Lachman test of the Knee Joint :
What is the Lachman Test?
The Lachman test is a physical examination test used by Doctors for the examination of knee joint mainly integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament if doctors have suspected that ACL injury. The test is mainly used to assess the anterior translation of the tibia in relation to the femur and is counted as a variation of the anterior drawer test.
- This test is used into the physical examination which is apply in the maneuver by the therapist.
- It is assess to the integrity of to the anterior cruciate ligament means [ ACL ] in to the suspected of to the anterior cruciate ligament means ACL injury.
- The test is also used to for the evaluate of to the anterior translation of to the tibia into the relation of to the femur
- This is also considered with the variant of to the anterior drawer test.
Purpose of the test :
- This test is do the passive accessory movement of the knee .
- It is performed by to the identify of the integrity of to the anterior cruciate ligament means ACL .
- This test is designed for to the assess of the single & sagittal plane instability.
- This test is also check the one -plane anterior instability .
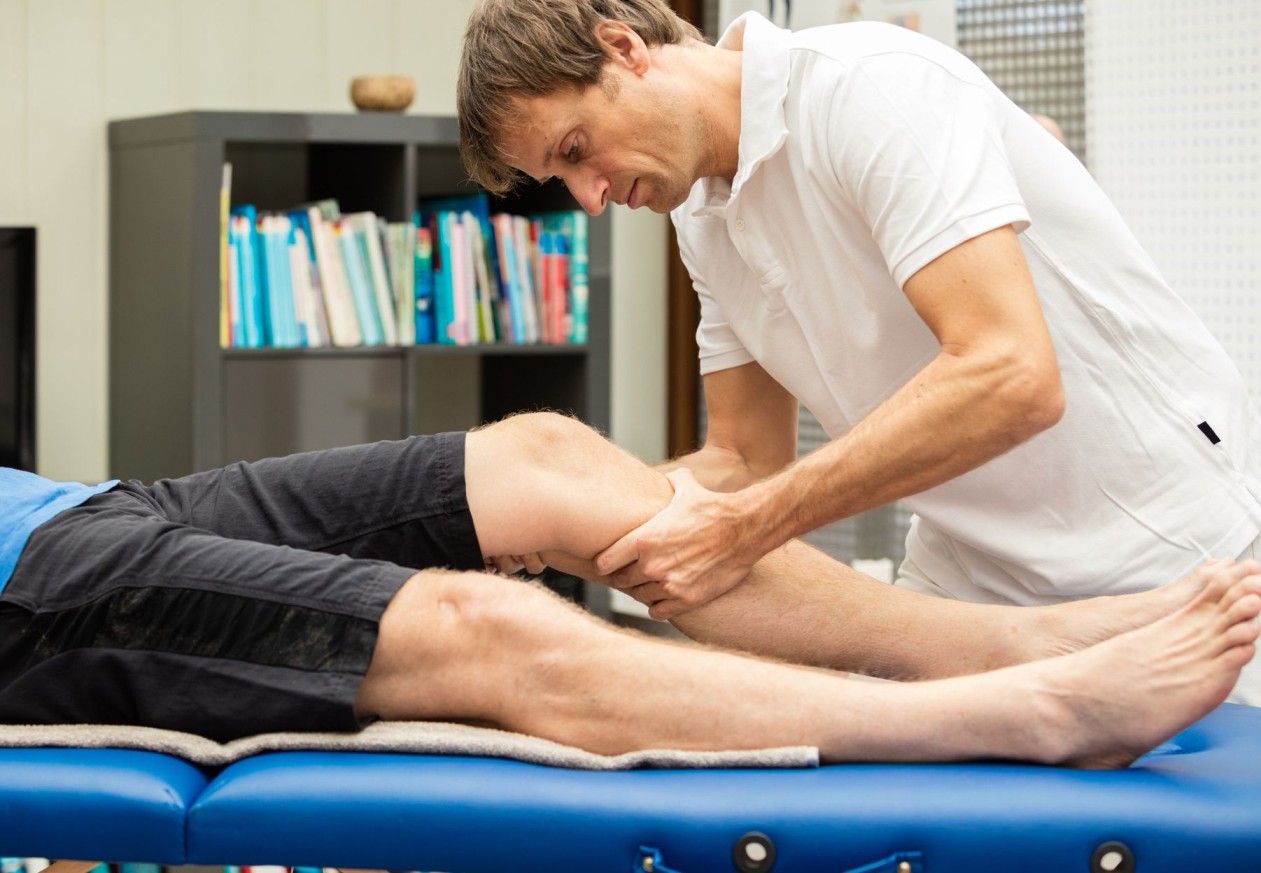
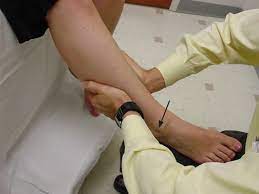
How do you perform of this test ?
