Test for the intermittent claudication:
- Intermittent claudication implies arterial insufficiency to the tissue.
- It is most commonly evident when activity occurs because of the increased vascular demand of the tissues.
- There are two types of intermittent claudication – vascular & neurogenic.
- The vascular type is most commonly the result of arteriosclerosis, article embolism, or thrombi – angiitis obliterans & commonly manifests itself with symptoms in the legs.
- The neurogenic type of some times called pseudo claudication/claudaquina syndrome & is commonly associated with spinal stenosis & its effect on circulation to the spinal cord & cauda equina.
- The symptoms, in this case, maybe manifested in the back/sciatic nerve distribution.
Name of the special test of the intermittent claudication
- Bicycle test of van gelderen
- Stoop test
- Treadmill test
Bicycle test of van gelderen:-
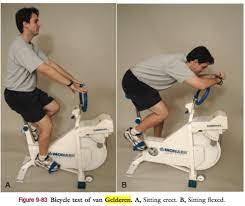
- Purpose = This bicycle test of van gelderen is used to determine whether the patient has neurogenic intermittent claudication.
- Technique = the patient is seated position on an exercise bicycle.
- In the test, the patient starts pedaling on the bicycle while leaning backward to accentuate the lumbar lordosis.
- If the patient feels pain in the buttock & posterior thigh which is occurring, followed by tingling in the affected lower extremity means lower limb so that the first part of the test is positive.
- Then the examiner instructs the patient for doing the is the lean forward while continuing to pedal.
- If the pain subsides over a short period, the second part of the test is positive.
- If the second part of the test is positive.
- If the patient sits upright again, the pain returns in staring position.
- The test determines whether the patient has neurogenic intermittent claudication.
Stoop test:-
- Purpose = this stoop test is used to check the assess neurogenic intermittent claudication to determine whether a relationship exists among neurogenic symptoms, posture,&walking.
- Technique = When the patient with neurogenic intermittent claudication walks briskly, pain ensues in the buttock & lower limb within a distance of 50 m [ 165 feet ].
- Result = To relieve the pain, the patient flexes forward.
- These symptoms may also be relieved when the patient is sitting & forward flexing.
- When the flexion movement does not relieve the symptoms, the test is negative.
- An extension may also be used to bring the symptoms back.
Treadmill test:-
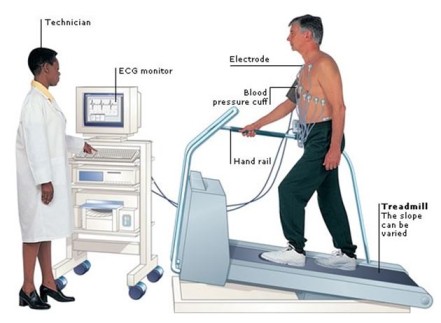
- Purpose = this test is also used to check the determine if the patient has intermittent claudication.
- Technique = two trials are conducted – one at 1.2 mph & one at the patient’s preferred walking speed.
- The patient walks upright means no leaning forward or holding handrails is allowed on the treadmill for 15 minutes or until the onset of severe symptom’s[ symptoms that would make the patient stop walking in usual life situations.
- Tme to first symptoms, total ambulatory time,& precipitating symptoms is recorded.