Slocum test of the Knee: Purpose, How to Perform?
- Slocum Test is (1976) the modification of the Anterior Drawer test which is a test of the anteromedial rotary instability means AMRI & anterolateral rotary instability means ALRI of the knee joint.
- Anterior drawer test evaluates the anterior cruciate ligament.
- But in this test inserting the internal/external rotation of to the test so that the anterolateral/anteromedial rotary instability is evaluated.
What is the Purpose of the slocum test?
- This Test is used to for the both anterior rotatory instability means anteromedial rotary instability or anterolateral rotary instability of the knee.
Part of this test :
- Anteromedial rotary instability
- Anterolateral rotary instability
How to perform slocum test?
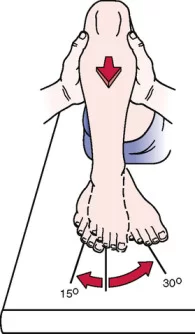
First part of the test :
- It is check the anterolateral rotary instability of the joint.
- Patient position is supine.
- In the supine position the knee is flexed up to 90 degrees/ hip is flexed to 45 degrees.
- Foot is to the fixed at of to the examining table by the examiner.
- At the this position do the 30 degrees of IR means internal rotation / medial rotation on to the tibia by the rotating of the foot.
- Then the examiner is pulls the anteriorly on to the tibia for the assess of the anterolateral rotary instability.
- Results of this test is compared to the bilaterally.
Second part of the test:
- It checks the anteromedial rotary instability of the joint.
- The patient position is supine.
- In the supine position with the knee is flexed up to 90 degrees/ hip is flexed into the 45 degree.
- Foot is fixed with to the examining table by the therapist
- At the this position do the 15 degrees of ER means external rotation / lateral rotation on to the tibia by the rotating of the foot.
- Then the examiner is pulls the anteriorly on to the tibia for the assess of the anteromedial rotary instability.
- Results of this test is compared to the bilaterally.
- This test is also performed in the sitting position.
What is result of this test?
first part of the test
- When to the Increased of the amount of to the anterior tibial translation.
- With to the tibial internal rotation / excessive of the movement onto the lateral aspect of to the knee which is indicates to the anterolateral instability.
- This Anterolateral rotatory instability means ALRI, it is a manifestation of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) deficiency of the knee.
- This technique also allows the hamstrings to relax because of the 90 degrees of flexion of the knee.
- In this situation, this test is considered to the positive.
Second part of the test :
- When the pathologically increased forward & outward displacement of the tibia onto the femur is possible & do the excessive anterior rotation of the medial tibial plateau indicates the laxity of the medial structures.
What is the structures is inured the positive of this test?
First part of the test :
- Posterolateral capsule
- Anterior cruciate ligament
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- Arcute – popiteus complex
- Lateral collateral ligament
Second part of the test:
- posterior oblique ligament
- posteromedial capsule
- anterior cruciate ligament
What is the stress radiographs of this test:
- When to take the stress radiographs of this test below result is produce
| Grade of injury | Translation |
| 1 | 1 mm or < 1 mm |
| 2 | 1 to 2 mm |
| 3 | > 2 mm |