Intersection syndrome: cause, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
What is Intersection syndrome?
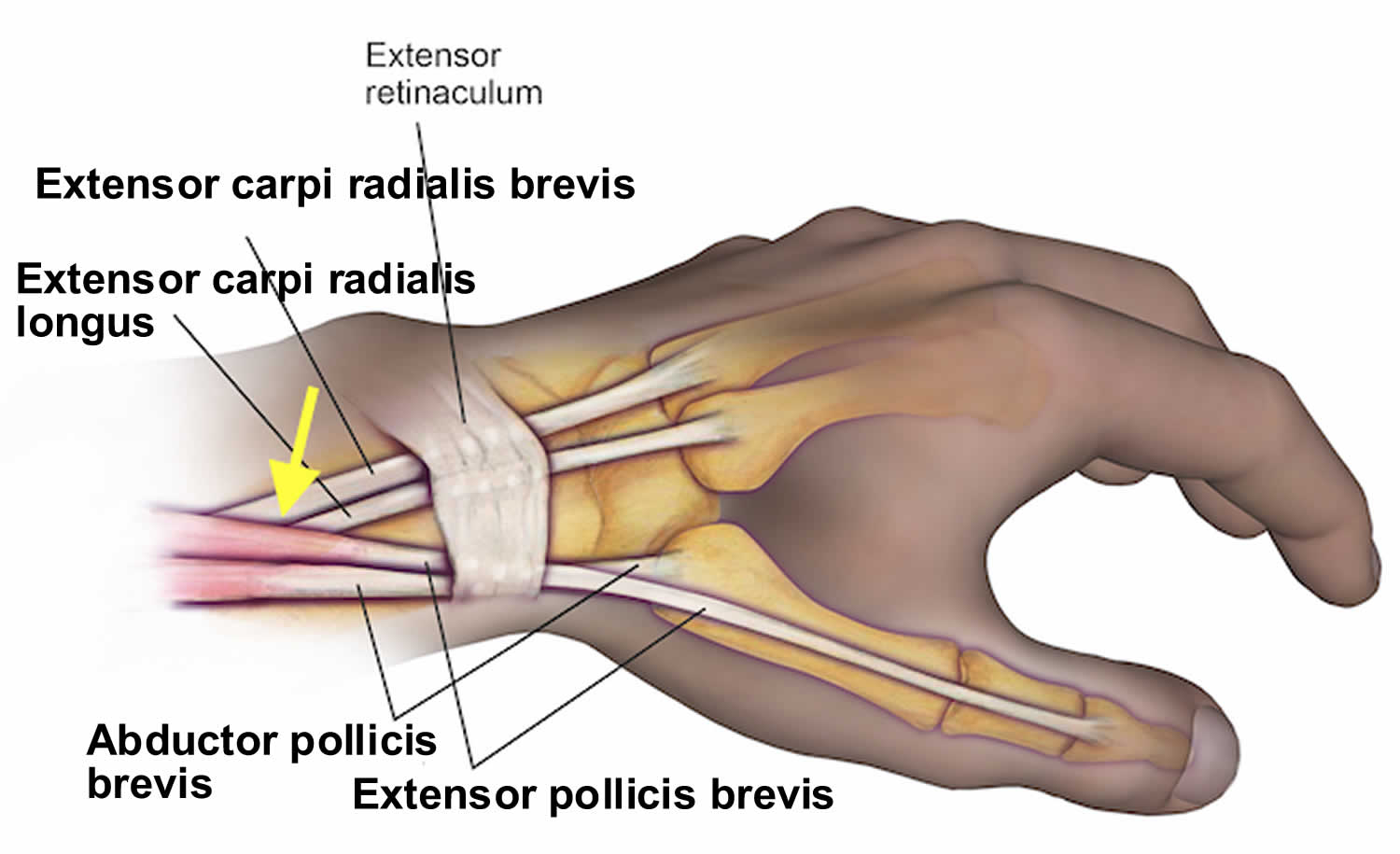
Intersection syndrome is also called tenosynovitis of the radial wrist extensors. It is a noninfectious inflammatory process of the second extensor compartment tendons of the forearm. this condition affects the first and second posterior compartments of the wrist extensors.
This condition is thought to occur as a result of constant friction at the junction in which the tendons of the first posterior compartment cross over the second, creating tenosynovitis. This is typically noted as pain just proximal and distal to the radial styloid, or also noted anatomically by 4 cm to 6 cm proximal to Lister’s tubercle. the problem is usually due to an injury and overuse.
The first posterior compartment of the wrist is comprised of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis Brevis. These tendons have a unique anatomical pathway proximally in which they cross over the second posterior compartment tendons just proximal to the extensor retinaculum and radial styloid.
The second posterior compartment of the wrist is comprised of the extensor carpi radialis brevis and extensor carpi radialis longus.
Which Muscles are involved in the intersection syndrome?
APL(Abductor pollicis longus)
- Origin: Posterior surface of the proximal half of the radius and ulna, interosseus membrane
- Insertion:Base of first metacarpal bone(trapezium bone)
- Action:Radiocarpal joint: Hand extension;
- Carpometacarpal(CMC) joint of the thumb: Thumb abduction and extension
- Innervation: Posterior interosseous nerve (C7andC8)
- Blood supply: Anterior interosseous artery and posterior interosseous artery
EPB(extensor pollicis brevis)
- Origin: From the Posterior surface of the distal third of the radius and the interosseus membrane
- Insertion: Posterior(Dorsal surface) aspect of the base of proximal phalanx of thumb
- Action:Carpometacarpal(CMC) and metacarpophalangeal(MCP) joint 1: Thumb extension
- Innervation: Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) of the radial nerve
- Blood supply: Posterior interosseous artery and anterior interosseous artery are the supply of this muscle.
