Special tests for the thoracic outlet syndrome :
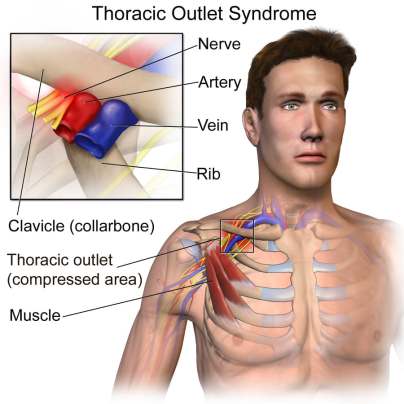
- Thoracic outlet syndrome is combined neurological & vascular signs,& symptoms of neurological; deficit, restriction of arterial flow, or restriction of venous flow may be seen individually.
- The patient may complain of fatigue in the shoulder, vague shoulder pain, achiness,& a sense of heaviness in the shoulder, all of which can affect speed & control while doing activity mostly with the arm in abduction& lateral rotation means external rotation.
- In this patient complaint physiotherapist applied a special test for thoracic outlet syndrome.
- In these tests that involve taking the pulse, the examiner must find the pulse before positioning the patient’s arm or cervical spine.
Purpose of the Special tests for thoracic outlet syndrome :
- These special tests are used o for checking the thoracic outlet syndrome of the shoulder.
Name of the special test of the thoracic outlet syndrome :
- Adson maneuver
- Costoclavicular syndrome test
- Halstead maneuver
- Roos test
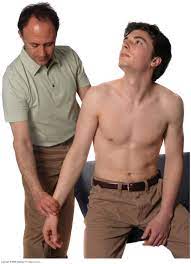
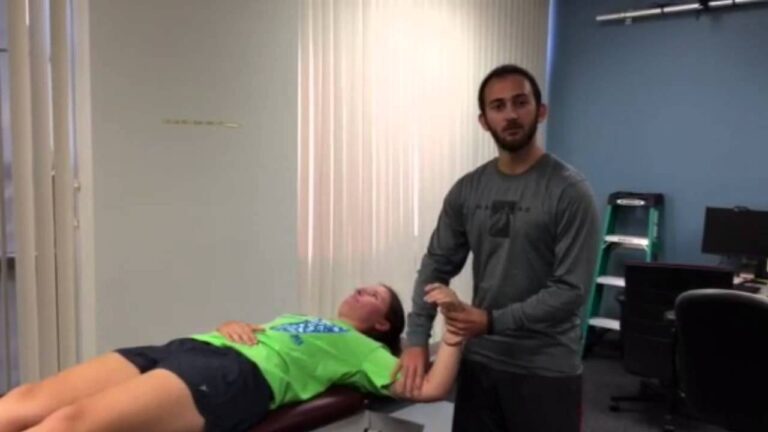
Adson maneuver :
- This Adson maneuver test is mostly one of the most common methods of testing for thoracic outlet syndrome reported in the literature.
- The examiner locates the radial pulse.
- After that, the patient’s head is rotated to face towards the affected shoulder.
- The patient then extends the head while the examiner laterally rotates means external rotation & extended the patient’s shoulder. then instructed
- The patient is to take a deep breath & hold it.
- Result = When the disappearance of the pulse, this situation indicates a positive test.
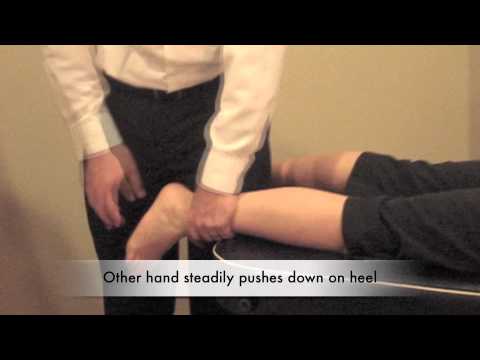
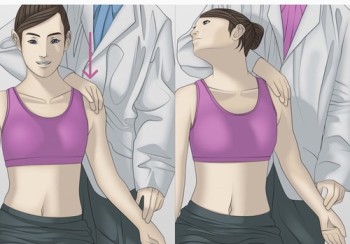
Costoclavicular syndrome test :
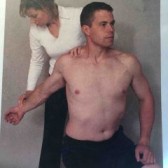
- This test is also known as the military brace test.
