Right Hemiplegia
What is a Right Hemiplegia?
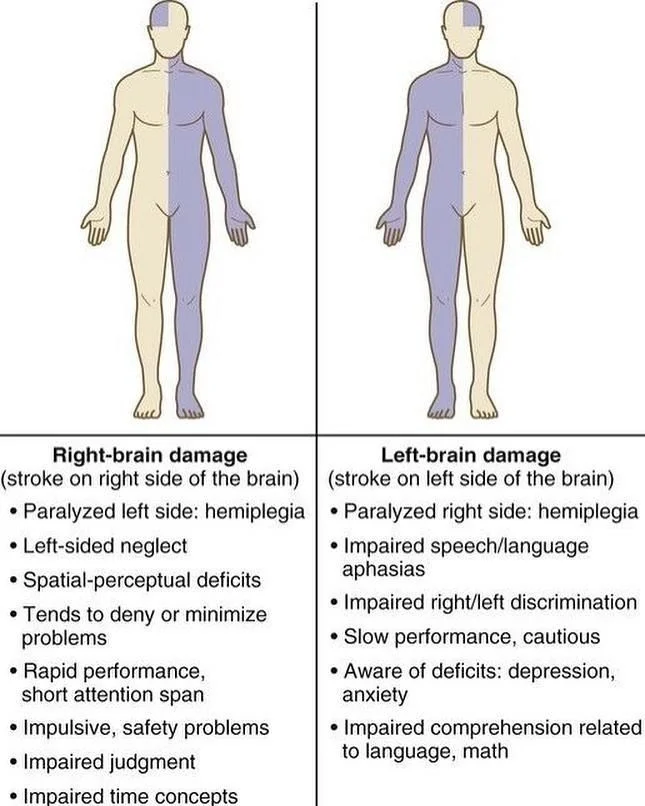
Right hemiplegia refers to paralysis or weakness affecting the right side of the body, typically caused by damage to the left side of the brain. The condition is often associated with stroke, specifically an ischemic stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked due to a blood clot or other obstruction.
When the left side of the brain is damaged, it can result in right hemiplegia because the brain’s motor functions are contralateral, meaning that the left side of the brain controls movement on the right side of the body, and vice versa. The severity of right hemiplegia can vary depending on the extent of the brain damage.
A multidisciplinary approach is frequently used in the treatment of right hemiplegia, including speech, occupational, and physical therapy. These therapies aim to help improve strength, coordination, mobility, and functional abilities. Medications, such as muscle relaxants or antispasticity drugs, may also be prescribed to manage muscle stiffness or spasticity.
Rehabilitation and support services play a crucial role in helping individuals with right hemiplegia regain independence and improve their quality of life. Assistive devices like braces, canes, walkers, or wheelchairs may be recommended to assist with mobility. In some cases, surgical interventions may be considered, depending on the underlying cause and individual circumstances.
It’s important for individuals with right hemiplegia to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan and receive ongoing care and support.
Causes of Right Hemiplegia
Right hemiplegia can be caused by various conditions or events that result in damage to the left side of the brain, which controls the right side of the body. The most common cause of right hemiplegia is a stroke, particularly an ischemic stroke. Here are some common causes of right hemiplegia:
- Stroke: Ischemic strokes occur when a blood clot or other obstruction blocks the blood flow to a part of the brain, leading to damage. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding in the brain. Both types of stroke can lead to right hemiplegia if the left side of the brain is affected.
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI): Severe head injuries resulting from accidents, falls, or other traumatic events can cause damage to the brain. If the left side of the brain is affected, it can lead to right hemiplegia.
- Brain tumors: Tumors that develop in the left side of the brain can exert pressure on surrounding structures, causing neurological symptoms, including right hemiplegia.
- Brain infections: Infections such as encephalitis (brain inflammation) or meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) can cause damage to the brain, potentially leading to right hemiplegia.
- Cerebral palsy is a condition that affects movement and coordination. If the underlying brain damage in cerebral palsy occurs on the left side of the brain, it can cause right hemiplegia.
- Congenital conditions: Some congenital conditions, such as certain types of brain malformations or genetic disorders affecting brain development, can lead to right hemiplegia.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples, and there can be other less common causes of right hemiplegia. The underlying cause of right hemiplegia should be evaluated and diagnosed by a healthcare professional based on the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and appropriate diagnostic tests.
