Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
It is normal to feel stressed sometimes. But if the stress builds up, or it continues for a period of a long time, it indicates that person might carry the tension in her muscles. A person could have muscle tightness without even realizing it.
One way to ease muscle tension is progressive muscle relaxation, also known as Jacobson’s relaxation technique. Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is a form of therapy that involves tightening and relaxing the muscle groups, one at a time, in a specific way.
The goal is to free tension from the muscles while helping a person recognize what that tension feels like.
When practiced daily, this technique may help the person to manage the physical effects of stress. It is found that this technique has therapeutic benefits for conditions like:
- High blood pressure
- Migraines
- Sleep issues
Let us know more about the Progressive Muscle Relaxation technique:
What is Progressive Muscle Relaxation?
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is an anxiety-reduction technique first introduced by American physician Edmund Jacobson in the year 1930s. The technique involves alternating tension and relaxation in all major muscle groups of the body.
It was based on the theory that physical relaxation may promote mental relaxation.
Jacobson found that a person can relax a muscle by tensing and then releasing it. Jacobson also discovered that doing this relaxation exercise can also relax the mind.
If you have an anxiety disorder, such as Generalized anxiety disorder or Social anxiety disorder (SAD), the muscles are probably tense quite often. By practicing PMR, a person will learn how a relaxed muscle feels different from a tense muscle.
PROGRESSIVE MUSCLE RELAXATION
PMR is an exercise that decreases stress and anxiety level in the body by slowly tensing and then relaxing each muscle. The theory behind this exercise technique is that you cannot have the feeling of relaxation and warm well-being in the body and at the same time experience anxiety symptoms. With practice, a person will become more aware of when they are experiencing tension and the therapist will have the skills to help them relax.
During the relaxation exercise, each muscle should be tensed, but not to the point of strain that may get damaged instead of relaxing. Pay special attention to the feeling of tension in every muscle and the feeling of relaxation as you release the tension. If the person has any injuries or pain, can skip the affected areas.
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is a technique where a person tenses and relaxes different muscles in their body to relieve tension and generate a relaxation response in the body.
The relaxation response is a physiological state that slows breathing patterns, decreases blood pressure, and lowers heart rate. It is totally the opposite of the stress response in the body.
PMR is a relaxation technique that concerns tensing the muscle and relaxing specific muscles in turn. Generally, a person starts with the feet and works their way up the body, taking deep, slow breaths throughout the exercise.
By concentrating on muscle tensing and relaxing muscles individually, a person gets focused on the present moment. If their attention strays, they have to refocus again on how their body feels as they work their way through the exercise. This facilitates mindfulness
The objective of PMR is to bring about a relaxation response in the body. The relaxation response causes the body to transition from an awake, active state into a more restful one. It causes some physiological changes, such as:
- Slower breathing
- Slower heart rate
- Lower blood pressure
- Lower cortisol levels
People can induce the relaxation response to lessen stress or anxiety, help them get better sleep, or ease tense muscles. Some people also use the PMR technique at the end of a yoga session or as a form of meditation.
Use of PMR:
Progressive muscle relaxation can be worthwhile for a range of reasons, which are given below
- Anxiety
- High blood pressure
- Lower back pain
- Migraine
- Muscle tension
- Neck pain
- Stress
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) symptoms
Chronic stress and anxiety can donate to various health problems. Health complications linked to chronic stress contain depression, diabetes, heart disease, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Reduces anxiety and tension:
Relief from anxiety is one of the main benefits of PMR. This possesses generalized anxiety disorder or anxiety due to a stressful situation.
PMR reduced symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. At the same time, it enhanced feelings of well-being and quality of life.
It was determined that PMR had the ability to reduce tension and anxiety in dental patients
PMR was as useful as acupuncture treatment in helping to lessen feelings of tension, anxiety, and anger.
It is also found that PMR may help relieve anxiety in people with COVID-19, suggesting benefits for coping with difficult situations.
Improves sleep
Because PMR induces relaxation, it may also help a person to get better sleep.
The patients often experience increased anxiety and poor sleep quality due to their physical and psychological disorders.
PMR allowed mothers with premature babies to sleep pleasingly during the postpartum period.
Eases neck pain
If a person tends to carry tension in the neck or shoulders, they might experience neck pain. It is a common condition that is frequently associated with mental and emotional stress.
PMR may help decrease symptoms of chronic nonspecific neck pain. In doing so, it may also enhance the quality of life and physical function.
Reduces low back pain
Low back pain is another ordinary condition. It has many possible causes, but stress can make it more impaired.
Doing some week this exercise may help reduce chronic low back pain.
Some sources discovered that the PMR technique given with music has the ability to reduce low back pain in pregnant women.
Improves systolic blood pressure
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, boosts the risk of heart disease and can also cause a stroke. Stress can deteriorate the condition, but PMR may help.
PMR with music therapy enriched systolic blood pressure in older adults.
Decreases the frequency of migraine attacks
Migraine is a neurological illness that causes intense pain in the face and head. Migraine attacks can be activated by stress, including normal everyday stressors.
PMR can lessen the frequency of migraine episodes. The researchers acknowledge that it helps by balancing levels of serotonin, that’s often low in people with migraine.
Reduces temporomandibular joint (TMJ) symptoms
Emotional stress in the body can provoke temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder, a condition in which there is stiffness and locking of the jaw.
The calming effect of PMR may help to decrease TMJ symptoms. The study’s participants experienced slightly intense pain and tension after practicing the technique.