- The examiner palpates the radial pulse & then draws the patient’s shoulder down & back.
- Result = A positive test is indicated by an absence of the pulse & implies possible thoracic outlet syndrome means costoclavicular syndrome.
- This costoclavicular syndrome test is particularly effective in patients who have complained of symptoms while wearing a heavy coat or a backpack.
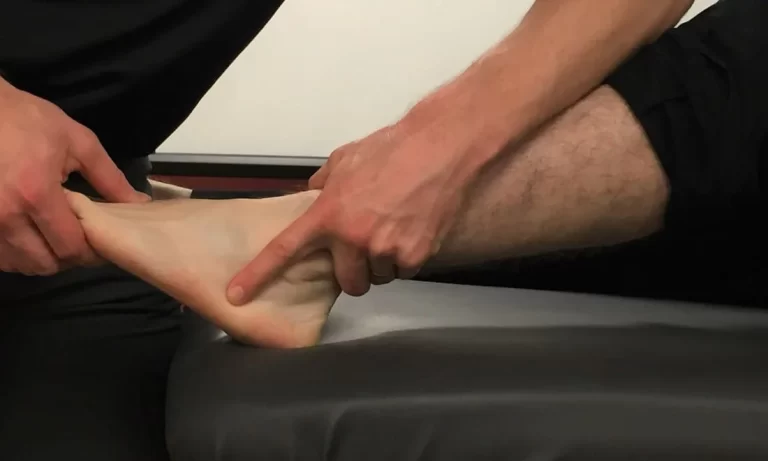
Halstead maneuver :
- The examiner finds the radial pulse & applies downward traction on the tested extremity while the patient’s neck is hyperextended & the head is rotated to the opposite side.
- Result = Absence or disappearance of a pulse indicates a positive test for thoracic outlet syndrome.
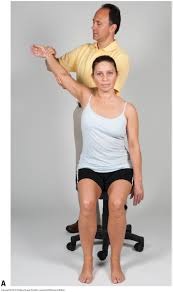
Roos test :
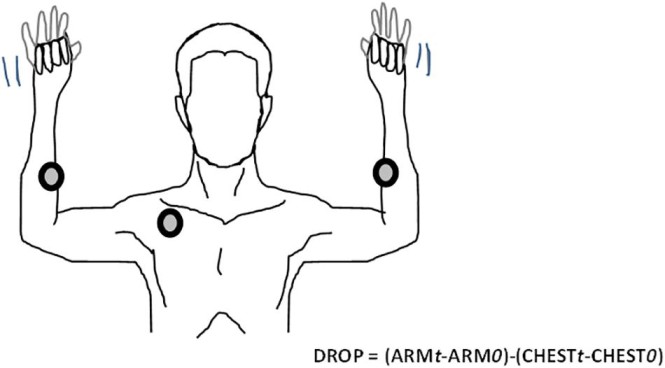
- This Roos test is also known as the elevated arm stress test = EAST
- The patient stands & abducts the arms to 90′, laterally rotates means external rotates the shoulder,&flexs the elbows to 90′ so that the elbows are slightly behind the frontal plane.
- After that the patient opens & closes the hands slowly for 3 minutes.
- Result = If the patient is unable to keep the arms in the starting position for 3 minutes or suffer ischemic pain, heaviness or profound weakness of the arm or numbness & tingling of the hand during the 3 minutes, the test is considered to be positive for thoracic outlet syndrome on the affected side.
- Minor fatigue & distress are considered negative tests.
- The test is sometimes called the positive abduction and external rotation = AER position test & the hands up to test.