Provocation test of the SI joint:
- These tests are applied to the clinic to check the dysfunction of the SI joint.
- These clinical tests are applied by a doctor or therapist when the patient is complaining about SI joint pain(Sacroiliitis).
- These tests are applied to the examination part of the assessment of the SI joint.
Name of the special test of the SI joint:
- Femoral shear test
- Gapping test
- Ipsilateral prone kinetic test
- Passive extension & medial rotation of ilium on the sacrum
- Passive flexion &lateral rotation of ilium on the sacrum
- Passive lateral rotation of the hip
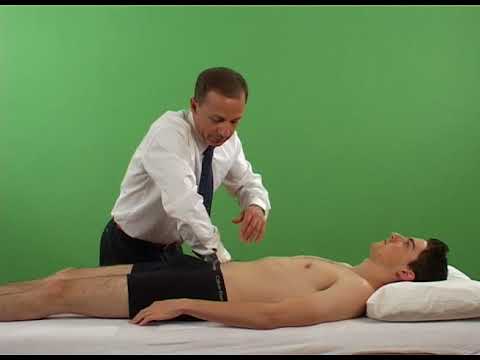
Femoral shear test:
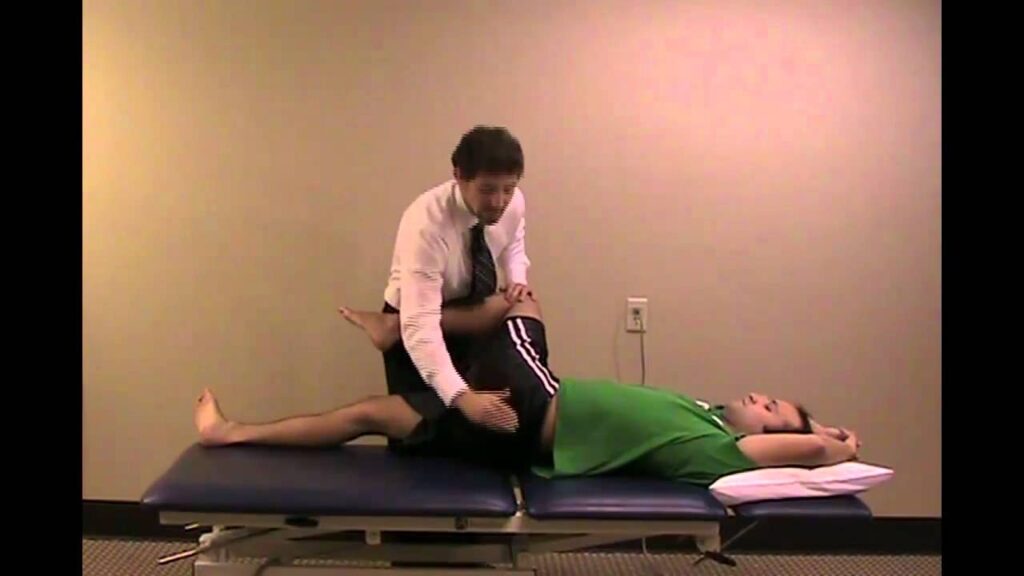
- Purpose = This femoral shear test is used to check the anterior-to-posterior shear stress of the SI joint.
- Technique = the patient lies in the supine position.
- The examiner slightly flexes, abducts & laterally rotates means externally rotates the patient’s thigh at approximately 45′ from the midline.
- The examiner [ therapist ] applies a graded force through the long axis of the femur, which causes anterior-to-posterior shear stress to the sacroiliac joint on the same side.
Gapping test:
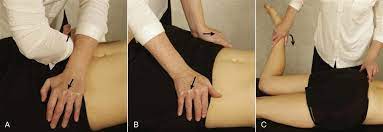
- This test is used to transverse anterior or distraction provocation test.
- Purpose = This gapping test is used to check the sprain of the anterior sacroiliac ligaments.
- Technique = The patient lies supine while the examiner [ therapist ] applies crossed-arm pressure to the ASIS.
- Then the therapist [ examiner ] pushes down & out with the arms.
- Result = The test is positive only if unilateral gluteal or posterior leg pain is produced, indicating sprains of the anterior sacroiliac ligaments.
- Care must be taken when performing this test.
- The examiner’s hand pushing against the ASIS can elicit pain because the soft tissue is being compressed between the examiner’s hands & the patient’s pelvis.
Ipsilateral prone kinetic test:
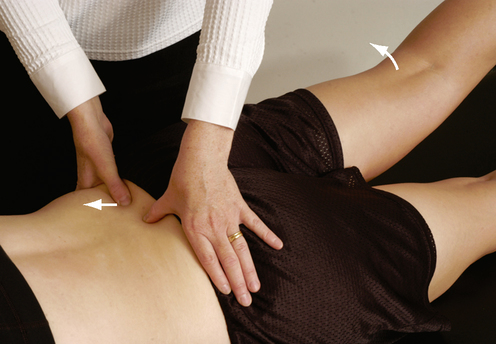
- This test is designed to assess the ability of the ilium to flex & rotate laterally/posteriorly.
- Purpose = this ipsilateral prone kinetic test is used to check the hypo mobility of the posteriorly rotated ilium.
- Technique = this patient lies prone while the examiner [ therapist ] places one thumb on the PSIS & the other thumb parallel to it on the sacrum.
- Then the therapist instructs the patient is for doing actively extend the leg on the same side.
- Normally, the PSIS means posterior superior iliac spine should move superiorly & laterally.
- If it does not, it indicates hypermobility with a posteriorly rotated ilium or outflare.
Passive extension & medial rotation of ilium on the sacrum:
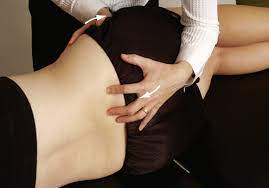
- Purpose = This passive extension & medial rotation of ilium on sacrum test is used to check the hypomobility & posterior rotated ilium / out flare.
- Technique = the patient is in a side-lying position for the test.
- In the side-lying position on the side that is not being tested.
- The examiner [ therapist ] places one hand over the ASIS area of the anterior ilium.
- The other hand is placed over the PSIS In such a way that the fingers of the hand palpate the posterior ilium & sacrum.
- The examiner [ therapist ] then pulls the ilium forward with the other hand over the ASIS & Pushes the posterior ilium forward with the other hand while feeling the relative movement of the ilium on the sacrum.
- The unaffected side is then tested for comparison.
- If the affected side moves less, it indicates hypomobility & a posteriorly rotated ilium, or outflare.
Passive flexion &lateral rotation of ilium on the sacrum:

- Purpose = This passive flexion &lateral rotation of ilium on sacrum test is used to check the hypomobility & anterior rotated ilium / out flare.
- Technique = The patient position of this test is the same as the passive extension & medial rotation of ilium on sacrum test.
- in this case, the examiner [ therapist ] pushes the anterior ilium backward with the anterior hand,& the posterior hand & arm pull the ilium posteriorly while palpating the relative movement.
- the unaffected side is then tested for comparison.
- if the affected side moves less, it is a sign of hypomobility & an anteriorly rotated ilium, or inflare.
- If both this test & the previously mentioned one are positive, it means a upsilp has occurred to the ilium relative to the sacrum.
Passive lateral rotation of the hip :
- The patient lies supine.
- The examiner [ therapist ] flexes the hip joint & knee joint to 90 ‘ & then laterally rotates the hip.
- This movement provided the hip is normal, stress the sacroiliac joint = SI joint on the test side.