How to do PMR exercise?
To try PMR:
- Find a relaxed and quiet place to do the exercise. Sit in a chair or lie down on the floor or on a bed. If you feel calm, close your eyes.
- Keeping the mouth closed, inhale slowly through the nose. Exhale slowly through the mouth and imagine the tension leaving the body.
- Repeat these deep breathing exercises three or four more times. If it causes dizziness or something, breathe normally instead.
- On the fifth inhale, squeeze the muscles of the lower limb in the toes and feet and count to four. Then exhale slowly through the mouth, slowly releasing tension from the feet.
- Repeat step four again, this time it is for the other muscles one by one. Tense the muscles while breathing in, then release when breathing out.
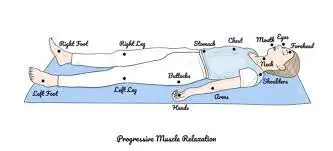
Continue exercise to repeat a pattern of tensing muscles while inhaling and then relaxing the muscle while exhaling for muscles all the way up the body. This includes the:
- Knees
- Thighs
- Buttocks
- Abdomen
- Hands, by making fists
- Arms
- Shoulders, by shrugging them toward the ears
- Jaw, by clenching the teeth and releasing
- Face, by scrunching the muscle of the face and releasing
After releasing tension from a body part, take a few deep breaths before moving on to the next body part. Think about breathing out tension with each exhale while breathing.
At the end of the exercise, rest for a while and notice how it feels. If a person wants to get up, they can slowly open their eyes and gently move from their position.
Most practitioners suggest tensing and relaxing the muscle groups one at a time in a specific order, typically beginning with the lower extremities and ending with the face, abdomen, and chest. A person can practice this technique seated or lying down position, and a person should try to practice with comfortable clothing on, and in a quiet place free of all distractions.
Start the exercise by lying or sitting down. Relax the entire body. Take five deep and slow breaths.
- Lift the toes upward. Hold it, then let go. Pull the toes downward. Hold it, then let go.
- Next, tense the calf muscles, Hold them then let go.
- Move the knees toward each other. Hold it, then let go.
- Squeeze the thigh muscles. Hold it, then let go.
- Clench the hands as making fists. Hold it, then let go.
- Tense the arms. Hold it, then let go.
- Squeeze the buttocks. Hold it, then let go.
- Contract the abdominal muscles. Hold it, then let go.
- Inhale and tighten the chest. Hold it, then exhale and let go.
- Raise the shoulders to the ears. Hold it, then let go.
- Purse the lips together. Hold it, then let go.
- Open your mouth wide. Hold it, then let go.
- Close your eyes tightly. Hold it, then let go.
- Lift the eyebrows. Hold it, then release.
Tips for Progressive muscle relaxation exercise
If someone is just getting commenced with PMR, they may find it helpful to:
- Set aside a regular time each day for PMR exercise, such as before sleep
- Choose a quiet, calm space in which to practice
- Use audio or video tutorials to learn the process
- Listen to relaxing music
- Silent the phone to avoid distraction
- Wear loose clothes to be comfortable
- Practice consistently in order to establish a routine
If someone does not find the PMR method effective, there are many other relaxation techniques, including:
- Breathing exercises
- Meditation
- Yoga, tai chi, or qi gong
- Visualization exercises
- Self-hypnosis
- Biofeedback-assisted relaxation
- Massage
People may try different types of techniques to find what works for them.
If a person finds that they are not able to easily relax, sleep, or manage mental health symptoms even when regularly making time to relax, they may wish to speak with a doctor or therapist.
Summary:
PMR is a type of relaxation technique that can help lessen the symptoms of stress. It involves tensing the muscle and then relaxing individual muscles at a time. This slows breathing brings a focus the person to the present moment and activates the body’s relaxation response.
Progressive muscle relaxation is also an amazing tool to help learn about the body and the signals it may be telling you. With a lot of practice and time, a person can learn to accurately identify and diminish the signs and signals of stress and tension in their body.
People can practice PMR at home by finding a quiet space with fresh air, sitting or lying down, and then gradually tensing and relaxing muscles from the feet up to the head.
If the exercise does not help, there are many other relaxation techniques also to try. People with continued mental health symptoms may find it helpful to have professional support from a doctor or therapist.
FAQs:
What is progressive muscle relaxation good for?
When a person has anxiety or stress in life, one of the ways the body responds is with muscle tension. Progressive muscle relaxation is a method that helps reduce that tension.
How does PMR reduce stress?
PMR is a type of relaxation technique that can help relieve the symptoms of stress. It concerns tensing the muscle and then relaxing individual muscles one at a time. This slows breathing brings a focus the person to the present moment and activates the body’s relaxation response.
What are the contraindications for progressive muscle relaxation?
If a person has a tendency to dissociate (e.g. feel like you are not in your body), have a history of childhood abuse/trauma, and/or experience psychosis, it is strongly advised that a person do not do this relaxation exercise except if the assistance of a mental health professional present.
How does progressive muscle relaxation affect the brain?
That PMR showed to few areas showing changed activity indicates that the technique may suppress the brain activity. Even beginners may be able to generate such a focused mental state.
Can tight muscles cause anxiety?
For many people, chronic muscle tension plays a big role in anxiety. It may not surprise you that psychological stress induces muscle tension, but it goes the other way as well: muscle tension causes psychological stress. This is good news, it means that by reducing muscle tension, a person can relieve their anxiety.



One Comment