Symptoms of Right Hemiplegia
The symptoms of right hemiplegia arise from paralysis or weakness affecting the right side of the body due to damage on the left side of the brain. The severity and specific symptoms can vary depending on the extent and location of the brain damage. Here are some common symptoms associated with right hemiplegia:
- Paralysis or weakness: The most prominent symptom is the inability to move or control the muscles on the right side of the body. This can affect the right arm, hand, leg, foot, and even the right side of the face.
- Difficulty with coordination and balance: Right hemiplegia can lead to difficulties with coordination and balance, making it challenging to perform activities that require precise movements. Walking may be affected, and individuals may have a tendency to lean or veer towards the affected side.
- Sensory changes: Along with motor impairments, right hemiplegia can cause sensory changes. These may include decreased sensation, numbness, tingling, or a lack of responsiveness to touch, temperature, or pain on the right side of the body.
- Speech and language difficulties: If the left side of the brain, particularly the areas responsible for language processing, is affected, it can result in speech and language impairments. This may manifest as difficulty speaking, finding the right words (word-finding difficulties), understanding language (receptive aphasia), or expressing thoughts coherently (expressive aphasia).
- Visual impairments: Right hemiplegia can be associated with visual problems, typically affecting the left visual field. This can include a loss of vision on the left side (hemianopia) or difficulties perceiving depth, judging distances, or attending to objects in the left visual space.
- Cognitive changes: Depending on the extent of brain damage, individuals with right hemiplegia may experience cognitive changes. These can include difficulties with attention, memory, problem-solving, reasoning, and executive functions.
- Emotional and psychological effects: Coping with right hemiplegia and the associated challenges can lead to emotional and psychological effects. Depression, anxiety, frustration, and decreased self-esteem are common emotional experiences.
It’s important to remember that each individual’s experience with right hemiplegia may be unique, and the severity and specific symptoms can vary. Rehabilitation, therapy, and support services are vital in helping individuals manage these symptoms and improve their quality of life. A healthcare professional or rehabilitation specialist can provide a comprehensive evaluation and develop a tailored treatment plan to address the specific needs of the person with right hemiplegia.
Risk Factors of Right Hemiplegia
The risk factors for right hemiplegia are generally associated with conditions that can lead to damage on the left side of the brain. Since the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body, any factor that increases the likelihood of brain damage can contribute to the development of right hemiplegia. Here are some common risk factors:
- Stroke: The most significant risk factor for right hemiplegia is a stroke. Certain factors increase the risk of stroke, including high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, atrial fibrillation (irregular heart rhythm), family history of stroke, and advancing age.
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI): Severe head injuries resulting from accidents, falls, sports-related incidents, or other traumatic events can increase the risk of right hemiplegia. Engaging in activities without appropriate protective measures, such as not wearing helmets while cycling or participating in contact sports, can increase the risk of a traumatic brain injury.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and heart valve disorders, can contribute to the development of blood clots that may cause a stroke, leading to right hemiplegia.
- Aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs): Abnormalities in blood vessels, such as weakened areas called aneurysms or tangled blood vessels known as arteriovenous malformations, can increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke, which can result in right hemiplegia.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension) is a significant risk factor for stroke. It can damage blood vessels over time, increasing the likelihood of a stroke occurring and causing right hemiplegia.
- Smoking: Smoking tobacco increases the risk of stroke by damaging blood vessels and contributing to the formation of blood clots. Smoking also exacerbates other risk factors such as high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including stroke. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can contribute to blood vessel damage, increasing the likelihood of a stroke and right hemiplegia.
- Sedentary lifestyle and obesity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle and being overweight or obese are associated with an increased risk of stroke. Lack of physical activity and excess body weight can contribute to the development of conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, which are risk factors for right hemiplegia.
- Family history: Having a family history of stroke or certain conditions that increase the risk of stroke, such as certain genetic disorders or inherited blood clotting disorders, can increase the likelihood of developing right hemiplegia.
- Age and gender: The risk of stroke and right hemiplegia increases with advancing age. Additionally, men have a slightly higher risk of stroke compared to women, although stroke can affect both genders.
