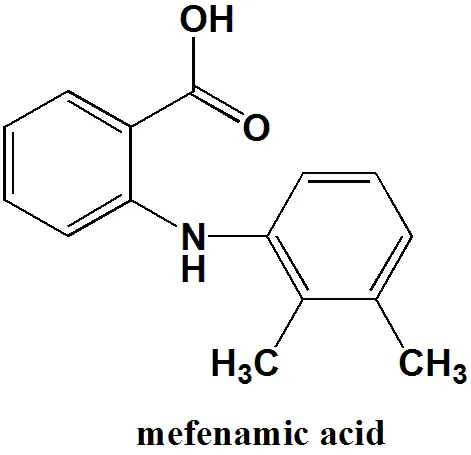
Mefenamic Acid
Description
Mefenamic acid is an associate of the anthranilic acid by-products of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Furthermore, it is used to alleviate minor to moderate aches. Its scientific term, dimethyl phenylamino benzoic acid, is where its moniker originates. It was uncovered and conveyed to the market by Parke-Davis as Ponstel in the 1960s.
- Brand Names – Mefenamic, Ponstel
- Molar mass: 241.285 g/mol
- Boiling point: 398.8 °C
- Formula: C15H15NO2
- CASE ID: 61-68-7
- ChemSpider ID: 3904
- ChEMBL Id: 686
- Pregnancy category: AU: C
- Type – Small Molecule
- Groups – Approved
How to use Mefenamic Acid?
Take this medicine by mouth as required by your doctor, usually 4 times a day. Unless your doctor advises you otherwise, take this capsule with a single 8-ounce/240-milliliter glass of liquid. Do not lie down for at most undersized 10 minutes after bringing this pill. If stomach upset ensues while taking this prescription, take it with food or milk. Do not take mefenamic acid with antacids unless recommended by your medic. Respective antacids may also alter the quantity of mefenamic acid absorbed by the body.
The dosage and dimensions of therapy are based on your medical condition and reaction to treatment. Take this medication at the lowest effective dose for the shortest amount of time to lower your risk of stomach bleeding and other adverse effects. Do not improve your dose or utilize this drug more often or for longer than prescribed. This drug usually should not be accepted for more than 7 days at a period. Discuss the dangers and benefits with your doctor or pharmacist.
If you are taking this tablet “as required” (not on a regular schedule), recognize that pain medications work best if they are used as the first signs of discomfort appear. If you wait until the pain has deteriorated, the antidote may not work as well. Mefenamic acid is employed for the short-term relief of soothing to moderate aches from diverse conditions such as headaches, dental aches, menstrual cramps, and muscle aches. Mefenamic acid is also named a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It performs by blocking your body’s presentation of certain natural substances that cause inflammation. This effect allows for to reduction of swelling, pain, or fever.
If you are using this pill for painful periods, take your first dose as soon as your period starts, or the pain starts. Usually, you will only require to take it for the first 2 to 3 days of your period. Notify your medic if your condition lasts or gets worse.
Mechanism of action
It inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2 isoforms of the cyclooxygenase enzyme, just like other Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs belonging to the anthranilic acid by-products (or fenamate) class. This contains the formation of prostaglandins, which play a position in pain sensitivity, inflammation, and fever, but also in hemostasis, kidney function, sustaining of pregnancy, and shelter of the gastric mucosa.
Absorption – Mefenamic acid is rapidly absorbed after vocalized administration.
The volume of distribution – 1.06 L/kg [Normal Healthy Adults (18-45 yr)
Protein binding – 90%
Route of elimination
Up to 20% of the substance is eliminated through the feces, especially when it comes to unconjugated 3-carboxy mefenamic acid. The elimination half-life of mefenamic acid is roughly two hours. Mefenamic acid, its metabolites, and/or conjugates are primarily excreted by the kidneys of human beings. Both renal and hepatic excretion are consequential pathways of elimination.