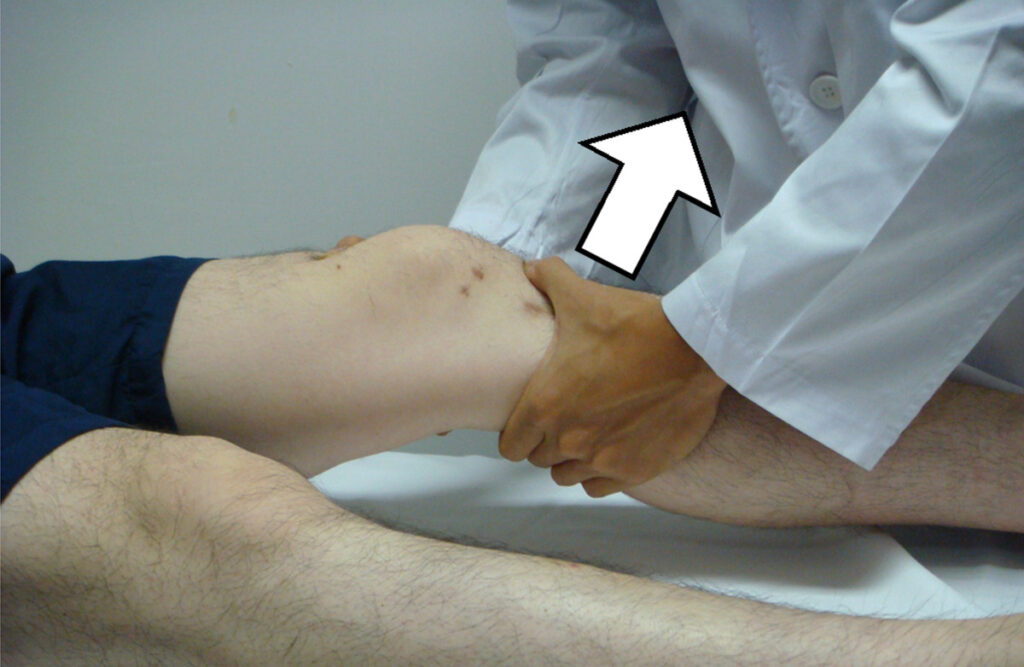
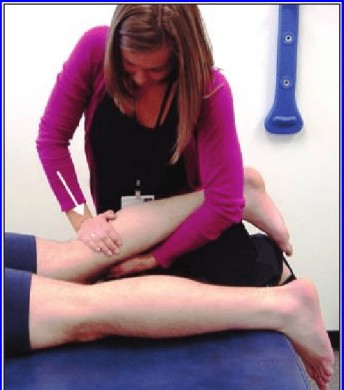
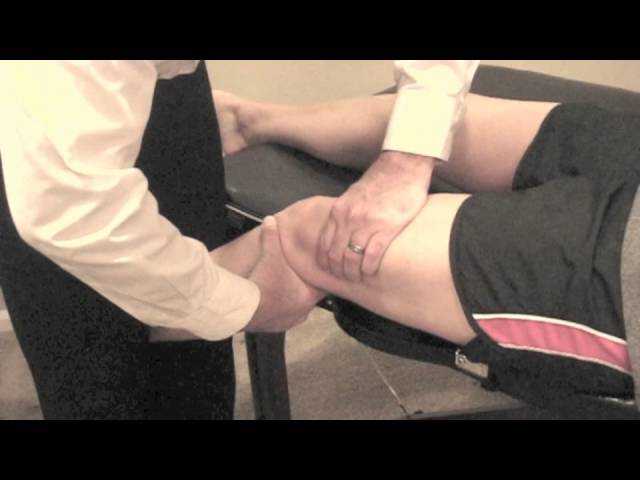
- Test position of the patient is the supine
- In to the supine position with of to the injured knee is flexed up to the 20 to 30 degrees & do to the also slightly externally rotating of the injured leg of to the relax of the iliotibial band.
- After that The examiner is uses to the one hand of to the stabilize of the distal femur when the use of the other hand is grasp of the proximal tibia.
- Next to the anterior force is apply on to the proximal tibia for to the attempt of to the sublux in to the tibia forward which is keep to the femur stabilized .