It’s important to note that while these risk factors can increase the likelihood of right hemiplegia, they do not guarantee its occurrence. It’s essential to manage and control these risk factors through lifestyle modifications, regular medical check-ups, and adherence to treatment plans to reduce the risk of stroke and associated complications.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of right hemiplegia involves a comprehensive evaluation to determine the underlying cause and extent of the condition. The diagnostic mostly requires the following steps:
- Medical history and physical examination: The healthcare provider will gather information about the individual’s medical history, including any previous medical conditions, symptoms, and risk factors. A physical examination will be conducted to assess motor function, coordination, reflexes, sensory perception, and other neurological signs.
- Imaging tests: Imaging studies are often employed to visualize the brain and identify any abnormalities or areas of damage. Common imaging tests used in the diagnosis of right hemiplegia include:
- CT scan (computed tomography): This test uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the brain, helping identify hemorrhages, tumors, or other structural abnormalities.
- MRI scan (magnetic resonance imaging): MRI provides highly detailed images of the brain using magnetic fields and radio waves. It can detect stroke-related changes, tumors, or other lesions.
- Angiography: This imaging technique involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels to visualize the blood flow in the brain. It can help identify any blockages or abnormalities in the blood vessels that may have led to a stroke.
- EEG (electroencephalogram): EEG records the electrical activity of the brain and can be used to evaluate brain function and detect abnormal brain waves associated with certain conditions.
- Laboratory tests: Blood tests may be ordered to evaluate various factors, such as cholesterol levels, blood glucose levels (to assess diabetes risk), blood clotting factors, and markers of inflammation or infection. These tests can help identify underlying conditions that may contribute to right hemiplegia.
- Neurological assessments: Specialized neurological assessments and tests may be conducted to evaluate specific aspects of brain function, such as language skills, cognitive abilities, and visual perception.
- Other diagnostic procedures: Depending on the suspected cause of right hemiplegia, additional tests or consultations may be necessary. For example, if a stroke is suspected, additional evaluations like Doppler ultrasound, transcranial Doppler, or echocardiography may be ordered to assess the blood flow, heart function, or presence of blood clots.
The specific diagnostic approach will vary based on individual circumstances, symptoms, and the suspected underlying cause of right hemiplegia. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can conduct a thorough evaluation and guide the diagnostic process accordingly.
Treatment of Right Hemiplegia
The treatment of right hemiplegia aims to improve motor function, enhance independence, and enhance overall quality of life. It typically involves a multidisciplinary approach and may include the following components:
- Rehabilitation therapies: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy are fundamental components of the treatment plan for right hemiplegia. These therapies focus on improving strength, coordination, mobility, balance, and functional abilities. Physical therapy helps with retraining movement and improving muscle strength and flexibility. Occupational therapy focuses on enhancing daily living skills and promoting independence in activities of daily living. Speech therapy addresses any speech and language difficulties and may also target swallowing difficulties, if present.
- Assistive devices and mobility aids: Various assistive devices and mobility aids can help individuals with right hemiplegia regain mobility and independence. These may include canes, walkers, braces, orthotics, and wheelchairs, depending on the individual’s needs. These devices can provide support, stability, and help compensate for the physical limitations caused by right hemiplegia.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms or complications associated with right hemiplegia. For example, muscle relaxants or antispasticity drugs may be prescribed to reduce muscle stiffness or spasticity. Medications to manage pain, prevent blood clots, or address underlying medical conditions may also be considered.
- Electrical stimulation techniques: Electrical stimulation techniques, such as functional electrical stimulation (FES), may be used to stimulate the affected muscles and promote muscle activation and movement. FES uses low-level electrical currents to contract muscles, helping improve muscle strength and coordination.
- Cognitive and psychological support: Individuals with right hemiplegia may benefit from cognitive rehabilitation programs that target cognitive difficulties, such as attention, memory, and problem-solving. Additionally, psychological support, counseling, and therapy can help address emotional challenges, including depression, anxiety, and adjustment to living with a disability.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle is important for overall well-being and may help reduce the risk factors associated with right hemiplegia. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity (as appropriate), managing chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, high blood pressure), and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Surgical interventions (in some cases): In certain situations, surgical interventions may be considered as part of the treatment plan. For example, if there is an underlying structural abnormality, such as a brain tumor or arteriovenous malformation (AVM), surgical removal or intervention may be necessary.
