Upper Limb Tension Tests = ULTT
The Upper Limb Tension Test (ULTT) is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess the tension or irritation of the nerves in the upper limb. It involves a series of movements and positions that place tension on specific nerves, allowing healthcare professionals to evaluate for nerve compression or injury.
The ULTT can help identify the source of symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arm, forearm, or hand. This test is commonly performed in the evaluation of conditions like thoracic outlet syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome, and cervical radiculopathy. It is important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on individual circumstances.
- This test is also known as the Brachial Plexus Tension test/Elvey Test.
- These Upper Limb Tension Tests are designed to put stress on the neurological structures of the upper limb by elongating the test.
- This Upper Limb Tension Test is first described by Elvey & so this test is also known as the Elvey test but this test is most commonly called the ULTT = Upper Limb Tension Tests.
- These ULTT = Upper Limb Tension Tests are equivalent to the straight leg raise test = SLR test designed for the lumbar spine.
What is the purpose of the Upper Limb Tension Tests?
- These Upper Limb Tension Tests are performed to check the compression of the peripheral nerve / as part of the neurodynamic assessment.
- These Upper Limb Tension Tests are performed as a cluster to make a confirmatory diagnosis for the nerve involvement.
- These Upper Limb Tension Tests are both diagnostic & therapeutic tests.
- Once upon a time this test is become for a diagnosis & made the mobilize the entrapped nerve
How do you perform the Upper Limb Tension Tests?
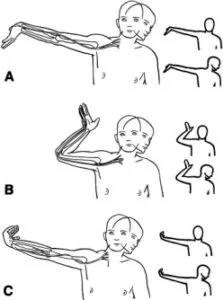
- This test is a tension test designed to put stress on the neurological structure of the upper limb by stretching them, although, in truth, stress is put on all the tissue of the upper limb.
- The neurological tissue is differentiated by what is defined as sensitizing tests.
- Modification of the position of the shoulder, elbow, forearm, wrist & fingers places greater stress on specific nerves.
- Each test begins by testing by good side first & positioning the shoulder, followed by the forearm, wrist, fingers & last, because of its large ROM, the elbow.
- Davis et al.felt the tests should be considered positive only if neurological symptoms were manifested before 60′ of elbow extension when elbow extension was the last movement performed.
- Each phase is added until symptoms are produced.
- To further sensitize the test, side flexion of the cervical spine may be performed.
- Symptoms are more easily aggravated into the upper limb than the lower limb when doing tensions tests & if the neurological signs are worsening or in the acute phase, or if a cauda equine or spinal cord lesions are present, their stress tests are contraindicated.
- When positioning the shoulder, a constant depression force must be applied to the shoulder girdle so that, even with abduction, the shoulder girdle remains depressed.
- If the shoulder is not held depressed the test is less likely to work.
- While the shoulder girdle is depressed, the glenohumeral joint is taken to the appropriate abduction position [ 110 ‘ or 10’, depending on the test ],& the forearm, wrist & fingers are taken to their appropriate end-of-range position; for example, in ULNT2 = Upper Limb Tension Test 2 the wrist is in full extension.
- Elbow extension stresses the ulnar nerve.
- Wrist & finger extension stresses the median & ulnar nerve while releasing stress on the radial nerve.
- If required ULNT2,3 & 4, The glenohumeral joint is appropriately rotated & held.
- The elbow position is often not performed until last because the large elbow ROM is easiest to measure when recording available is taken toward its extreme position, symptoms are usually felt.
- Some of these symptoms are normal & some are pathological.
- If symptoms are minimal or no symptoms appear, the head & cervical spine are taken into contra lame side flexion.
- This final movement is sometimes referred to as a sensitizing test.
- The sensitizing test may be within or near the test limb, or it may be in another quadrant.
- The tests are designed to stress tissues.
- Although they stress the neurological tissue, they also stress some contractile & inert tissues.
- Differentiation among the types of tissues depends on the signs & symptoms presented.
- Finally, although specific ULNT is described, if the patient describes neurological symptoms when doing functional movements, these movements should also be tested by positioning the limb & taking the joints toward their end range.
- Evans described a modification of the ULNT that he called the brachial plexus tension test.
- The sitting patient abducts the arms with the elbow extended, stopping just short of the onset of symptoms.
- The patient laterally rotates the shoulder just short of symptoms & the examiner then holds the position.
- Finally, the patient flexes the elbows so that the hand lies behind the head.
- Reproduction of radicular symptoms with elbow flexion is considered a positive test.
- This test is similar to ULNT4 & stresses primarily the ulnar nerve & the C8 & T1 nerve roots.
- Evans outlined a second similar test.
- The seated patient abducted the arm to 90′ with the fully flexed.
- The arm is extended at the shoulder & then the elbow is extended.
- If radicular pain results, the test is positive.
- The real test is a modification of the ULNT4 done activity.
What is upper limb neurodynamic test: normal & pathological signs & symptoms?
Normal [The negative result of the test ]:
- Deep ache or stretch in cubtial fossa.
- Deep ache or stretch into anterior & radial aspect of forearm & radial aspect of the hand.
- Tingling to the fingers supplied by appropriate never.
- Stretch in the anterior shoulder area.
- Above responses increased with contra lateral cervical side flexion [ 90 % ]
- Above responses decreased with ipsilateral cervical side flexion [ 70 % ]
Pathological [the positive result of the test ]:
- Production of patient’s symptoms
- A sensitizing test in the ipsilateral quadrant alters the symptoms.
