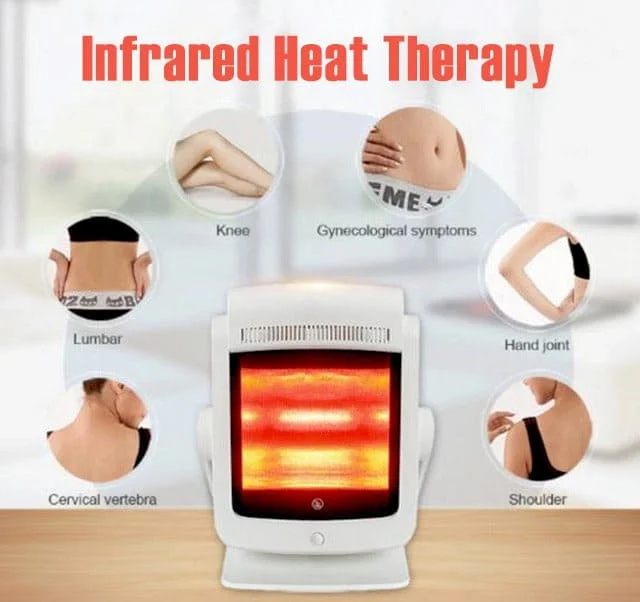
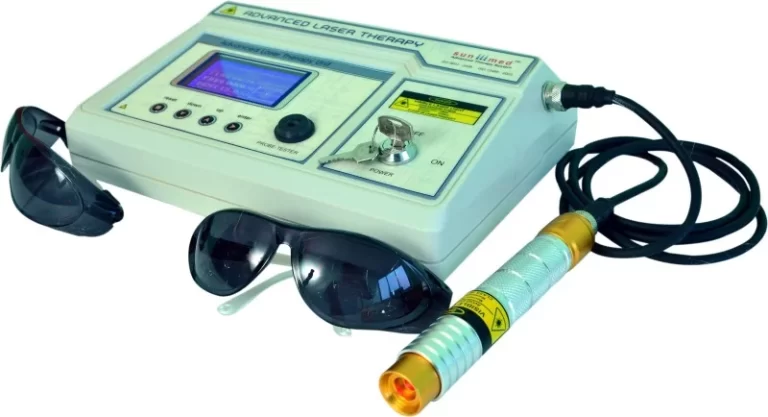
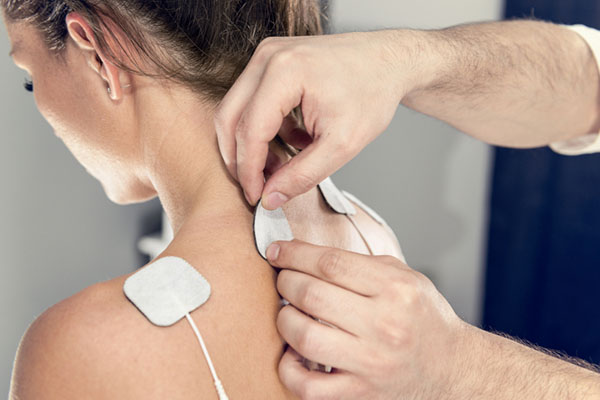
Electrical Stimulation Machine
Introduction of Electrical stimulation machine : Types of current use in ES therapy : Faradic type current : Electronic simulators : Modified faradic current : Electrical activity of nerves : Nerve transmission Electrical stimulation of nerves : Accommodation : Effect of nerve stimulation : Effects of frequency of stimulation : Strength of contraction : Physiological…