The treatment plan for right hemiplegia should be individualized based on the specific needs, goals, and underlying cause of the condition. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare team that specializes in stroke rehabilitation or neurorehabilitation to develop a personalized treatment approach. Regular follow-ups and ongoing rehabilitation and support services are important to monitor progress, make adjustments to the treatment plan, and promote optimal recovery.
Medical Treatment
The medical treatment of right hemiplegia focuses on addressing the underlying cause, managing symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting recovery. The specific medical treatments will depend on the underlying condition or event that led to right hemiplegia.
A few common treatment options are:
- Stroke treatment: If the right hemiplegia is caused by a stroke, the immediate priority is to restore blood flow to the affected area of the brain. The treatment will also depend on the type of stroke such as ischemic or Hemorrhagic.
- Ischemic stroke: Medications such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) or endovascular procedures like mechanical thrombectomy may be used to dissolve or remove blood clots blocking the blood vessels.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: Treatment may involve surgical interventions to repair ruptured blood vessels, control bleeding, and reduce pressure on the brain.
- After the acute phase, medications such as antiplatelet drugs, anticoagulants, or statins may be prescribed to prevent future strokes or manage underlying risk factors.
- Medications for symptom management: Medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms associated with right hemiplegia. For example:
- Muscle relaxants or antispasticity drugs: These medications help reduce muscle stiffness and spasticity, improving mobility and comfort.
- Pain management: Analgesic medications or other pain management strategies may be utilized to address any pain experienced in the affected muscles or joints.
- Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications: These medications may be prescribed if emotional or psychological challenges, such as depression or anxiety, are present.
- Medications for underlying conditions: If right hemiplegia is caused by an underlying condition such as multiple sclerosis or cerebral palsy, specific medications may be prescribed to manage the underlying disease process and associated symptoms.
- Prevention of complications: Individuals with right hemiplegia are at risk of developing complications such as blood clots, pressure ulcers (bedsores), urinary tract infections, or respiratory infections. Medications, preventive measures (e.g., compression stockings), and appropriate management techniques can be employed to minimize these risks.
- Botox injections: In some cases, Botox injections may be used to treat spasticity or muscle tightness in specific muscles, helping to improve mobility and functional abilities.
It’s important to note that medical treatment alone is typically not sufficient for optimal recovery in right hemiplegia. Rehabilitation therapies, as discussed earlier, play a crucial role in restoring function and improving independence. The medical treatment and rehabilitation interventions should be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals are important to monitor progress, adjust medications as needed, and address any emerging issues.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapy plays a vital role in the treatment and rehabilitation of individuals with right hemiplegia. The goals of physiotherapy are to improve motor function, increase strength and flexibility, enhance balance and coordination, and promote overall mobility and independence. A physiotherapy treatment plan for right hemiplegia may include the following components:
- Assessment and goal setting: The physiotherapist will conduct an initial assessment to evaluate the individual’s motor abilities, range of motion, strength, balance, and functional limitations. Based on the assessment, specific goals will be established in collaboration with the individual to guide the treatment plan.
- Range of motion exercises: Passive and active range of motion exercises are used to maintain or improve joint flexibility. Passive range of motion exercises involves the therapist moving the individual’s limbs, while active range of motion exercises involve the individual actively moving the affected limbs themselves.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises target the muscles affected by right hemiplegia. The therapist will guide the individual through exercises that focus on building strength in the affected limbs and core muscles. This may involve the use of resistance bands, weights, or specialized equipment.
- Balance and coordination training: Balance exercises aim to improve stability and reduce the risk of falls. Various exercises, such as weight shifting, standing on unstable surfaces, and specific balance training activities, are utilized. Coordination training focuses on improving the ability to perform controlled and precise movements, which may involve activities like reaching, grasping, and manipulating objects.
- Gait training: Gait training is an essential aspect of physiotherapy for individuals with right hemiplegia. It involves working on walking patterns, weight shifting, and improving the coordination of movements during walking. Assistive devices such as canes, walkers, or orthotics may be utilized to provide support and aid in gait training.
