Thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test:
- This thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test is also known as the thumb ulnar collateral ligament instability test.
- This thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test is applied to the clinic to check the tear of the collateral ligament.
- This thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test is applied by to physiotherapist when the patient is complaining about wrist joint pain.
What is purpose of the thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test?
- This thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test is used to check the tear in the ulnar collateral ligament.
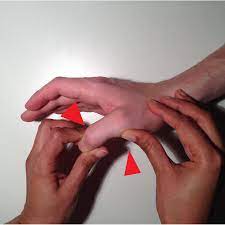
How do you perform the thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test?
- The patient is sitting position for the test.
- While the examiner stabilizes the patient’s hand with the help of one hand.
- While holding the thumb in extension position, the examiner applies valgus stress to the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb, stressing the ulnar collateral ligament & accessory collateral ligament.
- If the valgus movement is greater than 30′ to 35′, it indicates a complete tear of the ulnar collateral & accessory collateral ligaments.
- If the ligament is only partially torn, the laxity would be less than 30′ to 35′.
- In this case, laxity would still be greater than the affected side but not as much as a complete tear.
- To test the collateral ligament in isolation, the carpometacarpal joint is flexed to 30′ & valgus stress is applied.
- This is a test for gamekeepers or skier’s thumbs.
Sharpay’s sign :–

- This test is also known as the triangular fibrocartilage complex load test.
Purpose of the Sharpey’s sign:
- This Sharpey’s sign is used to check the pain around the TFCC.
How do you perform the Sharpey’s sign?
- The examiner holds the patient’s forearm with the help of one hand & the patient’s hand is held with the help of the other hand.
- The examiner [ therapist ] then axially loads & ulnar deviates the wrist while moving it dorsally & palmary or by rotating the forearm
Result of the Sharpey’s sign:
- A positive test is indicated by pain, clicking & crepitus in the area of the TFCC means triangular fibrocartilage complex.