Thessaly Test
What is a Thessaly test?
The Thessaly test is a valuable clinical screening tool used in the field of orthopedics to assess for meniscal tears or lesions in the knee joint. Meniscal tears are common knee injuries that can cause significant discomfort and functional impairment for affected individuals. Patients with suspected meniscal tears often report symptoms such as medial or lateral joint-line discomfort, as well as a sense of locking or catching in the knee during certain movements.
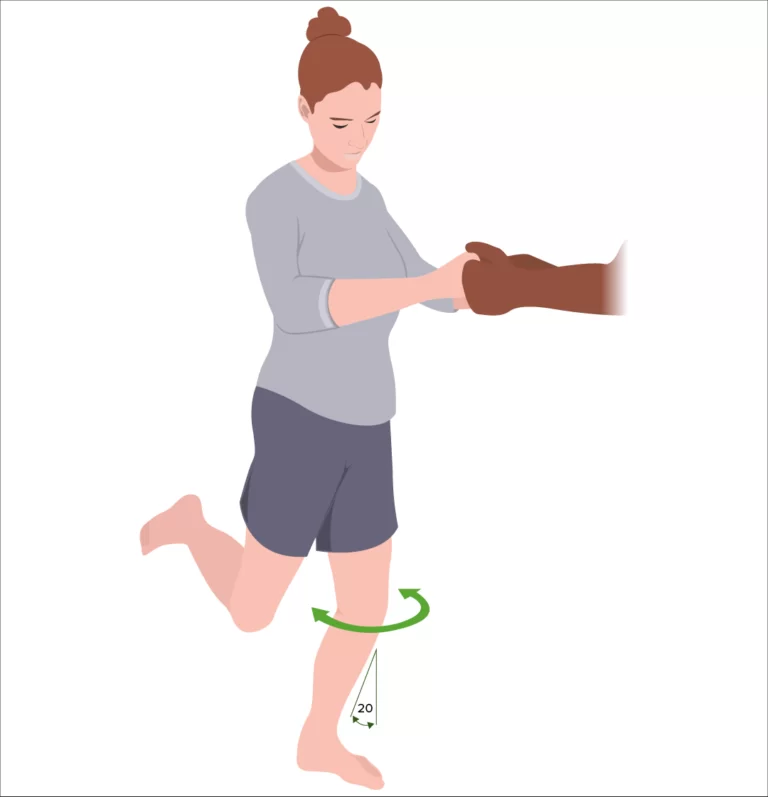
The Thessaly test aims to dynamically reproduce joint loading in the knee to elicit symptoms that patients have described. By carefully observing the patient’s response to specific rotational movements while standing on one leg with the knee slightly flexed, healthcare professionals can gather important diagnostic information. The idea behind this test is that a meniscal tear in the knee will result in symptoms that are similar to those that the patient has described.
Purpose
Examination Test for Meniscal tears and lesions
Patients with suspected meniscal tears complain of pain along the medial or lateral joint lines as well as possible locking or catching. The theory behind the Thessaly test is that a knee with a meniscal tear will elicit the same symptoms the patient observed. The test is a dynamic recreation of joint stress in the knee.
Technique
The patient is supported by the examiner’s outstretched hands as they stand flat-footed on one leg. The patient next flexes the knee to a 5° flexion while performing three medial and lateral rotations of the femur on the tibia. In order to instruct the patient on how to maintain the knee in the flexed position, the unaffected limb is tested first. Next, the test is performed with 20° of flexion. If the patient complains of medial or lateral joint line soreness or a sensation of locking or catching in the knee, the test is considered positive for a meniscus tear.