Half-life – 2 hours
Support – Oral cl=21.23 L/hr [Healthy adults (18-45 yrs)
Toxicity
Oral, rat LD50: 740 mg/kg. Symptoms of an overdose might also possess excessive stomach ache, coffee ground-like vomit, dark stool, ringing in the ears, variation in the amount of urine, unusually fast or slow heartbeat, muscle weakness, slow and/or shallow breathing, confusion, severe headache, or loss of consciousness.
Pharmacokinetics
Mefenamic acid is 3′-hydroxymethyl- and/or 3′-carboxy-metabolites in the middle and bottom. The carboxy classes at the bottom right of each essence can also be glucuronidated. Mefenamic acid enters the blood plasma at its highest concentration one to four hours after entering the gut. When in the bloodstream, over 90% of the importance is bound to plasma proteins. It presumably traverses the placenta and is found in breast milk in small amounts.
It is metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP2C9 to the only feeble active 3′-hydroxymethyl mefenamic acid. 3′-carboxy mefenamic acid has also been memorized as a metabolite, as well as carboxy glucuronides for all three objectives. Mefenamic acid and its metabolites are eliminated via the urine (52 to 67%) and the wastes (20 to 25%, or less than 20% following another source). The parent development has a bodily half-life of two hours; the half-life of its metabolites may be elongated.
Side Effects
Discomfortness of the stomach, nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, drowsiness, and/or blurred vision may occur. If any of these consequences last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Recognize that this drug has been prescribed because your medic has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the chance of side effects. Many someones utilizing this medication do not have serious side effects. This medication may increase your blood pressure. Check your blood pressure regularly and tell your medic if the results are high.
Tell your medic right away if you have any serious side effects, including a headache that is severe or does not go away, hearing differences (such as ringing in the ears), mental or mood changes, easy bleeding and/or bruising, demanding or painful swallowing, symptoms of heart defeat (such as swelling ankles or feet, uncommon tiredness, unusual and/or premature weight gain). Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including signs of kidney problems (such as a change in the amount of urine, pink/bloody urine), unexplained stiff neck.
Mefenamic acid may rarely induce serious (possibly fatal) liver disease. Get medical help right away if you have any symptoms of liver damage, including nausea or vomiting that doesn’t stop, loss of appetite, stomach or abdominal pain, yellowing eyes or skin, or dark urine. A very extreme allergic response to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including fever, swollen lymph nodes, rash, itching or swelling (especially of the face or tongue, and/or throat), severe dizziness, or problem breathing.
This inventory of potential adverse effects is not exhaustive. If you detect other effects not detailed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
Likelihood and Severity
COMMON side effects
If encountered, these manage to have a Severe expression
- Nausea
- Intense Abdominal Pain
INFREQUENT side effects
If participated, these overlook to have a Severe expression
- Anemia
- Hives Of The Skin Due To An Allergy
If trained, these tend to have a Smallish Severe expression
- Conditions Of Excess Stomach Acid Secretion
- Constipation
- Heartburn
- Gas
RARE side effects
If encountered, these tend to have a Powerful expression
- Water Retention
- High Levels Of Potassium In The Blood
- A Type Of Blood Disorder Where The Red Blood Cells Burst Named Hemolytic Anemia
- A Type Of Blood Disorder With A Reduction In All Types Of Blood Cells Called Pancytopenia
- Low Blood Counts Due To Bone Marrow Collapse
- Improved Risk Of Bleeding Due To Clotting Disorder
- Decreased Blood Platelets
- Very Low Levels Of Granulocytes, A Kind Of White Blood Cell
- Low Levels Of White Blood Cells
- Low Levels Of A Class Of White Blood Cell Called Neutrophils
- High Blood Pressure
- A Heart Attack
- A Stroke
- An Ulcer In The Esophagus
- A Stomach Ulcer
- An Ulcer From Too Much Stomach Acid
- Stomach Or Intestinal Ulcer
- Inflammation Of The Liver Called Hepatitis
- Damage To The Liver And Inflammation
- Acute Inflammation Of The Pancreas
- Bleeding Of The Stomach Or Intestines
- Damage To The Kidneys
- Kidney Failure
- Decreased Kidney Function
- Inflammation Of The Bladder
- A Skin Condition Called Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Causes Blistering And Peeling Skin
- A Skin Condition With Blistering And Peeling Skin Named Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- Skin Rash With Sloughing
- Visible Water Retention
- Difficult Or Painful Urination
- Abnormal Liver Function Tests
- A Significant Variety Of Allergic Reaction Called Anaphylaxis
- A Fracture In The Wall Of The Stomach Or Intestine
- A Yellowing Of The Eyes Or Skin From the Buildup Of Bilirubin Called Jaundice
- A Kind Of Critical Hypersensitive Skin Response Called DRESS Condition
- Heart Throbbing Or Pounding
Who should not take Mefenamic Acid?
