Test of the joint instability of the wrist joint:
- These tests are used to check the joint instability of the wrist joint.
- These tests are applied by the therapist when the patient is complain about the wrist joint.
Name of the test of the joint instability of the wrist joint:
- Murphy’s sign
- Piano keys test
- Pivot shift test of the mid carpal joint
- Scaphoid stress test
- Sitting hands test
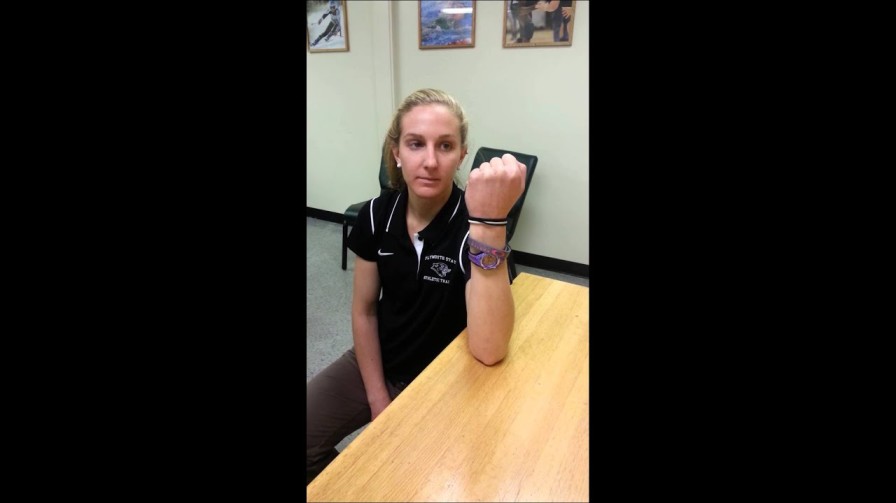
Murphy’s sign:-

- Purpose = This Murphy’s sign is used to check the lunate dislocation.
- Technique = Starting position of the patient for the Murphy’s sign is sitting position.
- Then the examiner asked the patient for doing make a fist.
- If the head of the third metacarpal of the hand is level with the second & fourth metacarpal of the hand.
- Result = This situation of the sign is positive & indicative of a lunate dislocation.
- Normally, the third metacarpal would project beyond the second & fourth metacarpal.
Piano keys test:-
- Purpose = this piano keys test is used to check the instability of the radio carpal joint.
- Technique = In the starting position of the patient is sitting with both arms in pronation.
- The examiner [ therapist ] stabilizes the patient’s arm with the help of one hand so that the examiner’s index finger can push down on the distal ulna.
- The examiner [ therapist ] supports the patient’s hand with the help of the other hand.
- The examiner pushes down on the distal ulna as one would push down on a piano key.
- Result = the results are compared with the non-symptomatic side.
- A positive test is indicated by a difference in mobility & the production of pain/tenderness.
- A positive test indicates instability of the distal radio carpal joint.
Pivot shift test of the mid carpal joint:-
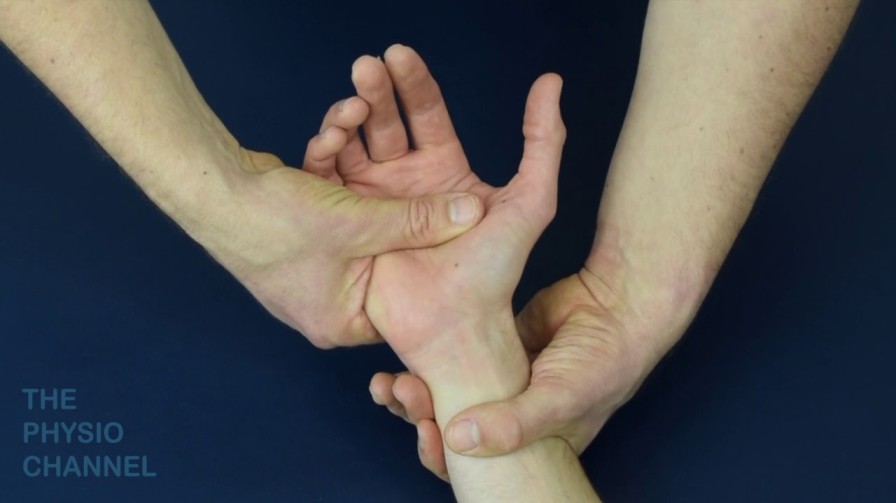
- Purpose = this pivot shift test of the mid carpal joint is used to check the instability of the capitate & injury of the interosseous ligaments / anterior capsule.
- Technique = in the starting position of patient pivot shift test of the mid-carpal joint test is sitting position.
- The patient is seated with the flexed to 90′ & resting on a firm surface & the hand fully supinated.
- The examiner [ therapist ] stabilizes the forearm with the help of one hand & with the help of the other hand takes the patient’s hand into full radial deviation with the wrist in neutral.
- While the examiner [ therapist ] maintains the patient’s hand position, the patient’s hand is taken into full ulnar deviation.
- Result = a positive test results if the capitate shifts away from the lunate, indicating injury to the anterior capsule & interosseous ligaments.
Scaphoid stress test:-
- This scaphoid stress test is the modification of the Watson test; which is done actively by the patient.
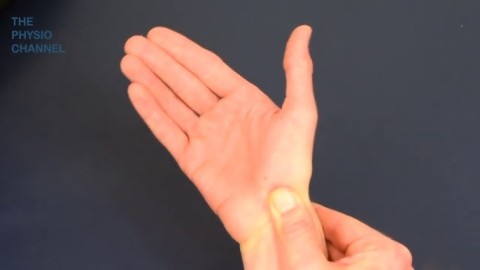
- Purpose = This scaphoid stress test is used to check the scapholunate instability & scaphoid fracture.
- Technique = For the starting position of the patient of scaphoid stress test is sitting position.
- The examiner [ therapist ] holds the patient’s wrist with the help of one hand so that the thumb applies pressure over the distal pole of the scaphoid.
- The patient then attempts to radially deviate the wrist.
- Result = if excessive laxity is present, the scaphoid is forced posteriorly out of the scaphoid fossa of the radius with a resulting clunk & pain indicating a positive test for scapholunate instability /a scaphoid fracture.
- The test done passively by the examiner is called the scaphoid shift test.
Sitting hands test :-
- This test is also known as the sitting hand’s press test.

Purpose = This sitting hands test is used to check the presence of significant wrist synovitis or wrist pathology.
- Technique = The starting position of the patient in the sitting position.
- the patient places both hands on the arms of a stable chair & pushes off, suspending the body while using only the hands for support.
- the test places a great deal of stress [ axial ulnar load ] at the wrist joint.
- This test is too difficult for performance.
- Result = this test is positive for the presence of significant wrist synovitis/ wrist pathology.