- Functional mobility training: Physiotherapy focuses on helping individuals regain functional abilities necessary for daily activities. This may include practicing transfers (e.g., getting in and out of a chair or bed), climbing stairs, getting in and out of a car, or performing specific tasks related to self-care or household chores.
- Assistive device training: If necessary, the physiotherapist will provide training on the use of assistive devices such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs. This includes proper techniques for safe and efficient use, as well as strategies for navigating various environments.
- Task-specific training: Task-specific training involves practicing activities that are meaningful and relevant to the individual’s daily life. The therapist will guide the person in performing activities specific to their goals, such as reaching for objects, manipulating utensils, or dressing oneself.
- Education and home exercise program: The physiotherapist will provide education on techniques for managing and maintaining physical function, including proper body mechanics, energy conservation strategies, and strategies for preventing falls and injury. They will also develop a home exercise program consisting of exercises and activities to be performed independently between physiotherapy sessions.
- Progress monitoring and adjustment: Regular monitoring of progress is essential to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment plan. The physiotherapist will make adjustments to the treatment approach as needed, modifying exercises, intensifying or progressing the program, and addressing any emerging issues or challenges.
Physiotherapy treatment for right hemiplegia is typically long-term and requires consistency and dedication. The frequency and duration of physiotherapy sessions will depend on the individual’s needs and progress. Working closely with a skilled and experienced physiotherapist is crucial to ensure an optimal and personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific challenges and goals of the individual with right hemiplegia.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is a crucial component in the treatment of right hemiplegia. It focuses on maximizing the individual’s functional abilities, promoting independence, and improving overall quality of life. Rehabilitation for right hemiplegia is typically a multidisciplinary approach involving various healthcare professionals, such as physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and rehabilitation nurses. The rehabilitation process may include the following aspects:
- Physical rehabilitation: Physical rehabilitation aims to improve motor function, strength, coordination, and mobility. It may involve exercises, therapeutic activities, and assistive devices to enhance movement and functional abilities. Physiotherapy, as mentioned earlier, is a key component of physical rehabilitation.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapy focuses on helping individuals with right hemiplegia regain independence in daily activities and develop strategies for adapting to their physical limitations. Occupational therapists work on improving fine motor skills, cognitive abilities, and functional tasks such as dressing, grooming, eating, and household activities. They may also provide guidance on home modifications and assistive devices to enhance independence.
- Speech and language therapy: Speech and language therapy addresses any speech, language, swallowing, or communication difficulties that may be present in individuals with right hemiplegia. Therapists work on improving speech articulation, language comprehension and expression, and swallowing abilities. They may use exercises, techniques, and assistive devices to facilitate communication and safe swallowing.
- Cognitive rehabilitation: Right hemiplegia can sometimes be associated with cognitive impairments, such as attention deficits, memory problems, and difficulty with problem-solving. Cognitive rehabilitation programs are designed to address these cognitive challenges through specific exercises, strategies, and techniques to improve cognitive function and facilitate independent living.
- Psychological and emotional support: Coping with the physical and emotional challenges of right hemiplegia can be overwhelming. Psychological support, counseling, and therapy may be provided to help individuals and their families adjust to the changes, manage stress, and address emotional well-being.
- Community reintegration and social support: Rehabilitation also focuses on helping individuals with right hemiplegia reintegrate into their communities and engage in social activities. This may involve community outings, participation in support groups, and connecting with resources that promote social interaction and participation.
- Assistive devices and technology: Rehabilitation professionals may assess the need for and provide recommendations on assistive devices, mobility aids, and adaptive technology that can enhance independence and functional abilities. This may include wheelchairs, orthotics, communication devices, or devices that facilitate activities of daily living.
- Family and caregiver education and training: Family members and caregivers play a crucial role in the rehabilitation process. Rehabilitation programs often include education and training for family members and caregivers on how to support and assist the individual in their recovery, use assistive devices, and manage any ongoing care needs.
Rehabilitation for right hemiplegia is a continuous and dynamic process, with a focus on setting individualized goals, monitoring progress, and making adjustments as needed. The duration and intensity of rehabilitation may vary depending on the severity of the hemiplegia, the underlying cause, and the individual’s response to therapy. Close collaboration between the rehabilitation team, the individual, and their support network is essential for optimal outcomes and long-term success.
