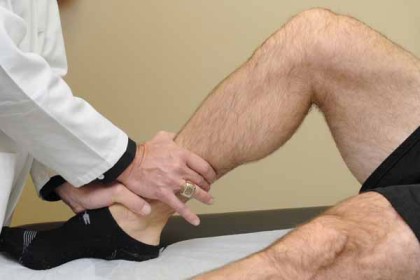
Tinel’s sign at the ankle & windless test
- This test is also known as the percussion test.
- This test is applied to the clinic to check the nerve compression means any nerve problems around the ankle.
- This clinical test is applied by the therapist when the patient is complaining about tingling or paresthesia on the foot.
Purpose of the Tinel’s sign at the ankle test :
- This test is used to check any nerve compression or nerve problems around the ankle joint.
How do you perform the Tinel’s sign at the ankle test?
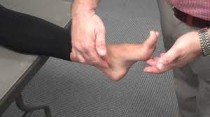
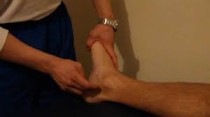
- Tinel’s sign at the ankle is elicited into two places of around the ankle.
- The anterior tibial branch of the deep peroneal nerve is percussed in front of the ankle joint.
- The posterior tibial nerve is percussed behind the medial malleolus which passes to the medial malleolus.
What is the result of the Tinel’s sign at the ankle test?
- In both cases, tingling or paresthesia felt distal is a positive sign.
Windless test
- The Windlass mechanism is a mechanical model that is described by the manner in which the plantar fascia supports the foot during the activities of weight-bearing & provides information regarding the stresses of biomechanical which are placed on the plantar fascia.
- This test achieves a direct stretch on the plantar aponeurosis which is effective in the examining dysfunction of the plantar fascia.
- The test is important in the decision-making process which is involved in the evaluation & treatment of plantar fasciitis.
Purpose of the windless test
- This test is used to check the plantar fasciitis.
How do you perform the windless test?
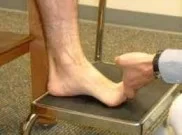
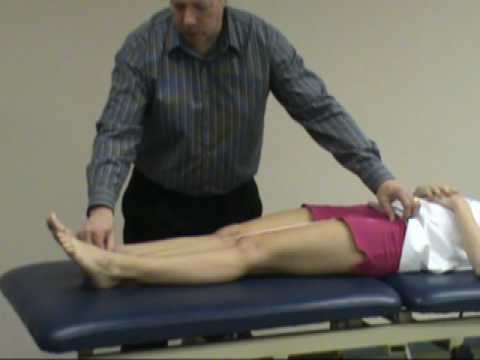
- The patient stands on a stool or chair with the foot positioned so that the metatarsal heads rest on the edge of the stool while the patient maintains weight through the leg.
- The examiner then passively dorsiflexes the big toe.
What is the result of the windless test?
- Pain or increased pain at the insertion of the plantar fascia indicates a positive test for plantar fasciitis.
- Lack of extension may indicate hallux rigidus.