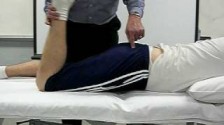
Kim test of shoulder
- This test is also known as the Biceps load test -I.
- This test is applied by to doctor or therapist to check the labrum tear.
- This test is applied in the clinic when a patient is doing complaining about shoulder pain & not present in any bone related pathology.
- This SLAP lesion is most common in throwing athletes where the labrum plays a key role in glenohumeral stability.
- Into young, the tensile strength of the labrum is less than the capsule so that gives anterior stress for more prone to injury.
- SLAP lesions are classic examples of the circle concept of instability.
What is the Purpose of this Kim test?
- It is used for Detection of the posteroinferior labral lesion.
- It is also used to check the torn or tear of the posteroinferior labrum.
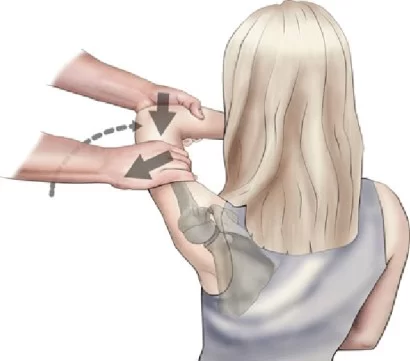
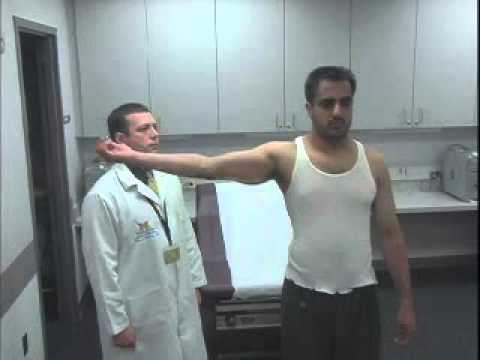
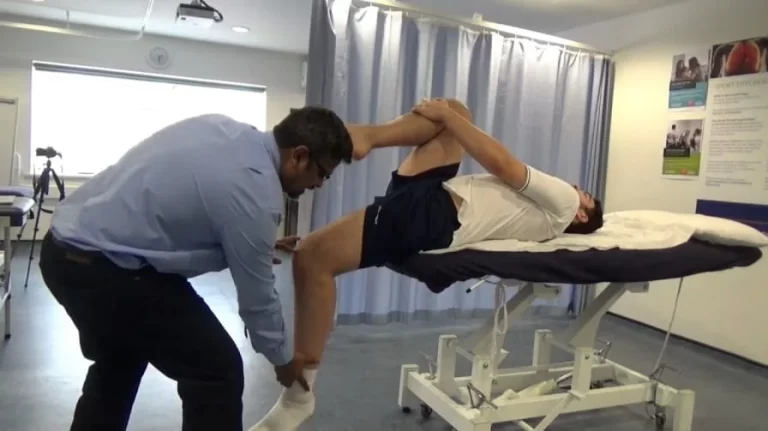
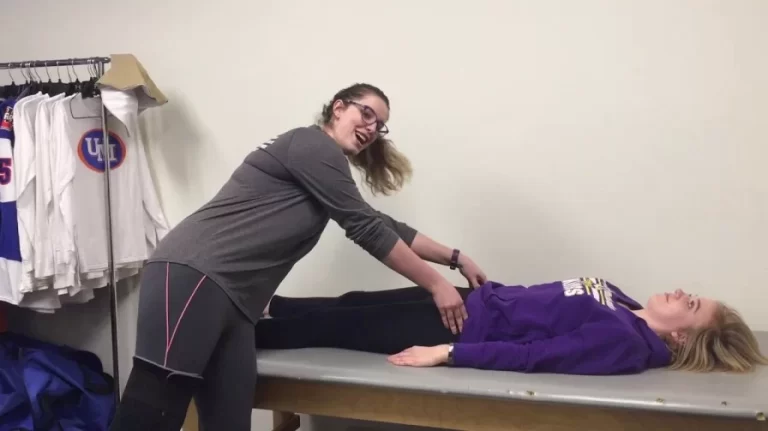
What is the Technique of this Kim test performance?
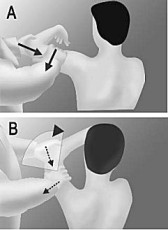
- The starting position of the patient for the test is sitting.
- The patient sits with the back supported.
- The arm is abducted to 90′ with the elbow supported in 90′ flexion.
- The examiner’s hand, while supporting the elbow & forearm, applies an axial compression force to the glenoid through the humerus.
- While maintaining the axial compression force, the arm is elevated diagonally upward using the same hand while the other hand applies a downward & backward force to the proximal arm.
What is the result of this Kim test?
- Sudden onset of posterior shoulder pain &click indicates a positive test for a posteroinferior labral lesions.
What is Evidence of this Kim test?
- Sensitivity of Kim test = 80%,
- Specificity of Kim test = 94%.
- Reliability of Kim test =0.91
- This Kim test is more sensitive for detecting predominantly inferior labral lesions, whereas the jerk test is more sensitive for detecting a predominantly posterior labral lesion.
- This sensitivity of detecting posteroinferior labral lesion is increased to 97% when the 2 tests are applied combined.