The following conditions are contraindicated with this drug. Review with your medic if you have any of the following conditions:
- the expanded danger of bleeding due to clotting disorder
- an increased risk of bleeding
- high blood pressure
- a heart attack
- chronic heart failure
- a stroke
- a blood clot
- an ulcer from too much stomach acid
- stomach or intestinal ulcer
- liver problems
- bleeding of the stomach or intestines
- kidney transplant
- pregnancy
- a break in the division of the stomach or intestine
- tobacco smoking
- the time immediately after coronary bypass surgery
- chronic kidney disease stage 4 (severe)
- chronic kidney disease stage 5 (failure)
- kidney condition with likely decrease in kidney function
- aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease
- history of gastric bypass surgery
- history of kidney donation
Does Mefenamic Acid Interact with Other Medications?
Interactions
Drug interactions may also change how your drugs work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This paper does not include all possible drug dealings. Keep a list of all the products you use (mainly medicine or nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your Doctor and pharmacist. Do not begin, stop, or vary the dosage of any drugs without your doctor’s approval.
Aliskiren, ACE inhibitors (like benazepril and lisinopril), angiotensin II receptor blockers (like losartan and valsartan), cidofovir, corticosteroids (like dexamethasone and prednisone), lithium, methotrexate, and “water pills” (diuretics like furosemide) are some additional medications that may interact with this medication.
This medication may enhance the chance of bleeding when taken with other medications that also may induce bleeding. Samples include anti-platelet drugs such as clopidogrel, and “blood thinners” such as dabigatran or enoxaparin, or warfarin, among others.
Since many drugs (including aspirin, NSAIDs like ibuprofen, ketorolac, and naproxen), as well as nonprescription drug brands, contain painkillers or fever reducers, it is important to carefully check all of these products. If you take these medications together, which are the same as mefenamic acid, you may experience more negative effects. However, if your doctor has directed you to take low-dose aspirin to prevent heart attack and/or stroke (usually 81-162 milligrams a day), you should keep taking the aspirin unless your doctor instructs you otherwise. Request your physician or pharmacist for more details.
This medication may also interfere with certain lab tests (such as urine bile test), possibly generating false test results. Make sure lab personnel and all your physicians know you use this drug.
Severe Interactions
These medications are not usually taken together. Confer your healthcare professional (e.g., medic and/or pharmacist) for more information.
- selected nephrotoxic agents and cidofovir
- selected nephrotoxic agents and bacitracin
- NSAIDs, aspirin ( >81 mg), salicylates, and ketorolac (injectable)
- NSAIDs, aspirin ( >81 mg), salicylates, and ketorolac (noninjectable)
Serious Interactions
These medications may also interact and induce very harmful effects. Confer your healthcare specialist (e.g., doctor or pharmacist) for more information.
