Sharp Purser Test:
- This Sharp Purser test assesses the integrity of the joint of Atlanto-Axial & more notably for the stabilizers of the dens on the Atlas vertebra.
- When the transverse ligament has maintained the position of the odontoid process relative of to C1 is in torn & C1 is for translate to forwards on the C2 in a flexion movement.
- Instability of the Atlantoaxial joint which is the most significant complication of rheumatoid arthritis = RA in the cervical spine for occurring in the 29-70% of the RA = rheumatoid arthritis patients.
- Compromise of the Cervical spinal cord is due to the subluxation of the atlantoaxial joint for having serious neurological consequences, including quadriplegia & even death.
- This Sharp Purser Test is performed with extreme caution.
What is the purpose of the Sharp Purser Test?
- This Sharp Purser test is used to specifically assess the integrity of the ligament of the Transverse around the cervical spine.
- This test is also used to determine the subluxation of the atlas on the axis.
How do you perform the Sharp Purser Test?
- In this test, the examiner may find the patient reticent to do forward flexion if the transverse ligament has been damaged.
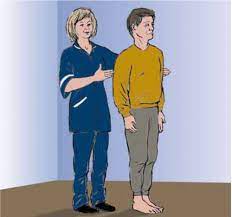
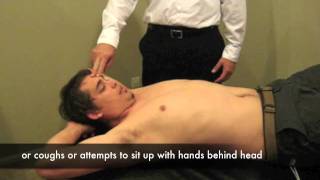
- The examiner [ therapist ] places one hand over the patient’s forehead while the thumb of the other hand is placed over the spinous process of the axis to stabilize it.
- The patient is asked to slowly flex the head while this is occurring the examiner presses backward with the palm.
What is the result of the Sharp Purser Test?
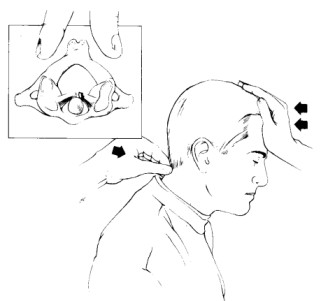
- A positive test is indicated if the examiner feels the head slide backward during the movement.
- The slide backward indicates that the subluxation of the atlas has been reduced,& the slide may be accompanied by a clunk.
- Aspinall advocates the use of an additional test if the sharp – purses test is negative.Tthe patient is placed in the supine position.
- The examiner [ therapist ] stabilizes the occiput on the atlas in flexion & holds the occiput in the flexed position.
- The examiner [ therapist ] then applies an anteriorly directed force to the posterior aspect of the atlas.
- Normally, no movement or symptoms are perceived by the patient.
- For the test to be positive, the patient should feel a lump in the throat as the atlas moves toward the esophagus.
- This is indicative of hypermobility at the atlantoaxial articulation.
- Rey – Einz et al advocated doing a similar test to test for hypomobility in the middle cervical spine [ posterior-anterior middle cervical spine gliding test.
- The head & cervical spine are held in neutral & the examiner pushes anteriorly on the lamina of C3, C4, or C5.
- Hypermobility for the test was defined as abnormal resistance to movement, abnormal end feel & reproduction of local or referred pain.
What is Evidence of the Sharp Purser Test?
- Uitvlugt & Indenbaum has compared the Sharp-Purser Test to a gold standard of the lateral flexion & extension movement radiographs in the 123 patients with the disease of rheumatoid arthritis = RA.
- It is reported to the sensitivity of the Sharp Purser Test is = 69%
- Specificity of the Sharp Purser Test is = 96% for the laxity >3mm.
- A positive likelihood ratio of the Sharp Purser Test is =17.3
- The negative likelihood ratio of the Sharp Purser Test is = 0.32 for laxity >4mm
- When the sensitivity is increased to 88%.
- So that All cases with neurological involvement & all laxities >5mm are detected.
- On the other way, Cattrysse et al.is found no tendency towards the consistent level of significance for Intra & interobserver reliability.