Special test for the SLAP lesions
- SLAP lesions mean superior labrum anterior-posterior.
- This lesion is most common in throwing athletes where the labrum plays a key role in glenohumeral stability.
- Into young, the tensile strength of the labrum is less than the capsule so that gives anterior stress for more prone to injury.
- SLAP lesions are classic examples of the circle concept of instability.
Name of special test of SLAP lesions :
- There are three special tests for the SLAP lesions :
- Biceps tension test
- Clunk test
- Compression rotation test
Purpose of this three-test:
- This test is used to check the presence of SLAP lesions = biceps tension test .
- This test is used to check the labrum tear of the shoulder = clunk test
- This test is used to check the torn of the labrum of shoulder = compression rotation test
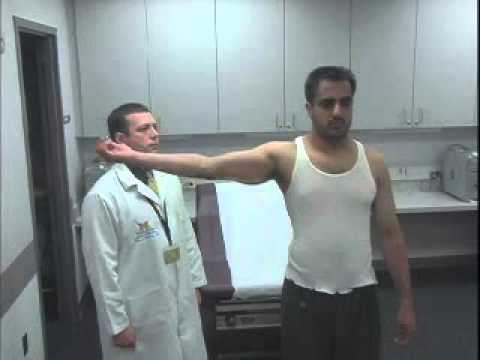
Biceps tension test
Technique of performance :

- Starting position of the test for the patient is the standing position.
- Into standing position do the arm abduction & laterally rotation means external rotation of the arm at 90′ with the elbow extended & forearm supinated.
- Then the examiner is applying to eccentric adduction force to the arm.
- A reproduction of the patient’s symptoms is a positive test.
- The examiner should also do a speed test to rule out biceps pathology.
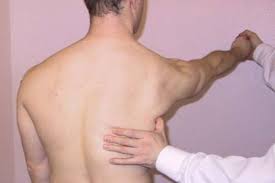
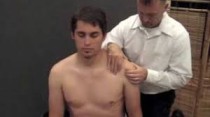
Clunk test
Technique of performance :

- Starting position of the test for the patient is the supine position.
- The examiner’s one hand is placed on the shoulder posterior aspect which is over the humeral head.
- Another hand of the examiner holds the humerus which is above the elbow.
- The examiner is fully abducts the arm over the patient’s head.
- Then the examiner pushes anteriorly of the humeral head with the help of a hand mostly a fist is used to apply anterior pressure.
- While the other hand rotates the humerus into lateral rotation means external rotation.
- A clunk or grinding sound indicates both a positive test & a tear of the labrum.
- Cause of this test is maybe apprehension if the anterior instability is present.
- Walse indicated that if the examiner follows these maneuvers with horizontal adduction that relocates the humerus.
- Patient or therapist is also hearing a clunk/a click, indicating a tear of the labrum.
- The examiner may also position the arm in different amounts of abduction and vertically circle the shoulder & perform the test.
- This will give to stress different parts of the labrum.
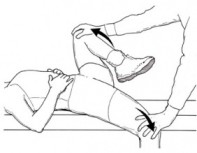
Compression rotation test:
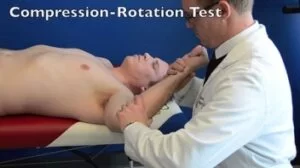
- Starting position of the test for the patient is the supine position.
- The examiner standing beside the test shoulder.
- The examiner passively abducts the shoulder to between 20′ &90′ with the patient’s elbow at 90′.
- The examiner applies an axial compression force through the long axis of the humerus means pushing up through the elbow.
- While passively rotating the humerus back & forth means small & large circles to try to trap the labrum within the joint.
- If pain/clicking & a catching sensation is elicited, this test is considered positive for a torn labrum.