Special test for the scapular stability
- This test is applied for the check to scapular stability.
- Muscles of the glenohumeral joint which is work in a normal coordinated fashion, the scapula must be stabilized by its muscles to act as a firm base for the glenohumeral muscles.
- When the application of this scapular stability test, the examiner must be watching the movements of the scapula as well as scapular dyskinesia.
Purpose of the scapular stability test:
- These tests are used to check the muscular weakness of the scapula.
- These tests also check the scapular stability.
Name of the scapular stability test:
- Scapular isometric test
- Scapular retraction test
- Wall push up test
Scapular isometric test:
- This test is also known as the squeeze test.
The technique of this test:

- The starting position for the test is the standing position.
- Then asked the patient for doing the actively pinch or retract the scapula together as hard as possible & to hold the position for as long as possible.
- Normally, in this position, a person can hold the contractions for 15 to 20 seconds with obvious muscle weakness/no burning pain.
- If the patient feels the burning pain in less than 15 seconds, it is indicated to be a weakness of the scapular retractors.
- During the test, the examiner must watch the patient carefully.
- subconsciously, many patients will relax the contraction a slight amount, which is barely noticeable but allows the patient to hold the contraction in a comfort zone for longer periods with no burning.
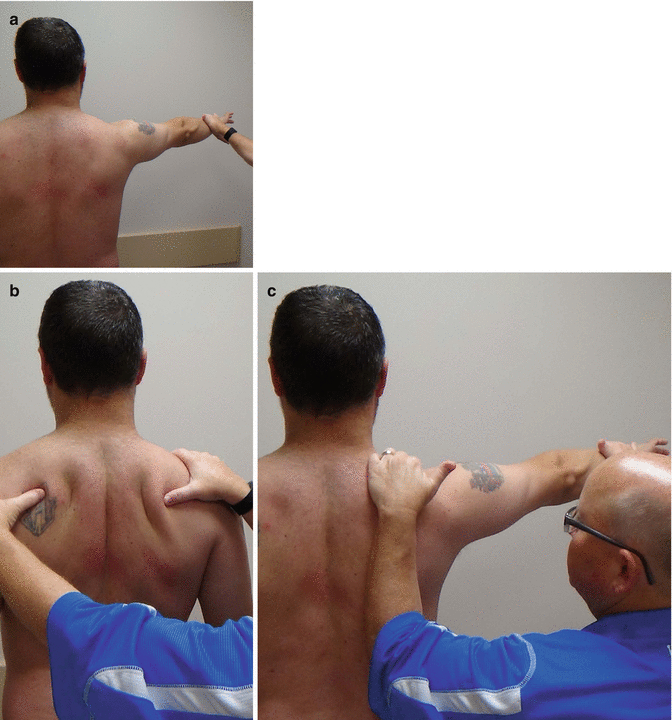
Scapular retraction test :-
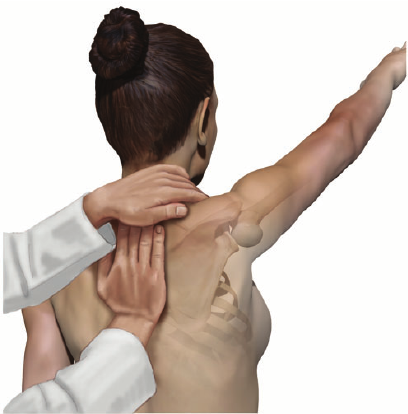
- This test is also known as the SRT test.
The technique of this test :
- The starting position for the test is the standing position.
- The examiner, standing behind the patient, places the fingers of one hand over the clavicle over the clavicle with the heel of the hand over The spine of the scapula to stabilize the clavicle &scapula &to hold the scapula retracted.
- The examiner’s other hand compress the scapula against the chest wall.
- Holding the scapula in this position provides a firm stable base for the rotator cuff muscles,&often rotator cuff strength [ if tested by a second examiner]improves.
- The test is also be positive in the patients which is already positive for relocation test.
- During the relocation test decreases the pain to scapular retraction
- If scapular retraction decreases the pain, when the relocation test is performed, it indicates that the weak scapular stabilizers must be addressed in the treatment.
- The test may also be done supine.
- In patients with a SICK scapula, if the scapula is re positioned, forward flexion improves.
Wall push up test :-

- The patient stands arm’s length from a wall.
- The patient is then asked to do a wall push up 15 to 20 times.
- If present to any weakness of the scapular muscles or winging it is usually shows up with to 5 to 10 push ups.
- For stronger or younger people, a normal push up on the floor shows similar scapular changes, usually with fewer repetitions.
- Goldbeck & Davies have taken this test further in what they describe as a closed kinetic chain upper extremity stability test.
- In this test, two markers mean tape are placed 91 cm [ 36 inches ]apart.
- Patients is assume the push up position with the one hand onto each marker.
- When the examiner says go, the subject moves one hand to touch the other, returns it to the original position,& then does the same with the other hand, repeating the motion for 15 seconds.
- The examiner counts the number of touche or crossovers made in the allotted time.
- the test is repeated three times,& the average is the test score.
- This test is designed primarily for young, active patients.