Interpretation of this test :
- This test is considered to positive when do the excessive anterior translation of the proximal tibia greater than of the unaffected side & also of the lack of to the firm endpoint.
- Endpoints of the knee is graded from to the hard to the soft .
- It is nominally classified into the two :
- A = firm or hard of the endpoint
- B = absent or soft endpoint .
- Hard endpoint which is appreciated to the abrupt endpoint ; it is preventing to the further anterior translation of to the tibia on to the femur.
- Soft endpoint which is regarded to the forward translation of to the tibia without of the distinct / clear or firm, endpoint.
What is the structure involved in this test :
- Anterior cruciate ligament
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- Arcute – popiteus complex
Which is Grading of to the ACL laxity ?
| Grade | Decrepitation | Translation |
| 1 | Mild | 3 to 6 mm |
| 2 | Moderate | 6 to 9 mm |
| 3 | Severe | 10 to 16mm |
| 4 | Very severe | 16 to 20 mm |
- When to translation is do the greater than 11mm so that The examiner is consider to the medial collateral ligament (MCL) & meniscal tears .
| Grade | Description |
| 1 | This is to the no notable injury of to the leg, especially into the comparison of the other leg. |
| 2 | Injured leg is moves to the 2 to 5 mm more than to the normal of the ROM & compared with to the other leg. |
| 3 | Injured leg is moves to the 5 to 10 mm more than to the normal of the ROM & compared WITH to the other leg. |
| 4 | Injured leg is moves to the 10 to 15 mm more than t the normal of the ROM & compared WITH to the other leg |
which is modification of this test ?
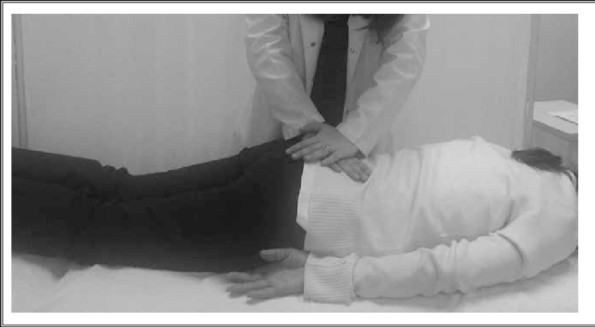
Prone Lachman test :
- It is used to the enhance of to the patient comfort.
- It is also to the reliable evaluation technique which is used to for the confirm of the presence of the ACL tear but it is also used into the sole of the criterion for to the rule out of the presence of to the injury.
- Patient is lies in the prone .
- Examiner is stabilizes the foot between the examiner’s thorax & arm or places to the one hand on the tibia .
- Other hand is stabilizes the femur .
- Then do the gravity assists movement .
- But in this method more difficult to determine the quality of the end feel .
Stable Lachman test :
- It is recommended for the examiners with to the small hands.
- Patient is lies to the supine with the knee resting on the examiner’s knee.
- Then the examiner ‘s hand is stabilizer the femur against the examiner’s thigh
- Then with the other hand applies an the anterior stress .
Drop leg Lachman test :
- This test is describe by the Adler & associates .
- Patient is lies to the supine.
- Then the test leg is abducted off to the side of to the examining table & the knee is flexed up to the 25°.
- One of to the examiner’s hands is stabilizes of to the femur against of the table while of to the patient’s foot is into the held between of to the examiner’s knees.
- Then the examiner’s other hand is free for to the apply of the anterior translation force.
- After that the researchers are found of the greater anterior laxity.

What is the Test Accuracy of this test ?
- Sensitivity = 87%
- Specificity = 93%.
Clinical Notes of this test :
- Frank is reported for to the achieve of the best result .
- The tibia is slightly laterally rotated & the anterior tibial translation force is applied from to the posteromedial aspect.
- Then the hand is on to the tibia which is apply to the translation force.
- In to of the acute trauma, swelling is to the prevents of to the examiner from of to the getting a true indication of to the joint’s mobility.
- The best time is to the assess of to the joint laxity which is immediately after to the injury,
- So that The examiner is need to the allow time for the swelling when the reduce of the swelling before of the true joint
Comparison of the Lachman test with to the an anterior drawer test?
- Anterior drawer test = it is commonly done at to the same time as to the Lachman test for to the help & confirm of to the diagnosis of an the ACL injury.
- This test is done with the bending of the hip 45 degrees & the knee is the 90 degrees .
- After that the pulling of the knee forward within the sudden jerk on to test with the leg’s ROM.
- If this movement is moves to the 6 mm beyond of the normal ROM so that it is the ACL tear / injury.