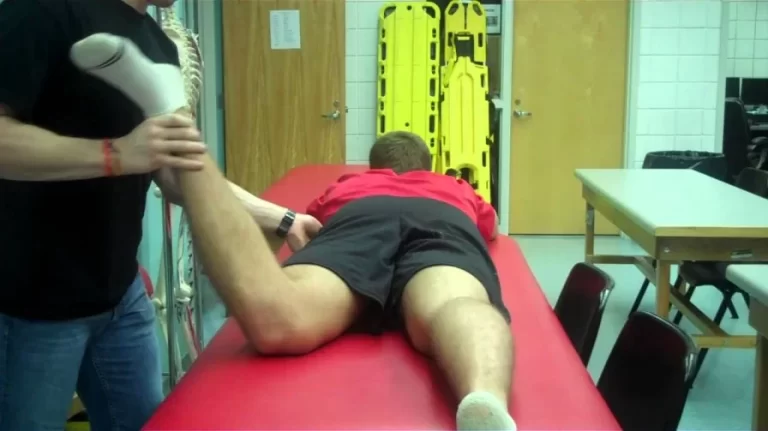
Posterior sag sign of the knee joint :
- It is also known as the gravity drawer test .
- This test is indicates to the presence of the posterior cruciate ligament means [ PCL] tear.
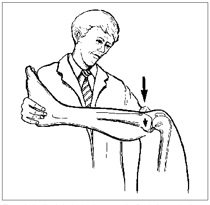
- To look for the sign, patient lies supine with to the hips flexed at to the 45˚ & knees are flexed up to 90˚.
- Normally, to the medial tibial plateau is lies at least to the 1 cm anterior of to the femoral condyle when to the viewed up directly from to the side.
What is Purpose of the Posterior sag sign :
- This test is assess for to the integrity of to the PCL.
- This test is also check the rotary instability of the posteriorly & torn of the PCL
- This test is also used for the check of the one – plane posterior instability .
How to perform of this test ?

- Test Position of the patient is Supine.
- In to the supine position with the 45 degrees of the hip flexion & 90 degrees of to the knee flexion.
- In this position , the tibia ‘ drops back ‘ or sags back on to the femur because of the gravity .
- This is occurs due to the torn of the PCL.
- This posterior tibial displacement is more noticeable when the knee is flexed 90 ‘ to 110 ‘ than to the knee is only slightly flexed .
- Normally the medial tibial plateau extended 1 cm anteriorly beyond the femoral condyle when the knee joint is flexed 90 ‘.
What is interpretation of this test ?
- If this step is lost , which is occurs with the positive posterior sag caused by the torn of the posterior cruciare ligament [ PCL] .
- So that this step -off or thumb sign is considered to the positive test .
- Say to in other way :
- Positive test = Posterior drop of the tibia.
- Negative test = Tibia remains straight.
Which structures is affected in this test?
- When the test is positive means posterior sag sign is present below structures is affected :
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- Arcute – popliteus complex
- Posterior oblique ligament
- Anterior cruciate ligament
What is the Diagnostic of the Accuracy?
- Sensitivity of this test = 79
- Specificity of this test = 1.0
- [+LR ]Positive Likelihood Ratio = 79
- [-LR ]Negative Likelihood Ratio= 21
What is the Importance of this Test :
- Posterior cruciate ligament means [ PCL ] is responsible for to the resisting against of the excessive posterior translation of to the tibia on to the femur, due to the its attachments posteriorly onto the tibial plateau & anteriorly on to the lateral side of to the medial femoral condyle .
- In this position of to the 45 degrees of to the hip flexion & 90 degrees of to the knee flexion this position is gravity places for to the force on to the tibia which is pulls onto the tibia posteriorly, but it is blocked to the an intact PCL.
- Into the absence of to the PCL, the tibia is appears to the “sag.”
- Most common of the mechanism for to the PCL injury is more of to the posterior translation at the 90 degrees of the knee flexion.
- While the PCL is ruptured through to the hyperextension & hyperflexion it is unlikely to the that only ligament torn in to the injuries.
- But The ACL is more stressed than to the PCL in both of the hyperflexion & hyperextension.