- Different symptoms between right & left [ contra lateral quadrant ]
What is the Positive Test result of this test?
- This Upper Limb Tension test is positive if one /more of the following reason occurs:
- Reproduced of the Symptoms.
- The difference in elbow extension movement Side to side is greater than 10 degrees.
- Cervical side bending of the Contralateral side increases the symptoms / ipsilateral to side bending decreases to symptoms.
ULTT1 = Upper Limb Tension Test 1 for Median nerve bias:-
Indications of this test:
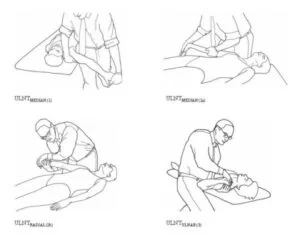
- Radiating the pain in the upper limb
- Tingling/sensations in the first 3 fingers
Movements performed in this test:
- Shoulder joint = Depression, Abduction 110′ or External rotation
- Elbow joint = extension
- Forearm = supination
- Wrist & finger = extension
Structural differentiation of this test:
- If the proximal symptoms are to be differentiated it is relieved to wrist extension
- If the distal symptoms to be differentiated so that do the Contralateral neck flexion
ULTT2A = Upper Limb Tension Test 2A for Median nerve bias:-
Indications of this test:
- Recent shoulder arthroplasty surgery of the shoulder
- Recent Dislocation of the shoulder joint & Instability
Movements performed in this test:
- Shoulder girdle = depression, abduction 100′ & External Rotation
- Elbow joint =extension
- Wrist, finger & thumb = extension
Structural differentiation of this test:
- If the Distal symptoms, it is Remove the small amount of the shoulder depression
- If the Proximal symptoms it is Relieve wrist & finger extension
ULTT2B = Upper Limb Tension Test 2B for Radial nerve bias:-
Indications of this test:
- De Quervain`s disease
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Supinator tunnel syndrome
Movements performed in the test:
- Shoulder girdle = depression, abduction 100′, Internal rotation
- Elbow joint = extension
- Wrist, finger & thumb = flexion
Structural differentiation of this joint:
- If the Proximal symptoms, it is Release to wrist joint flexion
- If the Distal symptoms, it is Release a small amount of the depression
ULTT3 = Upper Limb Tension Test 3 for Ulnar nerve bias:-
Indications of the test:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Pain radiating for to 4th & 5th digits
Movements performed in the test:
- Shoulder girdle = depression, abduction 110′, external rotation
- Forearm = pronation
- Wrist & Finger = extension
- Elbow joint = flexion
Structural Differentiation of the joint:
- If the Distal symptoms it is released to a small amount of the shoulder joint depression
- If the Proximal symptoms it is Released to wrist joint extension movement
What is Evidence of the Upper Limb Tension Test?
- Sensitivity of the Upper Limb Tension Test = 50
- Specificity of the Upper Limb Tension Test = 86
- -LR of the Upper Limb Tension Test =58
- +LR of the Upper Limb Tension Test = 3.5
Reliability of the Upper Limb Tension Test :
- Inter-examiner Kappa of the Upper Limb Tension Test = 76
Summary of the Upper Limb Tension Test :
| ULNT1 Upper Limb Tension Test 1 | ULNT2 Upper Limb Tension Test 2 | ULNT3 Upper Limb Tension Test 3 | ULNT4 Upper Limb Tension Test 4 | |
| Shoulder | Depression ,abduction | Depression,abdution ,hand to ear,lateral rotation | Depression & abducyion, medial rotation | Depression, abdution ,hand to ear, lateral rotation |
| Elbow | Extension | Extension | Extension | Flexion |
| Forearm | Supination | Supination | Pronation | Supination or pronation |
| Wrist | Extension | Extension | Flexion & Ulnar deviation | Extension & radial deviation |
| Fingers & thumb | Extension | Extension | Flexion | Extension |
| Cervical spine | Contralateral side flexion | Contralateral side flexion | Contralateral side flexion | Contralateral side flexion |
| Nerve bias | Median nerve, anterior interosseous nerve, C5, C6, C7 | Median nerve, musculocutaneous nerve, axillary nerve | Radial nerve | Ulnar nerve, C8 & T1 nerve roots |
FAQs
What is the ULTT test?
ULTT full name is Upper Limb Tension Test
Always test the normal side first while performing tests. The median nerve, the anterior interosseous nerve, and the nerve roots of C5 to C7 are all targets of the ULTT1 or ULTTA. Depress the shoulder, abduct the arm to 110 degrees, and bend the elbow 90 degrees to do the test.
What is ULTT1 used for?
The ULTT1 test involves a series of movements and stretches to assess the flexibility and mobility of the median nerve and its associated structures. The test helps clinicians diagnose nerve-related issues, determine the source of pain or discomfort, and develop appropriate treatment plans.
What is a positive tension test?
In the context of tension tests like the Upper Limb Tension Tests (ULTT), a positive test result indicates the presence of symptoms or sensations that suggest nerve irritation or compression.
For example, in ULTT1 (Upper Limb Tension Test 1), which assesses the median nerve, a positive test might involve reproducing symptoms like pain or tingling in the arm, forearm, or hand that correspond to the distribution of the median nerve. This could indicate that there is tension or compression on the median nerve, potentially caused by conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or other nerve-related issues.
Which nerve is tested for upper limb tension test?
The median, ulnar, and radial nerves were tested for tension using the Upper Limb Tension Tests, as well as the Upper Limb Tension Tests combined with contralateral rotation and lateral bend of the cervical spine.




One Comment