Windlass Test
What is a Windlass Test?
The Windlass test is a physical examination maneuver used to assess the integrity of the plantar fascia, a thick band of connective tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot. This test is primarily employed to diagnose plantar fasciitis, a common condition characterized by inflammation and pain in the plantar fascia.
This windlass mechanism is a mechanical model that explains how the plantar fascia supports the foot when it is bearing weight and gives details on the biomechanical stresses that are applied to the plantar fascia.
The plantar aponeurosis is directly stretched during the windlass test, which can be useful in assessing plantar fascia problems. When deciding how best to diagnose and treat plantar fasciitis, the test may play a significant role.
The Windlass Mechanism
Originally, Hicks defined the foot and its ligaments as a triangular structure, or truss, resembling an arch. The truss’s arch was produced by the calcaneus, metatarsals, and midtarsal joint (the medial longitudinal arch). The tie-rod connecting the calcaneus to the phalanges was made of plantar fascia.
The tibia facilitates the downward movement of vertical stresses caused by body weight, which tends to flatten the medial longitudinal arch. Additionally, because ground response forces fall both anteriorly and posteriorly to the tibia, they can further reduce the flattening effect as they ascend upward on the calcaneus and metatarsal heads.
From the base of the calcaneus, the plantar aponeurosis spreads distally to the phalanges. The medial longitudinal arch is maintained and the calcaneus and metatarsals are kept from spreading by the stretch tension of the plantar fascia. The tensile strength and anatomical direction of the plantar fascia prevent foot collapse.
A rope or cable being tightened is called a “windlass.” The plantar fascia mimics a cable that is fastened to the metatarsophalangeal and calcaneus joints. During the propulsive phase of walking, the plantar fascia winds around the metatarsal head by dorsiflexion. The medial longitudinal arch is raised by the plantar fascia’s winding, which reduces the distance between the calcaneus and metatarsals. The fundamental idea behind the windlass mechanism is the shortening of the plantar fascia resulting from hallux dorsiflexion.
How to Perform Windlass Test?
A positive windlass test resulted in the reproduction of heel discomfort when the toes were passively bent.
There is an increased sensitivity in weight-bearing as compared to non-weight-bearing. De Garceau et al. demonstrated 32% sensitivity for non-weight-bearing tests and 100% specificity for weight-bearing testing.
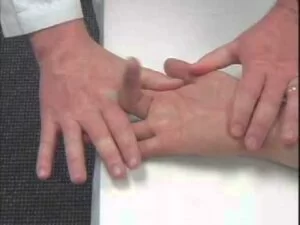
Non-weight bearing position:
While the patient is seated, gently elevate his or her toes to see if it hurts.
The patient is in a non-bearing position with their knee bent to a 90° angle. The examiner extended the MTP joint and stabilized the ankle by placing one hand slightly behind the first metatarsal head. This prevented motion limits caused by a short hallucis longus.
Positive test if the MTP extension’s end range caused pain.
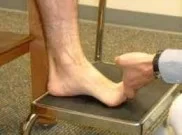
Weight-bearing position
When the patient is in a position where they can bear weight, the examiner extends their toes greatly.
Placing the foot to be tested’s metatarsal just over the step’s edge, the patient stands on a step stool.
It is required of the individual to balance equally on both feet.
Next, the examiner lets the interphalangeal joint flex and passively stretches the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
The first metatarsophalangeal joint should be passively extended, or dorsiflexed, until it reaches the limit of its range of motion or the patient experiences discomfort again.
It is crucial to remember that the Windlass test is only one part of a thorough physical examination that evaluates the health of the ankle and foot. To get a precise diagnosis, doctors usually combine it with patient history, imaging studies, and additional clinical evaluations.
Windlass Test Video
References
Windlass Test. (n.d.). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Windlass_Test