Special test for the tendon & muscle of the wrist joint
- These tests are applied to check the tendon & muscle of the wrist joint.
- These clinical tests are applied by to therapist [ examiner ] when the patient complies with wrist joint pain.
- These tests are applied to examine part of the assessment of the wrist joint.
Name of the Special test for the tendon & muscle of the wrist joint.
- Boyes test
- Bunnel – littler test
- Linburg’s sign
- Test for extensor hood rupture
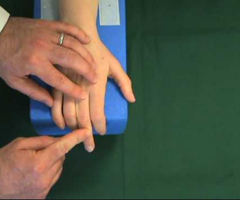
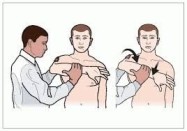
Boyes test:
- Purpose = This boyes test is used to check the distal interphalangeal joint.
- This test also tests the central slip of the extensor hood.
- Technique = the patient is in a sitting position for the test.
- The examiner [ therapist ] holds the fingers to be an examiner in slight extension at the proximal interphalangeal joint.
- Then the examiner instructs the patient for doing to flex the distal interphalangeal joint.
- Result = if the patient is unable or has difficulty flexing the distal interphalangeal joint, it is considered a positive test.
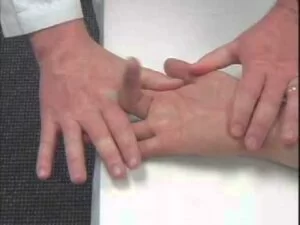
Bunnel – littler test:
- This bunnel – littler test checks the structures around the metacarpophalangeal joint.
- Purpose = This bunnel – littler test is used to check the tightness of the intrinsic muscle or contracture of the joint capsule.
- Technique = The patient is in a sitting position for the test.
- The metacarpophalangeal joint is held slightly extended while the examine [ therapist ] moves the proximal interphalangeal joint into flexion, if possible.
- Result = if the test is positive which is indicated by the inability to flex the proximal interphalangeal joint, there is a tight intrinsic muscle or contracture of the joint capsule.
- If the metacarpophalangeal joints are slightly flexed, the proximal interphalangeal joints are flexed fully if the intrinsic muscles are tight, but it does not flex fully if the capsule is tight.
- The patient remains passive during the test.
- This test is also known as the intrinsic – plus test.
linburg’s sign:

- Purpose = This linburg’s sign test is used to check the paratenonitis at the interconnection.
- Technique = The patient is in a sitting position for the test.
- The patient flexes the thumb maximally onto the hypothenar eminence & actively extended the index finger as far as possible.
- If limited index finger paratenonitis at the interconnection between flexor policis longus & flexor indices [ an anomalous tendon condition seen in 10 % to 15 % of hands.
Test for extensor hood rupture:

- Purpose = This test for extensor hood rupture is used to check the torn central extensor hood of the wrist joint.
- Technique = The patient is in a sitting position for the test.
- The finger to be examined is flexed to 90′ at the proximal interphalangeal joint over the edge of a table.
- The finger of therapist is held in position by the examiner.
- The patient is asked to carefully extend the proximal interphalangeal joint while the examiner [ therapist ] palpates the middle phalanx.
- Result = a positive test for a torn central extensor hood is the examiner’s feeling little pressure from the middle phalanx while the distal interphalangeal joint is extending.