Video of Thessaly Test:
Evidence
The following statistics for his test were discovered by Karachalios in his initial study from 2005:
Thessaly Test at 5°
| Injury | Sensitivity | Specificity | +LR | -LR |
| Medial Meniscus Injury | 0.66 | 0.96 | 16.5 | 0.35 |
| Lateral Meniscus Injury | 0.81 | 0.91 | 9 | 0.21 |
| Combined Injury of ACL and Meniscus | 0.65 | 0.83 |
Thessaly Test at 20°
| Injury | Sensitivity | Specificity | +LR | -LR |
| Medial Meniscus Injury | 0.89 | 0.97 | 29.67 | 0.11 |
| Lateral Meniscus Injury | 0.92 | 0.96 | 23 | .21 |
| ACL with Meniscus Injury | 0.80 | 0.91 |
The Thessaly test was proven to be no better than other tests like the McMurray test and Apley’s Test in more recent research from 2015. A 2016 research revealed the Thessaly test to be reliable when compared to McMurray, medial joint line pain, and lateral joint line tenderness.
The Thessaly test demonstrated a reasonable level of inter-examiner reliability in a Snoeker et al. research from 2015, with a kappa of 0.54.
Does the Thessaly test have any risks?
Thessaly tests have no risks associated with them.
During the test, you could have some little discomfort or soreness, but even if your meniscus is torn, you shouldn’t experience severe discomfort.
According to certain research, the Thessaly test is not perfect, even if it is better than other comparable tests at determining whether or not your meniscus is torn. To diagnose your injury, your physician will typically go beyond this initial stage. You’ll likely want at least one imaging test after your Thessaly test since they will provide a more definite conclusion.
Thessaly test vs McMurray test
Physical examination tests called the Thessaly test and the McMurray test can both aid your doctor in determining whether you have torn meniscus in your knee. Which exact motions you make make a difference.
You will turn side to side while standing on one leg during a Thessaly test as your physician supports your arms.
If a McMurray test is necessary, you will lie on your back while the medical professional bends and moves your knee.
Your doctor feels and listens for signs of a torn meniscus in your knee during both examinations. Tell them right away if you have any pain or discomfort.
Understanding its role as a part of the comprehensive knee examination process can aid healthcare providers in making accurate diagnoses and developing appropriate treatment plans for patients with knee complaints. However, it is crucial to emphasize that the Thessaly test is not a stand-alone diagnostic tool; it should be used in conjunction with other clinical findings and imaging studies to ensure a comprehensive evaluation.
Summary
The Thessaly test is a clinical screening tool used in orthopedics to assess for meniscal tears or lesions in the knee joint. Patients with suspected meniscal tears often report symptoms such as joint-line discomfort, locking, or catching in the knee. The test involves dynamic movements, where the patient stands on one leg with the knee slightly flexed and rotates the body and knee internally and externally three times.
The purpose of the Thessaly test is to reproduce the symptoms reported by the patient during specific rotational movements, helping healthcare professionals identify possible meniscal tears. It serves as a valuable part of the comprehensive knee examination process, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning for knee injuries. However, it should be used in conjunction with other clinical findings and imaging studies to ensure an accurate evaluation.
As with any medical test, the Thessaly test should be performed by trained healthcare professionals familiar with its administration and interpretation. For individuals experiencing knee problems or suspecting a knee injury, it is essential to seek consultation from qualified healthcare providers for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management.
FAQs
What does a positive Thessaly test mean?
During Thessaly test, If the patient complains of medial or lateral joint line soreness or a sensation of locking or catching in the knee, the test is considered positive for a meniscus tear.
What is the difference between McMurray and Thessaly test?
Physical examination tests called the Thessaly test and the McMurray test can both aid your doctor in determining whether you have torn meniscus in your knee. Which exact motions you make make a difference.
You will turn side to side while standing on one leg during a Thessaly test as your physician supports your arms.
If a McMurray test is necessary, you will lie on your back while the medical professional bends and moves your knee.
Your doctor feels and listens for signs of a torn meniscus in your knee during both examinations. Tell them right away if you have any pain or discomfort.
How accurate is Thessaly test?
When the Thessaly test was taken into account alone in this investigation, the total accuracy was 62%, and when both the Thessaly and McMurray tests were positive, it was 54%.
What is the Best test for meniscus tear?
For the initial investigation of potential meniscal tears, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the Best option and preferred method.