How to Prevent Right Hemiplegia?
Preventing right hemiplegia involves addressing the underlying causes and minimizing the risk factors associated with conditions that can lead to hemiplegia. While some causes of right hemiplegia, such as genetic disorders or congenital conditions, may not be preventable, there are several steps you can take to reduce the risk of certain conditions that can lead to right hemiplegia. Here are some preventive measures:
Stroke prevention:
Maintain healthy blood pressure: Keep your blood pressure within a healthy range by adopting a balanced diet, limiting sodium intake, exercising regularly, managing stress, and, if necessary, taking prescribed medications.
Manage diabetes: If you have diabetes, work with your healthcare provider to keep your blood sugar levels under control through diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring.
Control cholesterol levels: Follow a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, exercise regularly, and, if prescribed by your doctor, take medications to manage cholesterol levels.
Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of stroke. Seek support, such as counseling or nicotine replacement therapy, to quit smoking.
Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of stroke. Reduce the use of alcohol or avoid it altogether.
Maintain a healthy weight: Aim for a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to reduce the risk of stroke.
Stay physically active: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to promote cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of stroke.
Recognize and manage atrial fibrillation: If you have atrial fibrillation, work with your healthcare provider to manage it effectively, as it increases the risk of stroke.
Avoid illicit drug use: Illicit drugs, particularly those that increase blood pressure or have neurotoxic effects, can contribute to the risk of stroke. Avoid using illicit drugs and seek help if you have substance abuse issues.
Injury prevention:
Take precautions to prevent falls: Remove hazards in your living environment, use assistive devices if necessary, keep rooms well-lit, wear appropriate footwear, and maintain good balance and strength through regular exercise.
Practice safe driving: Follow traffic rules, wear seatbelts, avoid distractions while driving, and never drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Manage underlying medical conditions:
Follow recommended medical treatments: If you have underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes, follow your healthcare provider’s treatment plan to manage these conditions effectively.
Seek early medical intervention:
Be aware of the warning signs of stroke, such as sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, sudden vision changes, severe headache, or dizziness. If you feel any of these symptoms, take immediate medical treatment.
Genetic counseling:
If you have a family history of genetic disorders or conditions that can lead to right hemiplegia, consider genetic counseling before planning a family. Genetic counseling can provide information about the risks and options for managing or preventing these conditions.
It’s important to note that these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of right hemiplegia caused by stroke or preventable conditions. However, some causes of right hemiplegia, such as congenital conditions or traumatic brain injuries, may not be preventable through lifestyle modifications alone. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific health conditions and risk factors.
Summary
Right hemiplegia refers to paralysis or weakness affecting the right side of the body. It can be caused by various underlying conditions, with stroke being the most common cause. Other causes include traumatic brain injury, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and genetic disorders.
The symptoms of right hemiplegia typically include weakness or paralysis on the right side of the body, difficulty with movement and coordination, sensory changes, and potential difficulties with speech and swallowing.
Risk factors for right hemiplegia include older age, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, atrial fibrillation, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and a family history of stroke or other related conditions.
Diagnosis of right hemiplegia involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various imaging and diagnostic tests, such as brain imaging, blood tests, and electroencephalogram (EEG).
The treatment of right hemiplegia involves a multidisciplinary approach. Medical treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause, managing symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting recovery. This may involve medications to treat stroke or underlying conditions, pain management, and preventive measures for complications.
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of right hemiplegia. It includes range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, balance and coordination training, gait training, functional mobility training, and assistive device training. Occupational therapy, speech therapy, cognitive rehabilitation, psychological support, and social reintegration are also important components of rehabilitation.
Preventing right hemiplegia involves addressing the underlying causes and minimizing risk factors. This includes stroke prevention through lifestyle modifications such as maintaining healthy blood pressure, managing diabetes and cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, recognizing and managing atrial fibrillation, and avoiding illicit drug use. Injury prevention, managing underlying medical conditions, and seeking early medical intervention are also important preventive measures.
It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and recommendations based on individual circumstances and risk factors.