament on anterior translation means dimple/suction sign.
- If pain & muscle spasms are minimal.
- In the plantar-flexed position, the anterior talofibular ligament is perpendicular to the long axis of the tibia.
- By adding inversion, which gives anterolateral stress, the examiner can increase the stress on the anterior talofibular ligament & the calcaneofibular ligament.
Result of the Anterior Drawer of the Ankle :
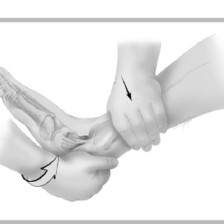
- A positive anterior drawer test may be obtained with a tear of only the anterior talofibular ligament, but anterior translation is greater if both ligaments are torn, especially if the foot is tested in dorsiflexion.
- If straight anterior movement or translation occurs, the test indicates both medial & lateral ligament insufficient.
- This bilateral finding, which is often more evident in dorsiflexion, means that the superficial & deep deltoid ligaments, as well as the anterior talofibular ligament & anterolateral capsule, have been torn.
- If the tear is on only one side, only that side would translate forward.
- For example, with a lateral tear, the lateral side would translate forward, causing medial rotation means internal rotation of the talus & resulting in anterolateral instability, which is increasingly evident with growing plantar flexion of the foot.
- Ideally, the knee should be placed in 90′ of flexion to alleviate tension on the Achilles tendon.
- The test should be performed in plantar flexion & in dorsiflexion to test for straight & rotational instabilities.
- The test may also be performed by stabilizing the foot & talus &pushing the tibia/fibula posteriorly on the talus.
- In this case, excessive posterior movement of the tibia & fibula on the talus indicates a position test.
Evidence of this test of the Ankle :
- This test is in 160 patients.
- Complain of the patient is an inversion ankle sprain
- Sensitivity of the Anterior Drawer of the Ankle = 86 %
- Specificity of the Anterior Drawer of the Ankle = 74 %
- This result is compared with to an arthrogram.
- Another test is in patient 66.
- Which is measured in lateral ankle sprain.
- Sensitivity of the Anterior Drawer of the Ankle = at 2.3 mm or greater = 0.74 & at 3.7 mm or greater = 0.83
- Specificity of the Anterior Drawer of the Ankle = at 2.3 mm or greater =0.38 & at 3.7 mm or greater = 0.40
- This result is compared with to an ultrasound.
- Positive likelihood ratios at 2.3 mm or greater = 1.2 & at 3.7 mm or greater =1.4
- The negative likelihood ratios at 2.3 mm or greater = 0.66 & at 3.7 mm or greater = 0.41.

One Comment