Special test for the hip pathology in pediatric:
- These tests are used by the doctor to check the hip abnormality in the infant.
- These tests are orthopedic test which is performed in newborn babies.
- These tests help to doctor detect the problems of hip like CDH &DDH.
- These all problems are genital problems, which may be amenable to conservative treatment if caught early.
Name of special test of hip pathology:
- Abduction test
- Galeazzi sign
- Telescoping sign
Purpose of this three-test :
- These tests are used to check the hip abnormality in newborn babies & detect many genital problems like as CDH &DDH.
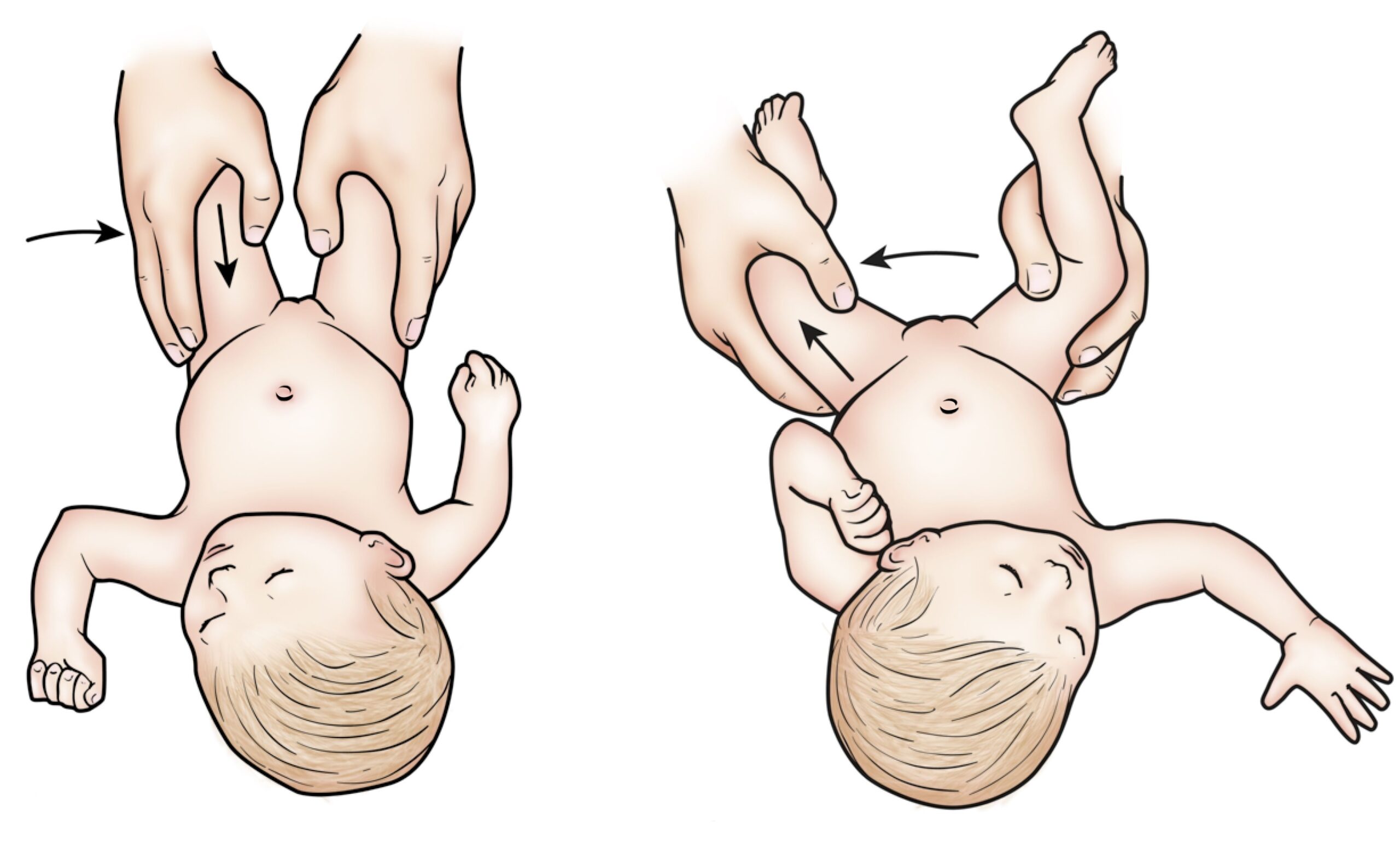
Abduction test :-
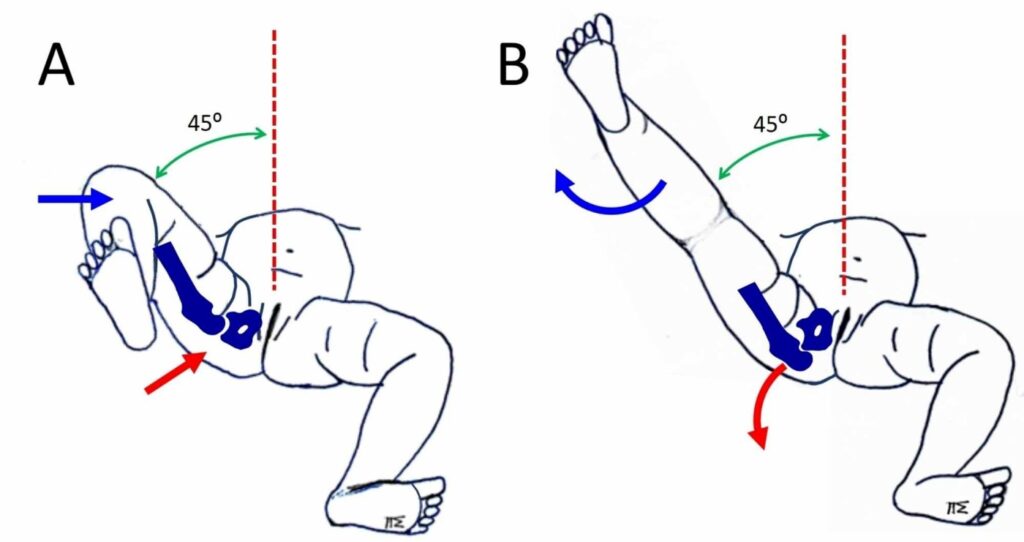
- This test is also known as Hart’s sign.
- If CDH is not diagnosed early or there is DDH, parents often note that when they change the child’s diapers, one leg does not abduct as far as the other one.
- This is basic for this test.
Technique :
- In the starting position child lies supine with the hips &knees flexed to 90′.
- The examiner then passively abducts both legs, noting any asymmetry or limitation of movements.