- SELECTED NEPHROTOXIC AGENTS/FOSCARNET
- ACETAMINOPHEN; NSAIDS/ALPROSTADIL
- ANTICOAGULANTS; ANTIPLATELETS/CAPLACIZUMAB
- NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS/INOTERSEN
- AGENTS AFFECTING GROWTH HORMONE/MACIMORELIN
- NSAIDS;SALICYLATES/APIXABAN;BETRIXABAN;EDOXABAN;RIVAROXABAN
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/DABIGATRAN
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/MIFAMURTIDE
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/SODIUM PHOSPHATE BOWEL CLEANSER
- SELECTED NEPHROTOXIC AGENTS/COLISTIMETHATE
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/SELECTED PLATELET AGGREGATION INHIBITORS
- SELECTED NSAIDS; ASPIRIN (>325 MG)/PEMETREXED
- NSAIDS/SELECTED ANTICOAGULANTS (VIT K ANTAGONISTS)
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/SELECTED IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS
- NSAIDS/METHOTREXATE; PRALATREXATE
Moderate Interactions
These medications may cause few side-effects when taken together. Consult your healthcare specialist (e.g., doctor or pharmacist) for more information.
- NSAIDS/CORTICOSTEROIDS
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/LOOP DIURETICS
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/LITHIUM
- NSAIDS; ASPIRIN (NON-CARDIOPROTECTIVE)/BETA-BLOCKERS
- SELECTED NEPHROTOXIC AGENTS/CISPLATIN
- SELECTED NEPHROTOXIC AGENTS/ADEFOVIR
- SELECTED NEPHROTOXIC AGENTS/IMMUNE GLOBULIN IV (IGIV)
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/SPARSENTAN
- ANTICOAGULANTS; ANTIPLATELETS/TISOTUMAB
- ANTICOAGULANTS; ANTIPLATELETS/PLASMINOGEN
- ANTICOAGULANTS; ANTIPLATELETS/FRUQUINTINIB; SURUFATINIB
- SELECTED NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/ACE INHIBITORS
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/ALISKIREN
- AGENTS WITH HYPONATREMIA RISK/DESMOPRESSIN
- AGENTS WITH HYPONATREMIA RISK/DESMOPRESSIN (NOCTURIA)
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS
- SELECTED ANTICOAGULANTS; ANTIPLATELETS/IBRUTINIB
- NSAIDS/ERLOTINIB
- SELECTED NEPHROTOXIC AGENTS/TENOFOVIR
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/DROSPIRENONE
- SELECTED NSAIDS; ASPIRIN/SSRIS; SNRIS
- NSAIDS/HEPARINS
- SELECTED NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/TRIAMTERENE; AMILORIDE
- NSAIDS; SALICYLATES/ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKER (ARB)
What Conditions Does Mefenamic Acid Treat?
- pain with menstruation
- pain
- headache caused by the disorder of cranial blood vessels
- a type of joint condition due to excess uric acid in the blood called gout
- joint inflammatory disorder in children and young adults
- non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis
What should I know about the warehouse and disposal of this medication?
Preserve this drug in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of kids. Store it at room temperature and away from leftover heat and moisture (not in the bathroom).
It is essential to keep all medicine out of reach of children as many receptacles (such as weekly pill reminders and those for eye drops, creams, patches, and inhalers) are not child-resistant and young children can also apply them easily. To rescue young youngsters from poisoning, always lock safety caps and immediately place the medication in a safe establishment – one that is up and away and out of their sight and reach.
Unnecessary drugs should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. Nevertheless, you should not flush this medicine down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your prescription is through a medicine take-back program. Talk to your pharmacist or contact your local garbage or recycling department to learn about take-back programs in your neighborhood. See the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines for more details if you do not have access to a take-back program.
Precautions
- Inform your doctor and/or pharmacist if you have any other allergies before using mefenamic acid, aspirin, or other NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or celecoxib). This development may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic responses or other problems. Converse with your pharmacist for more particulars.
- Before employing this pill, tell your medic or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: asthma (including a narrative of worsening breathing after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs), problems with clotting or bleeding, blood disorders (like anemia), nasal polyps, heart conditions (like a prior heart attack), elevated blood fat levels (cholesterol or triglycerides), high blood pressure, liver disease, stroke, swelling (edema, fluid retention), and stomach, intestinal, and/or esophageal issues (like bleeding, heartburn, ulcers).
