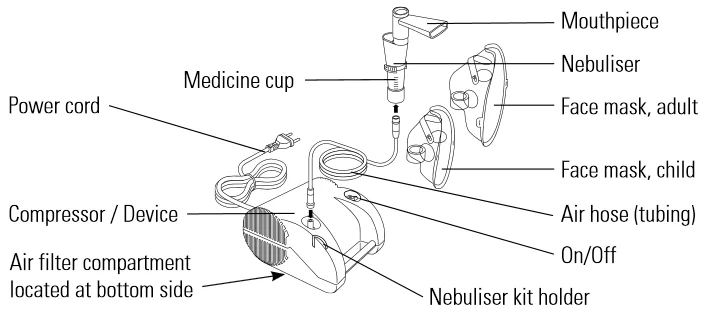
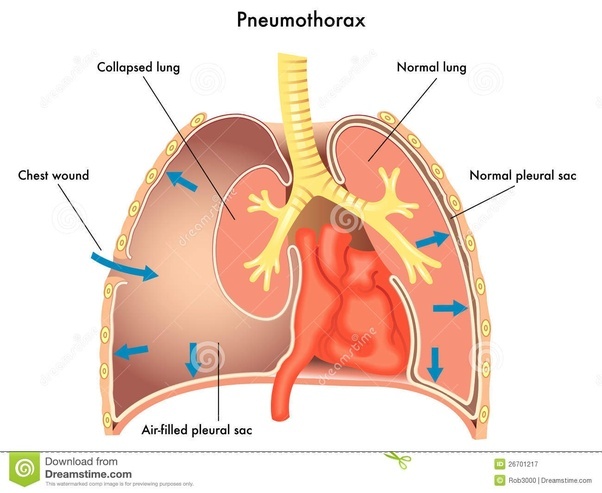
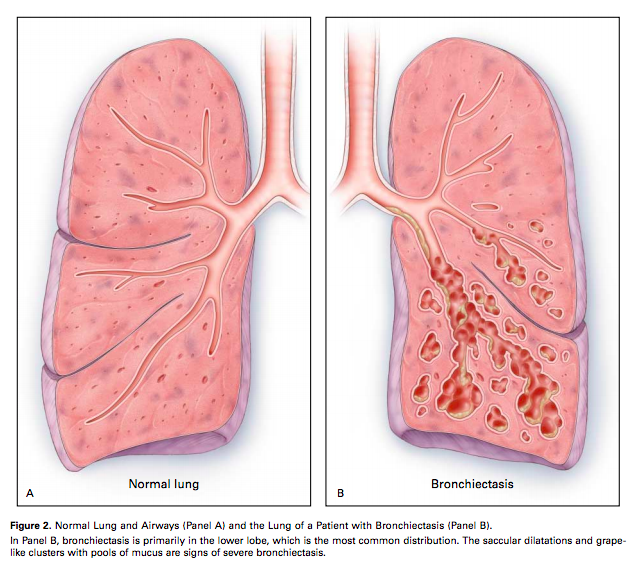
Postural Drainage: Method, Indication, Contraindication
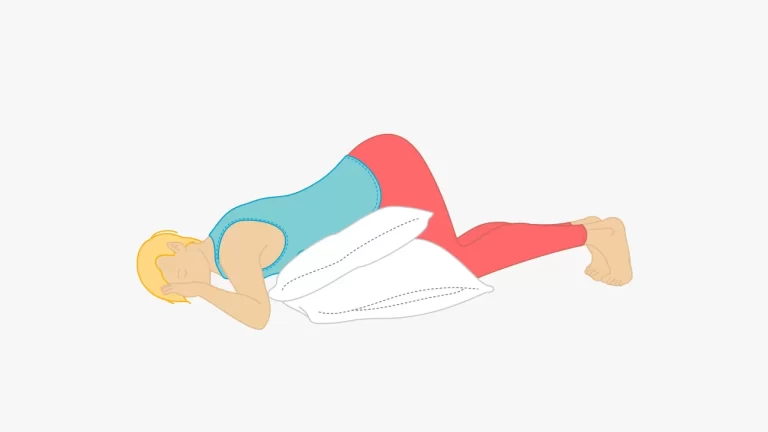
What is a Postural Drainage? Postural Drainage removes mucus from certain parts of the lungs by using gravity and proper positioning to bring the secretions into the throat where it is easier to remove them. The lungs are divided into segments called lobes, the right lung is divided into three lobes (right upper lobe, right…