- In addition, if one hip is dislocated, the child often demonstrates asymmetry of fat folds in the gluteal &upper leg area because of the riding up of the femur on the affected side.
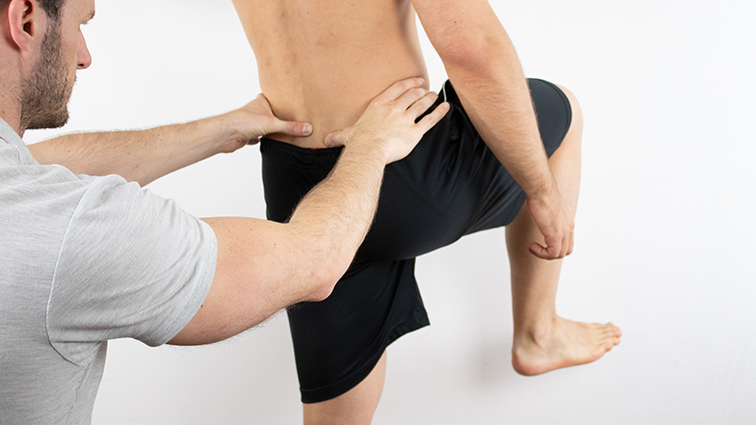
Galeazzi sign :-
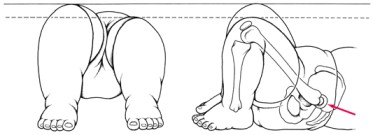
- This test is also known as the Allis test.
- This test is good for the check to unilateral DDH &may be used in children from 3 to 18 months of age.
Technique :
- In the starting position child lies supine with the knees flexed & hips flexed to 90′.
Result :
- A positive test is indicated if one knee is higher than the other.
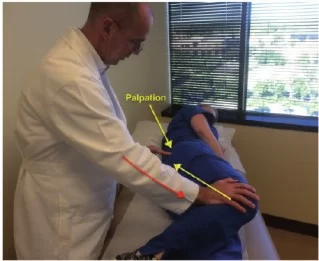
Telescoping sign :-
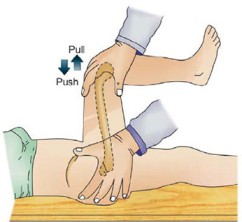
- This test is also known as Piston or Dupuytren’s test.
- The telescoping sign is evident in a child with a dislocated hip.
Technique :
- In the starting position child lies supine position.
- The examiner flexes the knee &hip to 90′.
- The femur is pushed down onto the examining table.
- The femur & leg are then lifted up & away from the table.
- With the normal hip, little movement occurs with this action.
- With the dislocated hip, however, there is a lot of relative movement.
- These excessive movements is called telescoping or pistoning.