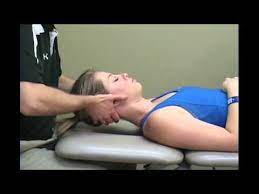
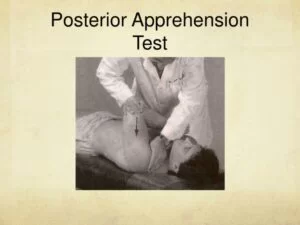
Posterior apprehension test
- This test is used to evaluate of posterior instability of the shoulder.
- This test is applied in to the examination part.
Purpose of test :
- This Test is used to check the dislocation / posterior instability of the humerus.
How to perform the apprehension test?
- Patient position for the test is supine or sitting.
- Then the examiner is elevates the patient’s shoulder into the plane of the scapula at the 90° & other hand is
- Stabilize the scapula.
- After that apply to the posterior force on the patients elbow by the examiner.
- While apply to the axial load , examiner is do the horizontally adducted & medial rotates means internally rotate the arm.
- This test is also perform into the 90 ‘ of to the abduction.
- In this position examiner palpates the head of the humerus with one hand while the other hand is pushes the head of humerus posterior .
- Translation of to the 50 % of its diameter or less is on considered normal, although results vary among patients.
What is the interpretation of this apprehension test?
- This test is positive which is indicated by of the look of the apprehension / alarm on the patient ‘s face which is to the patient’s resistance of to the further motion ; which is do the reproduction of the patient’s symptoms.
- Also indicates the posterior instability or dislocation of the shoulder.
- But if to the present of to the multi directional instability; for this condition test is negative .
- This movement is accompanied by the clunk as the humeral head passes over to the glenoid rim.
What is the Evidence of the test :
- Sensitivity of this test = 19.2
- Specificity of this test = 99.2
- LR of this test = 24.97



![Oppenheim test purpose = this test is used to check the lesion of the upper motor neuron. technique = starting position of the patient for the test is the supine position. the examiner runs a fingernail along the crest of the patient's tibia. result = a negative Oppenheim test is indicated by no rection or no pain. a positive test is indicated by a positive Babinski sign [ positive pathological reflex ] & suggests an upper motor neuron lesion.](https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/filp-test.jpg)