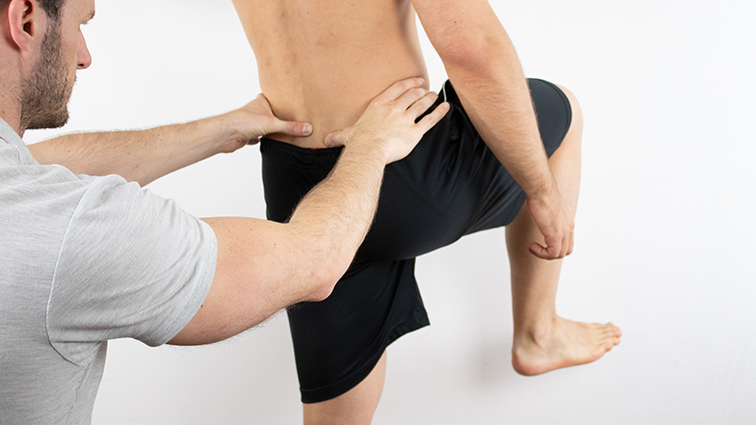
Ulnocarpal Stress Test
What is an Ulnocarpal stress test?
The ulnocarpal stress test, also known as the ulnar carpal stress test, is a medical examination performed to evaluate the integrity and stability of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) in the wrist. The TFCC is a group of ligaments and cartilage that provides support and stability to the wrist joint.
The test is usually conducted by a healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic surgeon or a physical therapist, and is typically indicated when a patient presents with symptoms like wrist pain, limited range of motion, or a history of a traumatic injury to the wrist. The test helps in diagnosing conditions like TFCC tears, ligament injuries, and other wrist joint problems.
How Ulnocarpal stress test is Performed?
Here’s how the ulnocarpal stress test is performed:
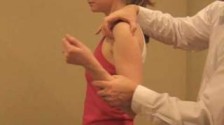
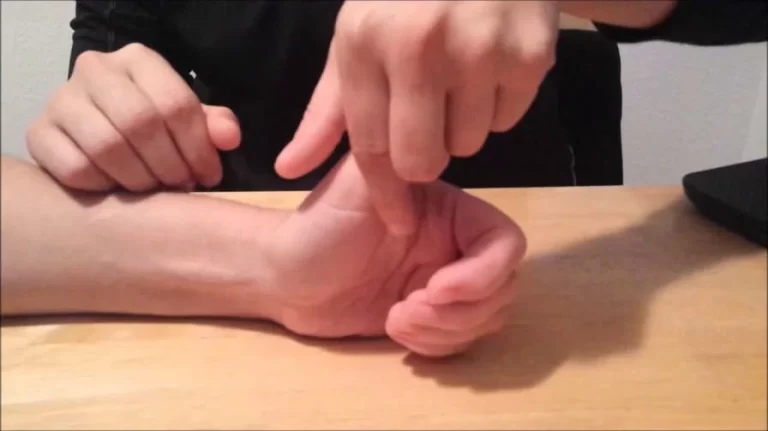
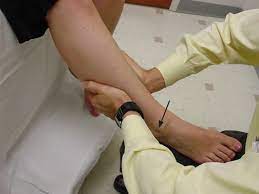
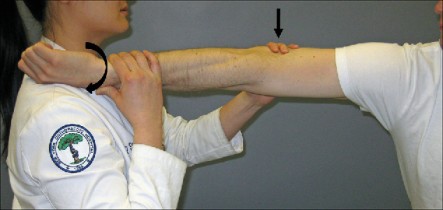
- The patient is relaxed and either seated or lying down.
- The examiner stabilizes the forearm and the wrist of the affected hand with one hand while using the other hand to apply stress to the ulnar side of the wrist.
- Stress is applied in a specific direction that tends to reproduce or exacerbate the patient’s symptoms.
- The examiner may move the wrist through various ranges of motion while applying the stress to assess the stability of the TFCC and the wrist joint.
During the test, if the patient experiences pain or an increase in symptoms, it may suggest a possible TFCC injury or instability. However, it’s important to note that this test is just one part of the overall clinical evaluation, and the healthcare provider will consider the patient’s history, physical examination findings, and potentially other diagnostic tests (such as imaging studies like MRI) to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Video:
It is crucial to seek professional medical advice if you have any wrist pain or concerns, as self-diagnosis and self-treatment can lead to further complications. Only a qualified healthcare provider can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan based on your specific condition.
Purpose of Ulnocarpal stress test
The ulnocarpal stress test serves the following purposes in a medical evaluation:
- Assess TFCC Integrity: The primary purpose of the ulnocarpal stress test is to evaluate the integrity and stability of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) in the wrist. The TFCC is a critical structure that helps stabilize the wrist joint and provides support to the ulnar side of the wrist.
- Diagnosis of TFCC Injuries: The test is commonly used to diagnose TFCC injuries, such as tears, sprains, or degenerative changes. TFCC injuries can result from trauma, overuse, or wear and tear over time.
- Identification of Ligament Instability: The test can also help identify ligament instability in the wrist joint, particularly on the ulnar side. Ligament injuries or laxity in this area can lead to wrist pain and decreased functional capacity.
- Differential Diagnosis: By reproducing or exacerbating the patient’s symptoms, the ulnocarpal stress test helps the healthcare provider differentiate TFCC injuries from other wrist pathologies with similar presentations, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, or other ligament injuries.
- Treatment Planning: The test results, in conjunction with other clinical findings and diagnostic tests, can aid in developing an appropriate treatment plan. Depending on the severity and nature of the TFCC injury, treatment options may include conservative measures (rest, physical therapy, splinting), medication, or even surgical intervention if conservative treatments are not effective.
- Follow-up Evaluation: In cases where the patient has already been diagnosed with a TFCC injury, the ulnocarpal stress test can be used to monitor the progress of healing and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment approach.
Conclusion
Overall, the ulnocarpal stress test is an important tool in the evaluation of wrist injuries and wrist pain, particularly when there is suspicion of TFCC involvement. However, it is essential to remember that the test is just one component of a comprehensive clinical assessment. Proper diagnosis and treatment planning requires a combination of history-taking, physical examination, imaging studies (e.g., MRI), and the expertise of a qualified healthcare professional.
FAQs
What is the special test for ulnar wrist pain?
A clinical test called the ulnar fovea sign is used to identify the origin of wrist pain on the ulnar side. A positive ulnar fovea sign test indicates damage to the ulnotriquetral ligament and foveal rupture of the distal radioulnar ligaments.
What is Ulnocarpal syndrome?
Ulnocarpal syndrome: Ulnar-sided wrist pain is frequently brought on by ulnar impaction syndrome, also known as ulnocarpal abutment syndrome. The ulnar head rubs against the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) and ulnar-sided carpals in this degenerative disease.
What is the function of Ulnocarpal joint?
In order for the hand and wrist to function properly, the ulnocarpal joint is crucial. It contributes to both carpal kinematics and the rotation of the forearm.
Where is the Ulnocarpal?
Ulnocarpal joint: One of the forearm bones, the ulna, meets the lunate and triquetrum wrist bones at this joint. When you sprain your wrist, you frequently hurt this joint.