ECRB(extensor carpi radialis brevis)
- Origin: From the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus (extensor tendon)
- Insertion: Posterior aspect of the base of the third metacarpal bone
- Action: Wrist joints: Hand extension, hand abduction, radial deviation of the wrist
- Innervation: Radial nerve (C5andC6)
- Blood supply: radial artery and deep brachial artery
ECRL(extensor carpi radialis longus)
- Origin: From the Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus and lateral intermuscular septum of the arm
- Insertion: Posterior aspect of the base of the second metacarpal bone
- Actions: Wrist joints: Hand extension, hand abduction, radial deviation of the wrist
- Innervation: Radial nerve (C5toC8)
- Blood supply: Radial recurrent artery and radial artery
What is the Cause of Intersection syndrome?
It is typically caused by repetitive extension and flexion exercises or activities or repetitive movements that stress the wrist extensor tendons.
it is commonly seen in sports activities such as horseback riding, and racquet sports.
it is frequent cellphone use such as texting.
What are the Symptoms of Intersection syndrome?
- The pain of the wrist tendons
- tenderness of the wrist tendons
- Swelling of the tendons
- A grinding sensation (crepitus)with the movement of the fingers
- Tenderness
- Irritation
- pain, swelling, and crepitus worse during flexion, extension, and twisting movements of the wrist
- Grinding sensation when moving the fingers
- Pain that radiates to the thumb and forearm
How is Intersection Syndrome Diagnosed?
- MRI(magnetic resonance imaging)
- Ultrasonography
- Clinical diagnosis is more important made with a careful history and physical examination
Differential diagnosis
- Boutonniere defect
- Drummer’s wrist
- Dupuytren contracture
- Extensor digitorum tenosynovitis
- Jammed finger
- Jersey’s finger
- Mallet finger
- Metacarpophalangeal ligament rupture
- Ring avulsion injury
- Scaphoid fracture
- Muscle strain
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
- Wartenberg’s syndrome
Treatment
Medical treatment
- Conservative treatment of this syndrome includes immobile, activity modification, and pharmacological intervention. Treatment is conservative management with rest.
- The radial wrist extensors can be immobile with a cock-up wrist splint.
- Anti-inflammatory medications may be beneficial for acute injury and pain relief.
- Common medications are ibuprofen, naproxen, meloxicam or diclofenac. these drugs are may be utilized for pain relief.
- injection into 2nd posterior compartment extensor carpi radialis brevis and extensor carpi radialis longus.Steroid injection has shown significant improvement and is a known next best step if little or improvement has not been made with other conservative treatments.
- Surgical debridement and release
- rarely indicated in recalcitrant cases
- release of the 2nd posterior compartment approximately 6 cm proximal to radial styloid.
- Activity modification is also important.
- Surgery is only required in case of remaining symptoms after an already adequate course of conservative treatment.
Physiotherapy Treatment:

Treatment is with bracing, rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications.
The RICE method includes:-
- Rest:-Take a break from your activity of choice for one week. In addition, don’t carry any items unnecessarily.
- Ice:-Ice pack to the affected wrist for 10-15 minutes at a time.it can help to relieve the symptoms of inflammation.
- Compression:-Wearing a compression bandage improves blood flow and provides support to the affected part.
- Elevation:-Keep your wrist at heart level and elevate your hand on pillows. This will help to reduce swelling.
- ultrasound and interferential therapy (IFT)
- these two modalities help to decrease the pain and inflammation post-surgery
- Deep therapy: helpful for reduction of pain
- TENS (Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) used the reduce pain and reduce inflammation.
- It is usually managed conservatively.
- first of this management includes modification of work and sports activities which will help to reduce stress on the wrist
- Therapeutic exercises
- Joint and scar mobilization
- soft tissue massage
- massage therapy is used for improving circulation through squeezing technique, picking up, shaking, wringing, rolling, MFR (myofascial release technique), kneading
- stretching exercise
- taping
- active assisted exercise
- finger movement exercise
- mobilize the wrist if the range of motion is slow
- strengthening exercises include gentle resistance and gripping, rubber band strengthened, ball squeeze
- Patient education concerning activity modification.
- local ice-pack placement can also reduce pain.
- A temporary splint for protection and comfort at night may also be helpful (a neutral position with a splint), an activity change and anti-inflammatory medication are normally appropriate to control the symptoms.
- Conservative treatment includes patient education, rest, analgesia, reduction of load, and immobilization of the affected wrist joint.
- A Splint is used to rest the thumb and the wrist.
- Thumb Spica brace
How to prevent Intersection Syndrome?
- avoid repetitive wrist movements
- avoid painful activity
- avoid weight lifting
- avoid heavy grasping, wringing, or turning and twisting movements of the wrist
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended or purposeful for your general informational purposes only and does not address particular circumstances. it is not a substitute for professional advice(or guidance) or help( or assistance) and should not be relied on to make decisions of any kind. A few or any actions you take upon the information presented in this article are strictly at your own risk and responsibility.


One Comment