Special tests of the neurological dysfunction :
- These special tests are also known as the neurodynamic tests.
- These neurodynamic tests check the mechanical movement of the neurological tissues as well as their sensitivity to mechanical stress /compression.
- Most of the special tests of the neurological dysfunction for neurological involvement are sequential/progressive
- The patient is positioned,& one maneuver is tried, if no symptoms result, a second provocative, enhancing, or sensitizing maneuver is carried out,& so on, while the examiner watches to see if the patient’s symptoms are reproduced.
Name of the special tests of the neurological dysfunction:
- Flip sign
- Gluteal skyline test
- Knee flexion test
- Naffziger test
- Oppenheim test
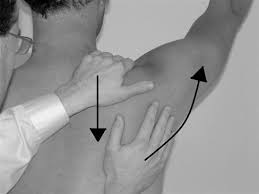
Flip sign:-

- Purpose = This test is used to check the problems in the lower lumbar spine.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient for testis sitting position.
- while the patient is sitting, the examiner extends the patient’s knee & looks for symptoms.
- the patient is then placed supine,& a unilateral straight leg raising test is performed.
- Result = For the sign to be positive, the examiner shoulder suspect problems in the lower lumbar spine.
- This is a combination of the classic lasegue test & the sitting root test.
Gluteal skyline test :-
- Purpose = This test is used to check the damage to the inferior gluteus nerve.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient for the test is the prone position.
- The patient is relaxed in a prone position with the head straight & arms by the sides.
- The examiners stand at the patient’s feet & observe the buttocks from the level of the buttocks.
- If the affected gluteus maximus muscle appears flat , it is indicate the atrophy of the muscle.
- After that instruct the patient for doing the contract the gluteal muscle.
- The affected side may show less contraction, or it may be atonic & remain flat.
- Result = if the occurs, the test is positive & may indicate damage to the inferior gluteal nerve or pressure on the L5, S1, or S2 nerve roots.
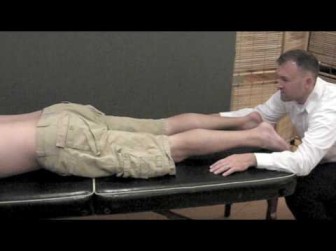
Knee flexion test :-
- Purpose = This test is used to check the compression of the sciatic nerve root.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient for the test is the standing position.
- The patient, who has complained of sciatica ,is in a standing position.
- The examiner instruct the patient for bend forward to touch the toes.
- If the patient bends the knee on the affected side while forward flexing the spine.
- Result = When the test is positive, it is indicate for the compression of the sciatic nerve root.
- Likewise,when the patient is not allowed to bend the knee fully ,spinal flexion is decreased.
Naffziger test :-
- Purpose = this test is used to check the compression of the spinal theca.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient for the test is the supine position.
- The patient lies supine while the examiner gently compresses the jugular veins which lie beside the carotid artery for approximately 10 seconds.
- The patient’s face flushes,& then the patient is asked to cough.
- Result = if coughing causes pain in the low back, the spinal theca is being compressed, leading to an increase in intrathecal pressure.
- the theca is the covering [ pia mater, arachnoid mater,& dura mater ] around the spinal cord.
Oppenheim test :-

- Purpose = This test is used to check the lesion of the upper motor neuron.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient for the test is the supine position.
- The examiner runs a fingernail along the crest of the patient’s tibia.
- Result = a negative Oppenheim test is indicated by no reaction or no pain.
- A positive test is indicated by a positive Babinski sign [ positive pathological reflex ] & suggests an upper motor neuron lesion.

![Oppenheim test purpose = this test is used to check the lesion of the upper motor neuron. technique = starting position of the patient for the test is the supine position. the examiner runs a fingernail along the crest of the patient's tibia. result = a negative Oppenheim test is indicated by no rection or no pain. a positive test is indicated by a positive Babinski sign [ positive pathological reflex ] & suggests an upper motor neuron lesion.](https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/filp-test.jpg)