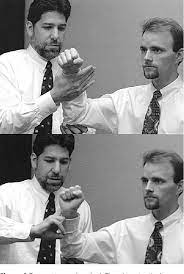
Zaslav test for to shoulder joint :
- It is also known as to internal means medial rotation resistance strength test [ IRRST].
- This test is used by to therapist of doctor for to check the impingement of shoulder.
- This test is follow up to Neer test .
- This test is mostly used to for the check anterior shoulder impingement.
- This impingement is give to compress to anterior ascept of to knee .
What is Purpose of to Zaslav test ?
- This Zaslav test is used to identify of to subacromial impingement syndrome.
- It is used to check the impingement of to shoulder joint .
- Tt is also used to check the differentiate between an outlet means subacromial impingement & an intra-articular means non outlet problem when to examiner is found to Neer test is to positive.
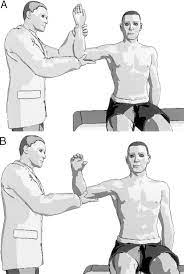
How to perform of to Zaslav test ?
- Starting position for to test is standing position .
- Into this position with to arm abducted to 90 ‘ & do the laterally rotated means external rotated of shoulder joint up to 80 ‘ – 85 ‘.
- After that examiner is applies to isometric resistance into lateral rotation followed by isometric resistance into medial rotation means internal rotation of to shoulder .
What is result of to Zaslav test ?
- This test is consider to positive in a patient who has good strength in lateral rotation means external rotation but not medial rotation means internal rotation so that it is indicate to internal impingement .
- If to patient exhibits more weakness on lateral rotation it is indicate to classic external anterior impingement .
Some other thing about to Zaslav test ?
- It is check to anterior impingement of to shoulder regardless cause of to impingement is rotator cuff pathology , scapular or humeral instability , labral pathology .
- Because of this causes structures being compressed into anterior aspect of to humerus between to head of to humerus & to corocoid process under to acromion process .
- Probability of this test is good for to check the impingement of to shoulder .
- But it is not best for to check the full thickness of rotator cuff tears .