- NSAID drugs, such as mefenamic acid, can occasionally cause kidney problems as well. Problems are additionally probable to occur if you are dehydrated, have heart failure or kidney condition, are an older adult, or if you take certain medications (see also Drug Interactions section). Drink an abundance of liquids as mandated by your medic to prevent dehydration and tell your doctor right away if you have pink or bloody urine or any unusual change in the amount of urine.
- This medicine may make you dizzy, and drowsy, or induce blurred vision. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can exacerbate these effects. Until you can do it safely, avoid using machinery, driving, or doing anything else that calls for attentiveness or clear vision. What are alcoholic beverages? If you utilize marijuana (cannabis), talk to your physician.
- This medicine may induce stomach bleeding. Daily usage of alcohol and tobacco, particularly when combined with this medicine, may increase your risk of stomach bleeding. Limit alcohol and stop smoking. Ask your physician and/or pharmacist about how much alcohol you may safely drink.
- This pill may make you additional sensitive to the sun. Limit your time in the sun. Avoid tanning booths and sunlamps. Utilize sunscreen and wear protective clothing when outdoors. Inform your medic right away if you get sunburned or have skin blisters and/or redness.
- Before including surgery, tell your doctor or medic about all the products you utilize (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and other herbal products). Older adults may be a greater chance of stomach or intestinal bleeding, kidney problems, heart attack, and stroke while using this drug.
- Before employing this drug, women of childbearing age should talk with their physician(s) about the benefits and risks. Inform your physician if you are pregnant or if you plan to become pregnant. This drug may harm an unborn baby and cause problems with normal labor or delivery. It isn’t proposed for usage in pregnancy from 20 weeks until conveyance. If your physician or medic decides that you need to utilize this medication between 20 and 30 weeks of pregnancy, you should utilize the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible duration. You should not employ this drug after 30 weeks of pregnancy.
This medication passes into breast milk. Consult your physician before breastfeeding.
What other information should I know?
Inform your doctor and the lab personnel that you are taking mefenamic acid prior to participating in any laboratory tests. Never permit another person to take your drug. Request your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription.
You require to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription (over-the-counter) medicines you are taking, as well as any developments such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you see a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important knowledge to carry with you in case of emergencies.
Important Warning :
People who take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) (other than aspirin) such as mefenamic acid may have a more increased risk of having a heart attack and/or a stroke than people who do not take these medications. These events may happen without notification and may induce death. This option might be higher for individuals who take NSAIDs for a long time. Try not to submit to an NSAID, for example, mefenamic corrosive if you have recently had a heart seizure except if commanded to do as such by your surgeon. Inform your doctor if you or anyone in your family has or has ever had a heart condition, a heart attack, or a stroke if you smoke and if you have or have ever had elevated cholesterol, raised blood pressure, and/or diabetes. Get emergency medical assistance right away if you experience any of the subsequent symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath, deficiency in one part or side of the body, or slurred speech.
If you’re going to have a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG); a sort of heart medical procedure), you shouldn’t take mefenamic corrosive right up until now or straightforwardly after the medical procedure.
NSAIDs such as mefenamic acid might also induce ulcers, bleeding, or holes in the abdomen and/or intestine. These problems may develop at any time during treatment, may ensue without warning symptoms, and may cause death. People who take NSAIDs for a long time, are older, are in poor health, or drink a lot of alcohol while taking mefenamic acid may have a higher risk. Convey your physician if you take any of the subsequent drugs: anticoagulants (‘blood thinners’) such as warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven); aspirin; additional NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn); oral steroids such as dexamethasone, methylprednisolone (Medrol), and prednisone (Rayos); and also demanding serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as citalopram (Celexa), fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem, Selfemra, in Symbyax), fluvoxamine (Luvox), paroxetine (Brisdelle, Paxil, Pexeva), and also sertraline (Zoloft); and/or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) such as desvenlafaxine (Khedezla, Pristiq), also duloxetine (Cymbalta), and venlafaxine (Effexor XR). Also communicate to your medic if you have or have ever owned ulcers, seeping in your stomach or intestines, or other bleeding disorders. If you participate in any of the following manifestations, discontinue taking mefenamic acid and call your doctor: stomach pain, heartburn, vomit that is bloody and/or glimpses like coffee grounds, blood in the stool, and/or black and tarry seats.
