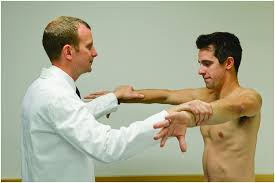
Craig’s test of hip
- This test is also known as the Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test means TPAT.
- The angle of Femoral anteversion is become between the femoral neck & femoral shaft.
- It is indicate to degree of torsion of the femur.
- This angle decreases during the growing period.
- There are available many ways for a measure of femoral anteversion.
- Some methods are which is used measure to femoral anteversion:
- Imaging studies = fluoroscopic, radiography, ultrasound (US), computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as well as used to functional assessments.
- MRI method is more reliable (r = 0.97) than to CT (r = 0.77)& any other tests.
- This test is the most commonly used in physical examination tests for femoral anteversion
Purpose of Craig’s test :
- This test is a passive test that is used to measure the femoral anteversion/forward torsion of the femoral neck.
The technique of Craig’s test :
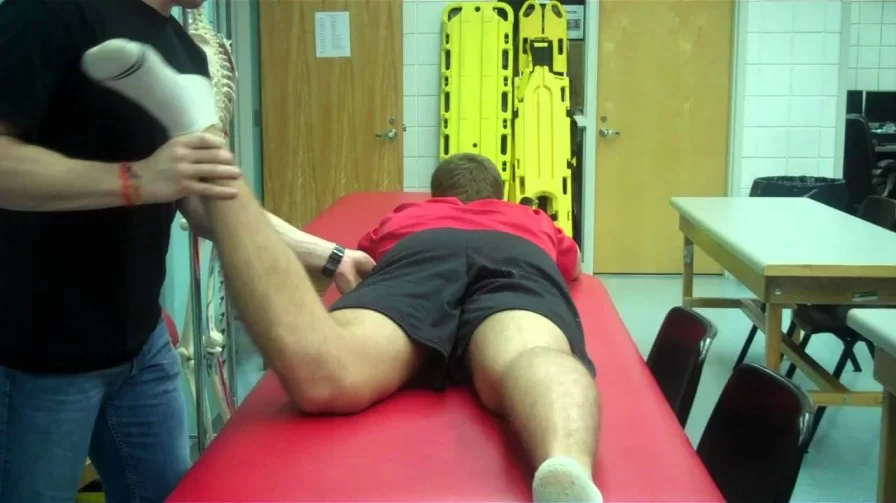
Patient position for test :
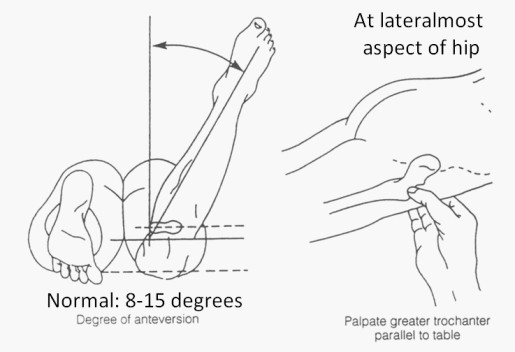
- Into starting position patient is in the prone position with to hip in neutral rotation means no internal or external rotation & do the knee flexion up to 90° of tested side on to examination table.
Therapist position for test :
- This test is complete with the help of 2 examiners
- It is stand on the contra lateral side of the subject’s hip which is being examined.
- The examiner stabilizes the sacrum with the help of the forearm & the help of the other hand palpate to the greater trochanter which was more cranial for the test.
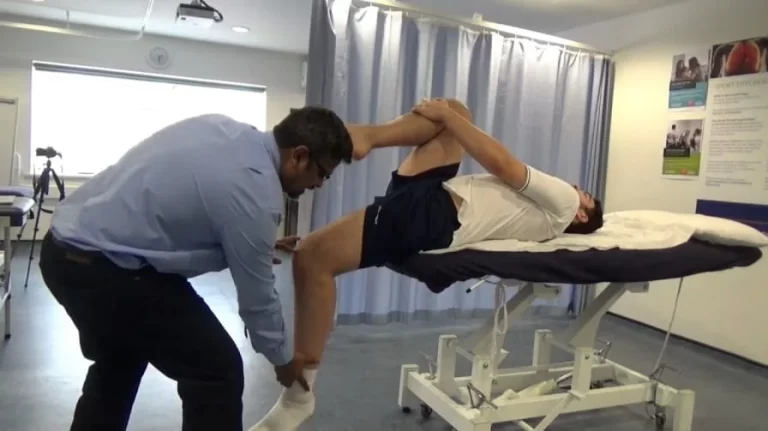
The procedure of this test :
- Examiner is palpated the greater trochanter of the affected side with the help of caudal hand then do the passively internally rotating means medial rotation of the hip till the most prominent portion of the greater trochanter is reached on most lateral position means external position.