Keep all assignments with your physician and the laboratory. Your medic intentionally watches your symptoms carefully and will presumably order certain tests to check your body’s response to mefenamic acid. Tell your doctor how you are feeling so that they can prescribe the ideal dosage of medication to suit your needs with the least chance of negative side effects.
Your physician and/or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer’s patient details sheet (Medication Guide) when you form a remedy with mefenamic acid each time you refill your prescription. Read the details carefully and ask your physician or pharmacist if you have any questions. You can also see the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the manufacturer’s website to obtain the Medication Handbook.
Overdose
If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, contact 911. Otherwise, reach a poison control center right away. US citizens can contact their local poison control center. Canadian citizens can contact a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may contain severe stomach pain, slow or shallow breathing, and excessive drowsiness.
Notes
Do not share this medicine with others. Lab and/or medical tests (such as complete blood count, liver or kidney function, and blood pressure) might be done while you are using this medication. Keep all medical and lab assignments. Confer your doctor for more details.
Missed Dose
If you are taking this medication on a regular schedule (not just “as needed”) and you forget a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the period of the next dose, miss the missed dose. Take your subsequent dose at the normal time. Do not crumple the dose to catch up.
Storage
Store at room temperature in a tightly impenetrable container away from light and moisture. Do not store it in the restroom. Keep all medications out of children and pets. Do not wash pharmaceuticals down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless recommended to do so. Properly dump this outcome when it is expired or no longer needed. Confer your apothecary or local waste disposal company.
FAQ
What is mefenamic acid used for?
Mefenamic acid is used to relieve gentle to moderate pain, including menstrual pain (discomfort that happens before or during a menstrual period). Mefenamic acid is in a category of medications called NSAIDs. It works by stopping the body’s presentation of a substance that causes pain, fever, and rash.
Is mefenamic stronger than ibuprofen?
Ibuprofen is non-inferior to Mefenamic Acid founded on a comparison of the course to meaningful relief (non-inferiority margin for threat ratio- 0.34 to 1.3) most or peak effect (non-inferiority margin of -2 to +2), global assessment scores for significance (non-inferiority margin of -1 to +1).
Is mefenamic acid used for toothache?
Is Mefenamic Acid good for a toothache? Yes, Mefenamic can be employed to ease toothache. It uses for pain-relieving conditions, Mefenamic may also uses in reducing toothache and/or other pain conditions. You can swallow it if your dentist has prescribed it after surgery or a routine check-up.
Is mefenamic better than paracetamol?
Mefenamic acid is an anti-inflammatory non-steroidal medication that is (NSAID). Mefenamic acid works by decreasing the hormones which induce inflammation and pain in the body. Paracetamol is a painkiller and functions as a fever reducer.
Does mefenamic acid have side effects?
Inform your physician right away if you have any serious side effects, including a headache that is severe or does not go away, hearing changes (such as ringing in the ears), mental or mood changes, easy bleeding or bruising, difficulty or painful swallowing, symptoms of heart failure (such as swelling ankles or feet, unusual tiredness.
Does mefenamic acid damage the kidney?
Kidney function: Long-term benefit of mefenamic acid may lead to a higher risk of decreased kidney function. This is most common for individuals who already have kidney disease, liver disease, or heart failure; for people who take diuretics (water pills); and/or seniors.
Can I take Mefenamic 3 times a day?
Dose. The standard dose of Ponstan is 500 mg 3 times a day. In the event that you are using Ponstan for deplorable periods, accept your premier portion when your term begins and additionally torment starts until the aggravation facilitates. Take it for no more than seven days if you are treating heavy bleeding.
Which is better nimesulide or mefenamic acid?
Both drugs reduced fever, but the antipyretic activity of nimesulide was greater and more rapid than that exerted by mefenamic acid. Normal body temperature was achieved on the third day for most nimesulide-treated patients, and on the fifth day for those treated with mefenamic acid.