- One examiner holds the position of the leg into starting position of the test.
- Then Another examiner measures the angle between the shaft of the tibia means a line that is bisecting medial&lateral malleoli& a line that is perpendicular to the table means an imaginary vertical line which is extending from the table with to help of either a goniometer &inclinometer.
- It becomes the angle of femoral anteversion.
Interpretation of Craig’s test :
| Position | Angle | Other thing |
| Normal | 30 degrees 8-15 degrees | At birth In adults |
| Increased anteversion angle | Angle >15 degrees | Leads to pigeon-toed walking &squinting patellae It is twice then boys or common into girls. |
| Decreased anteversion angle | Angle <8 degrees | Retro version |
Evidence of Craig’s test :
Psychometric Properties :
- This study is published in 2015.
- This study used three different methods to measure the femoral anteversion angle during Craig’s test:
- In three methods including :
- A goniometer
- A goniometer with a laser beam
- An inclinometer
- Also measured inter & intra- reliability of these three methods.
- Both examiners in study of intra-examiner reliability with to all three measurement methods:
| Examiner | Goniometer | Goniometer with the laser beam | Inclinometer |
| 1 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.73 |
| 2 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.72 |
- In this study is showed to the inter-examiner reliability is below moderate for both the goniometer = 0.25 ,in inclinometer = 0.27 & moderate for to goniometer with the laser beam = 0.62.
- It is suggested the use of a goniometer with to laser beam for measure the Craig’s test.
Another study :
- This study is published in 2020.
- In this study compared to Craig’s test & computed tomography (CT) for measuring to femoral anteversion angle means FAA in patients with to anterior cruciate ligament – ACL injuries.
- But No significant correlation is found between this angle of Craig’s test & CT measurements on both sides which is involved side – r=0.12, p=0.59
- Uninvolved sides – r=0.04, p=0.84.
- In the study which is published in 2009.
- in this study compared to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) & Craig’s test for measuring to FAA means femoral anteversion angle in 18 healthy adults.
It is shown to which is representing interstate reliability for by the two examiners :
| Examiner | Intra-class correlation means ICC values | Standard error of measurement means SEM values |
| 1 | 0.88 | 3.2° |
| 2 | 0.90 | 3.1° |
Clinical Significance of Craig’s test :
- This angle is affected to bio mechanics of to hip, so that the moment arms & the line of action of muscles around the joint are altered.
- This alteration affects the position of the trochanter so that the line of the action surrounds the region.
- Higher of this angle :
- Results = slightly do the shorter hip extension moment arm & an increase too in hip flexion moment arm of to abductor’s muscles.
- Other result of high FAA results = shorter abductor lever arm & also considerably to increases the internal rotation moment length.
- Reduced this angle :
- Results = it is given to higher shear forces on the femoral neck-head junction.
- This force is an increase of 42% increase with the angle of 0° & increase of force 86% with an angle of 12.5′
- When the increased to this angle it is associated with to progressive increase to patellofemoral contact pressures.
- Increased this angle leads to pelvic instability during to gait &in-toeing gait which is often accompanied by compensatory external rotation means lateral rotation of to tibia.
- Greater this angle is also associated with the number of orthopedic pathologies including to increased risk of
- Anterior cruciate ligament injury
- Femoral trochlear dysplasia
- Lower hip abductor
- Impaired tracking of the patella
- Femoral acetabular impingement.
- Unilateral hip osteoarthritis
- Vastus medialis activity
- Reduced of this angle is associated with to slipped capital femoral epiphysis.